0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views28 pagesBusiness Research Methods Overview
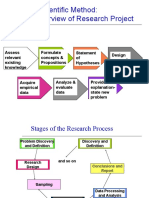
This document provides an overview of business research methods. It discusses the objectives of studying this subject, which are to understand the importance of research, various methods for investigating problems, data collection, and interpreting data to make meaningful decisions. The contents include research problems, hypotheses, research design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. Business research is defined as a systematic inquiry that provides information to guide managerial decisions through a process of planning, acquiring, analyzing, and disseminating relevant data. Examples of applied business research involving developing strategies for new products are also provided.
Uploaded by
Tanvi DeshmukhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views28 pagesBusiness Research Methods Overview
This document provides an overview of business research methods. It discusses the objectives of studying this subject, which are to understand the importance of research, various methods for investigating problems, data collection, and interpreting data to make meaningful decisions. The contents include research problems, hypotheses, research design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. Business research is defined as a systematic inquiry that provides information to guide managerial decisions through a process of planning, acquiring, analyzing, and disseminating relevant data. Examples of applied business research involving developing strategies for new products are also provided.
Uploaded by
Tanvi DeshmukhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd