0% found this document useful (0 votes)
313 views13 pagesFinancial Analysis for Managers
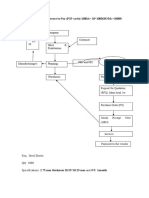
This document provides an introduction to financial statement analysis. It discusses (1) what financial statement analysis is, which involves critically studying financial statements to interpret a business's performance and identify key areas of concern, (2) the key elements of financial statements that are analyzed, including the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and notes, (3) the process of financial statement analysis which involves identifying key performance indicators, defining relevant ratios, establishing trends, drawing conclusions, and identifying areas for improvement, and (4) the importance of financial statement analysis for management, shareholders, creditors, and others in evaluating a business's performance and making investment decisions.
Uploaded by
PRACHI DASCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
313 views13 pagesFinancial Analysis for Managers
This document provides an introduction to financial statement analysis. It discusses (1) what financial statement analysis is, which involves critically studying financial statements to interpret a business's performance and identify key areas of concern, (2) the key elements of financial statements that are analyzed, including the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and notes, (3) the process of financial statement analysis which involves identifying key performance indicators, defining relevant ratios, establishing trends, drawing conclusions, and identifying areas for improvement, and (4) the importance of financial statement analysis for management, shareholders, creditors, and others in evaluating a business's performance and making investment decisions.
Uploaded by
PRACHI DASCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd