0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views11 pagesGender and Sex Impact on Disease Patterns
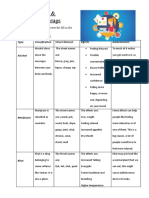
Gender and biological sex influence disease patterns. Gender refers to socially constructed roles while sex refers to biological characteristics. Cultural norms can impact health outcomes, such as fewer women accessing health clinics. Some diseases are more common in one sex, for example higher lung cancer rates in men and higher HIV/AIDS rates in women. Hormones also influence disease, like Alzheimer's and autoimmune diseases being more common in women. Research aims to increase awareness of how gender impacts health and promote societal changes to reduce barriers to good health for all.
Uploaded by
Alexis JonesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views11 pagesGender and Sex Impact on Disease Patterns
Gender and biological sex influence disease patterns. Gender refers to socially constructed roles while sex refers to biological characteristics. Cultural norms can impact health outcomes, such as fewer women accessing health clinics. Some diseases are more common in one sex, for example higher lung cancer rates in men and higher HIV/AIDS rates in women. Hormones also influence disease, like Alzheimer's and autoimmune diseases being more common in women. Research aims to increase awareness of how gender impacts health and promote societal changes to reduce barriers to good health for all.
Uploaded by
Alexis JonesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd