0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views26 pagesEssential Guide to Physical Security
This document discusses physical security. It defines physical security as barriers placed between potential intruders and protected assets. It identifies threats, hazards, vulnerabilities, and risks as factors that compromise security. The document outlines the components of a comprehensive security program and describes different types of physical barriers, including natural, human, animal, structural, and energy barriers. It provides details on perimeter barriers, building exteriors, interior controls, and the use of proprietary and contract guards.
Uploaded by
Tara beruCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
208 views26 pagesEssential Guide to Physical Security
This document discusses physical security. It defines physical security as barriers placed between potential intruders and protected assets. It identifies threats, hazards, vulnerabilities, and risks as factors that compromise security. The document outlines the components of a comprehensive security program and describes different types of physical barriers, including natural, human, animal, structural, and energy barriers. It provides details on perimeter barriers, building exteriors, interior controls, and the use of proprietary and contract guards.
Uploaded by
Tara beruCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Physical Security
- Basic Concepts of Physical Security
- Factors of Insecurity
- Comprehensive Security Program
- Types of Physical Barriers
- Perimeter Barrier Functions
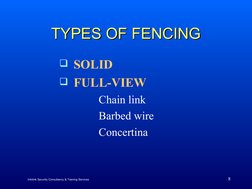
- Types of Fencing
- The Top Guard
- Types of Protective Alarm Systems
- Protective Lighting
- Clear Zones
- Defense Lines
- Proprietary Guards
- Contract Guards
- Principles of Physical Security
- Review Questions
- Conclusion