0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views8 pagesReverse Engineering
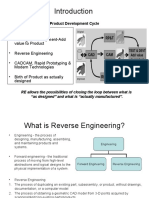
Reverse engineering involves rebuilding or analyzing existing parts or systems to understand their design, function, and production. The process typically involves scanning or measuring a part to obtain its dimensions, using that data to create 2D or 3D models, and then building prototypes. Reverse engineering is used for faster prototyping, to recreate older parts, and to understand how existing products work. It requires significant equipment, skills, and understanding of the subject.
Uploaded by
api-636982850Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views8 pagesReverse Engineering
Reverse engineering involves rebuilding or analyzing existing parts or systems to understand their design, function, and production. The process typically involves scanning or measuring a part to obtain its dimensions, using that data to create 2D or 3D models, and then building prototypes. Reverse engineering is used for faster prototyping, to recreate older parts, and to understand how existing products work. It requires significant equipment, skills, and understanding of the subject.
Uploaded by
api-636982850Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd