0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views4 pagesExample 3 For Classless IP Address
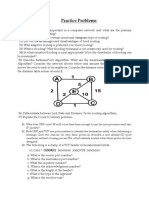
An ISP was granted a block of 65,536 IP addresses starting with 190.100.0.0/16. The ISP needs to allocate addresses to three customer groups: 64 customers needing 256 addresses each, 128 customers needing 128 addresses each, and 128 customers needing 64 addresses each. 40,960 addresses were allocated, leaving 24,576 still available.
Uploaded by
DEABELA GAMING 2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views4 pagesExample 3 For Classless IP Address
An ISP was granted a block of 65,536 IP addresses starting with 190.100.0.0/16. The ISP needs to allocate addresses to three customer groups: 64 customers needing 256 addresses each, 128 customers needing 128 addresses each, and 128 customers needing 64 addresses each. 40,960 addresses were allocated, leaving 24,576 still available.
Uploaded by
DEABELA GAMING 2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd