100% found this document useful (2 votes)
171 views87 pagesBasic First Aid - Hotel
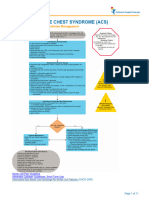
Check for circulation, breathing, severe bleeding. Call 999/112 for emergency services. Prioritize casualties and treat life-threatening conditions first.
Uploaded by
MR ACopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
171 views87 pagesBasic First Aid - Hotel
Check for circulation, breathing, severe bleeding. Call 999/112 for emergency services. Prioritize casualties and treat life-threatening conditions first.
Uploaded by
MR ACopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd