0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views7 pagesCounting Sort Algorithm Explained
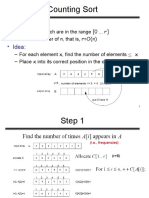
Counting sort is a sorting algorithm that works by counting the number of objects that have distinct key values and using arithmetic to determine the position of each object in the sorted output array. It runs in O(n+k) time where n is the number of items and k is the range of possible key values. It requires an auxiliary array of size k to store the count of each key value. Counting sort can only be used to sort integers when the possible values are known and are a small number compared to the list size.
Uploaded by
Badnaam RajaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
97 views7 pagesCounting Sort Algorithm Explained
Counting sort is a sorting algorithm that works by counting the number of objects that have distinct key values and using arithmetic to determine the position of each object in the sorted output array. It runs in O(n+k) time where n is the number of items and k is the range of possible key values. It requires an auxiliary array of size k to store the count of each key value. Counting sort can only be used to sort integers when the possible values are known and are a small number compared to the list size.
Uploaded by
Badnaam RajaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd