0% found this document useful (0 votes)
477 views8 pagesRapid Application Development Guide
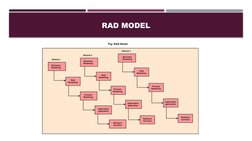
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development model that emphasizes concise development cycles through prototyping and quick feedback. The RAD model involves business modeling, data modeling, process modeling, and application generation phases. It is suitable for projects that can be modularized quickly within 2-3 months when requirements are clear. RAD allows for flexible and adaptable changes through iterative development and testing. However, it requires skilled designers and user involvement, and may not be suitable for high risk or smaller projects.
Uploaded by
peterbrightgeniusnyavorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
477 views8 pagesRapid Application Development Guide
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a software development model that emphasizes concise development cycles through prototyping and quick feedback. The RAD model involves business modeling, data modeling, process modeling, and application generation phases. It is suitable for projects that can be modularized quickly within 2-3 months when requirements are clear. RAD allows for flexible and adaptable changes through iterative development and testing. However, it requires skilled designers and user involvement, and may not be suitable for high risk or smaller projects.
Uploaded by
peterbrightgeniusnyavorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Rapid Application Development Overview
- RAD Model
- Phases of the RAD Model
- When to Use RAD Model
- Advantages of RAD Model
- Disadvantages of RAD Model