0% found this document useful (0 votes)
680 views8 pagesAdvanced QoS for Network Engineers
QoS provides mechanisms to provide different priority to different types of traffic and applications. It is implemented through different models like Integrated Services (IntServ) and Differentiated Services (DiffServ). In 3G networks, QoS is implemented using QoS Class Identifiers (QCI) that define characteristics like priority, packet delay budget and error loss rate. Key nodes in the network perform functions like scheduling resources, radio resource management, negotiation of QoS parameters and prioritization of packets to ensure required QoS levels are provided.
Uploaded by
Artty NumattiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Firewall Ports,
- Negotiation of QoS Parameters,
- QoS Profiles,
- End-to-End QoS,
- Resource Allocation,
- DNS Server,
- Service Differentiation,
- Event Detection,
- Computer Network,
- QoS Tools
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
680 views8 pagesAdvanced QoS for Network Engineers
QoS provides mechanisms to provide different priority to different types of traffic and applications. It is implemented through different models like Integrated Services (IntServ) and Differentiated Services (DiffServ). In 3G networks, QoS is implemented using QoS Class Identifiers (QCI) that define characteristics like priority, packet delay budget and error loss rate. Key nodes in the network perform functions like scheduling resources, radio resource management, negotiation of QoS parameters and prioritization of packets to ensure required QoS levels are provided.
Uploaded by
Artty NumattiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Firewall Ports,
- Negotiation of QoS Parameters,
- QoS Profiles,
- End-to-End QoS,
- Resource Allocation,
- DNS Server,
- Service Differentiation,
- Event Detection,
- Computer Network,
- QoS Tools
- QoS Overview: An introductory section providing an overview of Quality of Service (QoS) in networks.
- IP QoS: Explains IP Quality of Service models and prioritization of network traffic using DiffServ and IntServ approaches.
- Traffic Class (TC) in IP V4 & IPV6: Describes traffic classification in IP V4 and IPV6 networks, detailing allocation retention priorities and traffic handling per bearer.
- Why and What is QoS?: Outlines the importance of QoS in network management, focusing on service differentiation and load management.
- Computer Network Architecture: Provides an architectural overview of computer networks explaining the role of each node in QoS management.
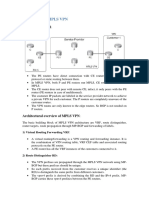
- E2E QoS Architectural Overview – 3G: Describes the end-to-end architectural components in 3G networks for implementing QoS.
- 3G QoS Solution Summary: Summarizes the process and parameter mapping for QoS solutions in 3G systems.
- Per User Service QoS Profile in 3G: Details the QoS profiles per user service in 3G networks, focusing on traffic class and type of subscriber parameters.