0% found this document useful (0 votes)
143 views11 pagesDesign Thinking
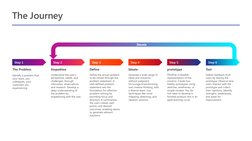
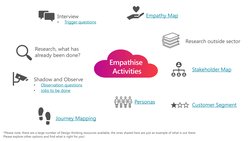
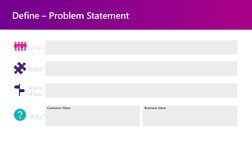
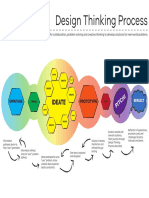
This design thinking journey aims to identify and address problems through collaboration and focused effort. The process involves six steps: 1) Identifying a problem, 2) Empathizing with users to understand their perspectives and needs, 3) Defining the problem clearly, 4) Ideating innovative solutions, 5) Prototyping potential solutions, and 6) Testing prototypes with users to identify areas for improvement. The current focus is on empathizing with users of an occupational health team to gain insights and define the problems around managing appointments that could be addressed innovatively.
Uploaded by
Adrian VasnicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
143 views11 pagesDesign Thinking
This design thinking journey aims to identify and address problems through collaboration and focused effort. The process involves six steps: 1) Identifying a problem, 2) Empathizing with users to understand their perspectives and needs, 3) Defining the problem clearly, 4) Ideating innovative solutions, 5) Prototyping potential solutions, and 6) Testing prototypes with users to identify areas for improvement. The current focus is on empathizing with users of an occupational health team to gain insights and define the problems around managing appointments that could be addressed innovatively.
Uploaded by
Adrian VasnicCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd