0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views32 pagesOverview of Organizational Behavior
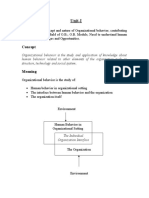
This document provides an overview of organizational behavior. It defines organizational behavior as the study of how individuals, groups, and structure influence behavior within organizations. The document outlines three levels of analysis in OB: individual, group, and organizational. It also discusses how OB complements managerial intuition with systematic study and applies various disciplines like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. The document concludes by examining some challenges and opportunities for OB, such as responding to globalization, empowering employees, and managing diversity.
Uploaded by
Gizaw BelayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views32 pagesOverview of Organizational Behavior
This document provides an overview of organizational behavior. It defines organizational behavior as the study of how individuals, groups, and structure influence behavior within organizations. The document outlines three levels of analysis in OB: individual, group, and organizational. It also discusses how OB complements managerial intuition with systematic study and applies various disciplines like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. The document concludes by examining some challenges and opportunities for OB, such as responding to globalization, empowering employees, and managing diversity.
Uploaded by
Gizaw BelayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd