0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views52 pagesUntitled Presentation
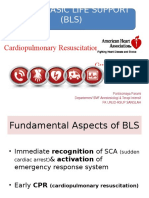
Basic life support (BLS) is a systematic approach to assess and treat cardiac arrest and acutely ill or injured patients. The goal of BLS is to support and restore effective oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation with return of intact neurologic function through interventions like chest compressions, rescue breathing, and defibrillation if needed. BLS involves assessing responsiveness, calling for help, checking breathing and pulse, performing chest compressions and rescue breaths in a 30:2 ratio for 2 minutes before reassessing the pulse and rhythm. An automated external defibrillator may be used to deliver shocks if a shockable rhythm is detected.
Uploaded by
lakshmiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views52 pagesUntitled Presentation
Basic life support (BLS) is a systematic approach to assess and treat cardiac arrest and acutely ill or injured patients. The goal of BLS is to support and restore effective oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation with return of intact neurologic function through interventions like chest compressions, rescue breathing, and defibrillation if needed. BLS involves assessing responsiveness, calling for help, checking breathing and pulse, performing chest compressions and rescue breaths in a 30:2 ratio for 2 minutes before reassessing the pulse and rhythm. An automated external defibrillator may be used to deliver shocks if a shockable rhythm is detected.
Uploaded by
lakshmiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd