0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views17 pagesAppendectomy
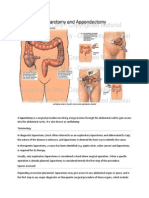
The document outlines the anatomy, investigation methods, surgical approaches, and procedures for appendectomy, including potential complications and issues that may arise during surgery. It also discusses incidental appendectomy and its contraindications. Key surgical steps involve ligation of the appendicular artery and removal of the appendix while ensuring proper management of the surgical site to prevent complications.
Uploaded by
70 SASI KUMAR .RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views17 pagesAppendectomy
The document outlines the anatomy, investigation methods, surgical approaches, and procedures for appendectomy, including potential complications and issues that may arise during surgery. It also discusses incidental appendectomy and its contraindications. Key surgical steps involve ligation of the appendicular artery and removal of the appendix while ensuring proper management of the surgical site to prevent complications.
Uploaded by
70 SASI KUMAR .RCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd