0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views31 pagesProgramming Essentials (Sequence, Iteration and Selection)
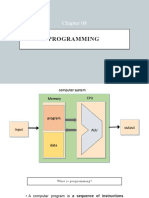
This document outlines a Year 7 programming lesson focused on sequencing and selection using Scratch. It includes activities where students give commands to a robot, explore programming concepts, and learn about conditions and expressions in programming. The lesson emphasizes the importance of executing instructions in order and using selection statements to control program flow.
Uploaded by
win win myoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views31 pagesProgramming Essentials (Sequence, Iteration and Selection)
This document outlines a Year 7 programming lesson focused on sequencing and selection using Scratch. It includes activities where students give commands to a robot, explore programming concepts, and learn about conditions and expressions in programming. The lesson emphasizes the importance of executing instructions in order and using selection statements to control program flow.
Uploaded by
win win myoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd