0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views9 pagesUnderstanding HDLC Protocol Basics
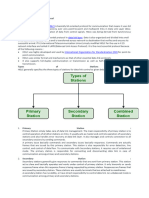
HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol for reliable transmission of data over serial lines. It uses flags to delimit frames and error checking sequences. There are two connection modes - normal response mode for one-way communication and asynchronous response mode for two-way communication. There are three types of frames - information frames for data, unnumbered frames for system messages, and supervisory frames for error and flow control using sequence numbers. The frame format includes the flag, address, control field, data (for I-frames only), and frame check sequence.
Uploaded by
Abhishek KumarCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views9 pagesUnderstanding HDLC Protocol Basics
HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol for reliable transmission of data over serial lines. It uses flags to delimit frames and error checking sequences. There are two connection modes - normal response mode for one-way communication and asynchronous response mode for two-way communication. There are three types of frames - information frames for data, unnumbered frames for system messages, and supervisory frames for error and flow control using sequence numbers. The frame format includes the flag, address, control field, data (for I-frames only), and frame check sequence.
Uploaded by
Abhishek KumarCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9