0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views18 pagesWorking Capital Needs and Calculations
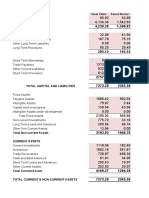
The document discusses factors that affect working capital needs and methods for calculating working capital needs. It outlines factors related to firm characteristics, turnover rates, production processes, costs, and external environment. It then describes four methods for calculating working capital needs: operating cycle coefficient method, daily cost method, Schmallenbach method, and Mellerowicz method. Each method uses different inputs like daily costs, inventory levels, time periods, and profit margins.
Uploaded by
İsmail Can KorkmazCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views18 pagesWorking Capital Needs and Calculations
The document discusses factors that affect working capital needs and methods for calculating working capital needs. It outlines factors related to firm characteristics, turnover rates, production processes, costs, and external environment. It then describes four methods for calculating working capital needs: operating cycle coefficient method, daily cost method, Schmallenbach method, and Mellerowicz method. Each method uses different inputs like daily costs, inventory levels, time periods, and profit margins.
Uploaded by
İsmail Can KorkmazCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd