0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views19 pagesColor Wheel: History and Techniques
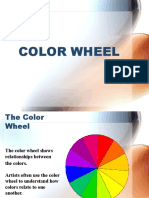
The first color wheel was presented by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century after discovering the visible light spectrum. At the time, color was thought to be a mixture of light and dark. Newton saw flaws in this theory and conducted experiments with white light using a prism, discovering that white light is composed of colors. He mapped these colors into the first color wheel known as ROY G BIV. His experiments also showed that secondary colors are made by mixing primary colors, resulting in the modern hue wheel used in art classes depicting primary, secondary, and tertiary colors that can be combined to create other hues. The document then discusses common color combinations used in design including complementary, monochromatic, analogous, triadic,
Uploaded by
Zenia Fe Llausas McVeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views19 pagesColor Wheel: History and Techniques
The first color wheel was presented by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century after discovering the visible light spectrum. At the time, color was thought to be a mixture of light and dark. Newton saw flaws in this theory and conducted experiments with white light using a prism, discovering that white light is composed of colors. He mapped these colors into the first color wheel known as ROY G BIV. His experiments also showed that secondary colors are made by mixing primary colors, resulting in the modern hue wheel used in art classes depicting primary, secondary, and tertiary colors that can be combined to create other hues. The document then discusses common color combinations used in design including complementary, monochromatic, analogous, triadic,
Uploaded by
Zenia Fe Llausas McVeyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd