0% found this document useful (0 votes)
187 views15 pagesMemory Representation of 2D Arrays
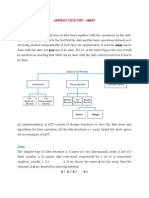
The document discusses multi-dimensional arrays, specifically two-dimensional arrays. It covers topics such as the memory representation of two-dimensional arrays in both column-major and row-major order, and provides examples of how to calculate the address of an element in a two-dimensional array. Sample programs for declaring and initializing two-dimensional arrays as well as concatenating strings are also included.
Uploaded by
Amar ThakurCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
187 views15 pagesMemory Representation of 2D Arrays
The document discusses multi-dimensional arrays, specifically two-dimensional arrays. It covers topics such as the memory representation of two-dimensional arrays in both column-major and row-major order, and provides examples of how to calculate the address of an element in a two-dimensional array. Sample programs for declaring and initializing two-dimensional arrays as well as concatenating strings are also included.
Uploaded by
Amar ThakurCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd