0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views14 pagesElements of Biomechanics and Movement
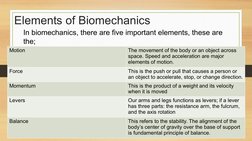
Here are the 24 words on the BINGO card:
B: Balance, Bend, Bingo
I: Flex, Stretch
N: Walk, Gallop, Jump
G: Hop, Slide, Skip
O: Run, Pull, Step, Roll, Shake, Swing, Turn, Wiggle, rotate, Curl
The teacher will call out definitions or phrases that correspond to the words on the BINGO card. When a student has all the words in a row (horizontal, vertical, or diagonal) they shout "BINGO!".
Uploaded by
Steffany Anne PobladorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views14 pagesElements of Biomechanics and Movement
Here are the 24 words on the BINGO card:
B: Balance, Bend, Bingo
I: Flex, Stretch
N: Walk, Gallop, Jump
G: Hop, Slide, Skip
O: Run, Pull, Step, Roll, Shake, Swing, Turn, Wiggle, rotate, Curl
The teacher will call out definitions or phrases that correspond to the words on the BINGO card. When a student has all the words in a row (horizontal, vertical, or diagonal) they shout "BINGO!".
Uploaded by
Steffany Anne PobladorCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd