Adrenergic
Neurotransmitters
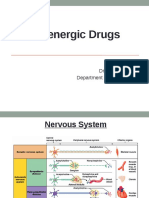
�Adrenergic nervous system
• Group of organs and nerves with adrenaline or noradrenaline as
neurotransmitters
• Adrenergic nerve release neurotransmitters as noradrenaline,
dopamine, adrenaline
• Neurotransmitters referred to as catecholamines
�Biosynthesis of catecholamines
1. Hydroxylation of acid L-tyrosine to form L-DOPA
2. Decarboxylation of L-DOPA to form Dopamine
3. Side chain beta hydroxylation of dopamine to give
norepinephrine
4. N-methylation of norepinephrine to give
epinephrine
�Metabolism
�Adrenergic receptors
• Membrane bound receptors located throughout the body
• G protein coupled receptors
• Responsible for fight and flight response
��Sympathomimetic drugs
• Also known as adrenergic drugs
• Stimulant compounds which mimics effects of endogenous agonist of
sympathetic nervous system
�Mechanism of action
• Mimic the action of sympathomimetics neurotransmitters
• By binding to and stimulating adrenergic neurotransmitters
• Increases the neurotransmission rate
�Classification
�Direct acting agents
• Drugs that directly bind with adrenergic receptors and gives its action
• Action produced is rapid and of short duration of action
1. Nor-epinephrine:
Uses: vasoconstrictor properties, treatment of hypotension, used in
myocardial shock
�2. Epinephrine
• Uses: used as a sympathomimetic, broncholytic and anti-asthmatic
• Used to prevent bleeding during surgery or organ bleeding as it causes
vasoconstriction
• Treatment of heart block drug of choice in allergic disorders and
histamine reactions
• Emergency treatment of anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shick in cardio
pulmonary disease
�3. Phenylepherine
• Uses: acts on peripheral arterioles resulting in rise in systolic and
diastolic pressure
• Used as nasal decongestant, mydriatic and vaso-pressor
• Vasoconstriction of arterioles, iris and constriction of uterus
• Increase in BP in acute hypotension
�Synthesis
�4. Dopamine
Uses: used in treatment of shock, increased blood
flow to kidneys, used in heart attack, trauma and
surgery
5. Methyldopa:
Uses: used alone or in combination to treat high
blood pressure
Lowering blood pressure helps to prevent strokes,
heart attacks and kidney problems
�Sympathomimetic agents
6. Clonidine:
• Uses: used in treatment of hypertension, nasal
decongestant , open eye glaucoma
• Potent sedative-hypnotic drug and can
prevent post-operative shivering
7. Dobutamine:
Used in ICU for treatment of CHF, cardiogenic
shock, pulmonary oedema and to increase
cardiac output
�Sympathomimetic agents
8. Isoprenaline:
• Primary use in treatment of bronchial asthma
• Used as antiarrhythmic agent in treatment of
shock
• CNS stimulant and vasodilator
9. Terbutaline:
• Used in patients with asthma but cause less
direct cardiac stimulation
�10. Salbutamol
• Uses: useful in treatment of acute MI
• Used to arrest premature labor and effective in ocular hypotension
• Bronchodilator; drug of choice in treatment of asthma
• Treatment of emphysema (damage to walls of air sacs)
�Synthesis of salbutamol
�• 11. Bitolterol: used in relieving bronchospasm in asthma, chronic
bronchitis and emphysema
12. Naphazoline:
• Used as local vasoconstrictor for nasal congestion
• Relieve ocular congestion and blepharospasm
�• Oxymetazoline:
• Acts as decongestant during allergy
• Or infection of nasal passage
• Xylometazoline:
• Local Vasoconstrictor for nasal congestion caused by sinusitis and
rhinitis
�Indirect acting agents
• Drugs that indirectly increase the concentration of
endogenous neurotransmitter
• Enter the nerve ending by active uptake and
displace NE from storage granules
• Hydroxyamphetamine:
• In narcolepsy (sudden attack of sleep in completely
inappropriate situations)
• It act an anorexiant (appetite suppressant)
• Used in children with hyperkinetic syndrome
�• Pseudoephedrine:
• Optically active isomer of ephedrine
• Used as vasoconstrictor to treat nasal and sinus
congestion of tubes that drain fluid from inner
ears
• Increases blood pressure by increasing cardiac
output
• Propylhexedrine:
• Used for relief of congestion due to cold,
allergies and rhinitis
�Mixed acting drugs
• Activate adrenergic receptors as well increases the release of
endogenous NE
• Ephedrine:
• Used as bronchodilator, nasal decongestant
• Used in orthostatic hypotension and myasthenia gravis
• Used in various allergic reactions and urticaria
�• Metaraminol:
• It can be used parenterally as vasopressor
in prevention of acute hypotension due to
spinal anasthesia
�SAR
• SAR is the relationship between the chemical structure of a molecule
and its biological activity
�SAR
• Studied by 3 different substitutions:
• Catechol ring substitution
• Substitution on ethylene linkage
• Substitution on amine group
�SAR
• 1. Catechol ring substitution:
• 3- hydroxy substitution is essential for alpha activity
• 4-hydroxy substitution essential for beta activity
• Replacement of catechol ring by resorcinol ring, increases beta-2
selectivity and
• Decreases metabolism by COMT resulting in longer duration of action
�• Replacement of m-hydroxyl of catechol increases selectivity for beta-2
and
• Decreases metabolism by COMT
�• Removal of p-hydroxyl group of catechol produces alpha selectivity
�• non-catecholamines tent to have better oral absorption and longer
duration of action
• As they are not acted upon by COMT
• Easily cross BBB and have central activity
�2. Substitution on ethylene linkage
• Hydroxy group on beta carbon decreases central stimulant activity
• As it lowers lipid solubility but enhances agonistic activity
• Example: ephedrine
• Substitution on alpha carbon blocks deamination by MAO
• Resulting in longer duration of action
• Example: metaraminol
�3. Substitution on amine group
• The nature of amino substituent determines alpha and beta receptor
selectivity.
• Substitution of alkyl group on nitrogen decreases alpha selectivity
• Primary and secondary amines having good adrenergic activity.
• Example: - isoprenaline (isoproterenol).
�Distance between aromatic ring and amino
group
• Max activity when separated by two carbons
• However, there are few exceptions
• Example: naphazoline (powerful alpha receptor)
�Adrenergic antagonist
• Drugs that inhibit functions of adrenergic receptors by blocking the
active site
• Also called sympatholytics, anti-adrenergics or adrenolytics or
adrenergic blockers
��Alpha adrenergic blockers
• Non- selective alpha blockers
• Reversible: phentolamine, tolazoline
• Irreversible: phenoxybenzamine
• Selective alpha blockers:
• Alpha-1 blockers: prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin
• Alpha-2 blockers: Yohimbine, idozoxan
• Miscellaneous: dihydroergotamine, methysergide
�Alpha blockers
• Phenoxybenzamine:
• Used in pheochromocytoma (tumor of adrenal medullary cells)
• Hypertension, shock and PVD
• Phentolamine
• non-selective alpha blocker
• Used in ED, hypertension and pheochromocytoma
�Alpha blockers
• Tolazoline
• Used in PVD
• Pulmonary HT of newborn
• Prazosin
• Selective to alpha-1 receptors
• Used as antihypertensive
• Raynaud’s disease
• Benign prostatic hyperplasia
• Left ventricular failure not controlled by digitalis and diuretics
�Alpha blockers
• Dihydroergotamine:
• Competitive alpha blocker
• Principal use in migraine
�Alpha blockers
• Methysergide:
• neutralize serotonin in the blood vesssels, tissues and CNS
• Used in episodic and chronic migraine and cluster headaches
�Synthesis of Tolazoline
• Heteroacylation of ethyl ester of iminophenyl acaetic acid
�Uses
• Mostly used for CV diseases
• Widely used for lowering BP and relieving hypertension
• Proven to relieve pain caused by MI and infarction size
�Side effects
• Palpitation
• Postural hypotension
• Diarrhea
• Nasal blockade
• Fluid retention
• Inhibition of ejaculation and impotence
�Beta adrenergic blockers
• Competitive pharmacologic antagonist
• Most widely used antihypertensives
• Block the effects of NE on beta-1 and beta-2
• Mask early signs of hypoglycemia
��Beta blockers
• Propranolol:
• For use in angina pectoris, past MI, hypertension
• Migraine and CNS disorders
• Metipranolol:
• Indicated in treatment of increased intraocular pressure or open angle
glaucoma
��Beta blockers
• Atenolol:
• Used for hypertension, angina, long QT syndrome
• Acute MI and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal
• Betazolol:
• Used to lower BP, helps prevent strokes
• Prevent heart attacks and kidney problems
�Beta blockers
• Bisprolol:
• Used for hypertension
• Heart failure
• Esmolol:
• To terminate supraventricular tachycardia, episodic atrial fibrillation
or flutter, arrythmia during anasthesis
• Reduce heart rate during surgery
�Beta adrenergic blockers
• Metoprolol:
• Acute MI
• Angina
• Labetalol:
• Hypertension
• Angina
• Cardiac arrythmia
�• Carvedilol:
• t/t of hypertension
• Angina pectoris
• Cardiac arrythmia