0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views10 pagesPresentation of Design Analysis and Algorithm On Approximation
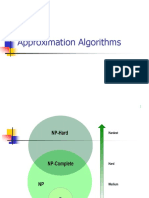
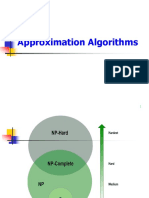
The document discusses approximation algorithms, specifically in the context of the vertex cover and set cover problems, both of which are NP-complete. It outlines the principles of approximation algorithms, their goals, and provides algorithms for solving the vertex cover and set cover problems using greedy methods. Examples illustrate how these algorithms work to cover all edges or elements efficiently.
Uploaded by
swativijay.aiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views10 pagesPresentation of Design Analysis and Algorithm On Approximation
The document discusses approximation algorithms, specifically in the context of the vertex cover and set cover problems, both of which are NP-complete. It outlines the principles of approximation algorithms, their goals, and provides algorithms for solving the vertex cover and set cover problems using greedy methods. Examples illustrate how these algorithms work to cover all edges or elements efficiently.
Uploaded by
swativijay.aiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10