0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views15 pagesAbg Analysis: Presented by Anuja Nair Sy MSC Nursing
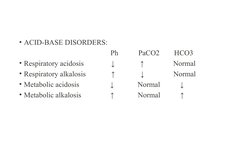
This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It defines ABG as the sampling of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels from arteries. An ABG test measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels to evaluate lung and respiratory function. It lists the normal ranges for pH, pO2, pCO2, HCO3, and other values. Common acid-base disorders like respiratory acidosis and alkalosis and their effects on pH, pCO2 and HCO3 are outlined. Steps for ABG analysis and potential complications are also discussed.
Uploaded by
Anuja NairCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views15 pagesAbg Analysis: Presented by Anuja Nair Sy MSC Nursing
This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis. It defines ABG as the sampling of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels from arteries. An ABG test measures pH, oxygen, and carbon dioxide levels to evaluate lung and respiratory function. It lists the normal ranges for pH, pO2, pCO2, HCO3, and other values. Common acid-base disorders like respiratory acidosis and alkalosis and their effects on pH, pCO2 and HCO3 are outlined. Steps for ABG analysis and potential complications are also discussed.
Uploaded by
Anuja NairCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Title Page
- Introduction
- Definition
- Components of Blood Gas
- Indications
- Normal ABG Parameter Normal Value
- 6 Steps to ABG Analysis
- Acid-Base Disorders
- Acid-Base Disorders Chart
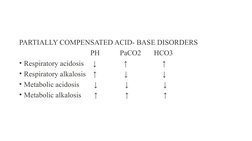
- Partially Compensated Acid-Base Disorders
- Complications
- ABG Report Example
- Metabolic Alkalosis Compensated Respiratory Acidosis
- Second ABG Report Example