0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views56 pagesPyrrole and Furan Synthesis Methods
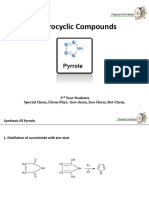
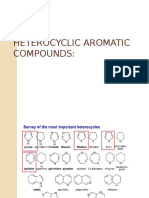
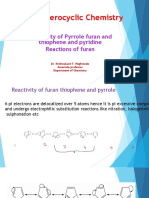
The document discusses various five-membered heterocycles, focusing on pyrroles, furans, and thiophenes, including their synthesis methods such as the Knorr and Paal-Knorr syntheses. It covers the mechanisms of these reactions, the reactivity of the compounds with bases and electrophiles, and specific reactions like halogenation and Diels-Alder reactions. Additionally, it includes practice problems related to the synthesis and reactions of these heterocycles.
Uploaded by
kavyabanthiya123Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views56 pagesPyrrole and Furan Synthesis Methods
The document discusses various five-membered heterocycles, focusing on pyrroles, furans, and thiophenes, including their synthesis methods such as the Knorr and Paal-Knorr syntheses. It covers the mechanisms of these reactions, the reactivity of the compounds with bases and electrophiles, and specific reactions like halogenation and Diels-Alder reactions. Additionally, it includes practice problems related to the synthesis and reactions of these heterocycles.
Uploaded by
kavyabanthiya123Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd