0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views39 pagesKidney
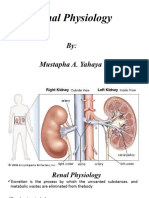
The kidneys perform vital functions including excretion, fluid balance, blood pressure regulation, and hormone production. The kidney structure consists of stroma and parenchyma, with the parenchyma divided into the cortex and medulla, housing nephron components such as Bowman's capsule and glomerulus. The juxtaglomerular apparatus plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Uploaded by
Waqar AhmadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views39 pagesKidney
The kidneys perform vital functions including excretion, fluid balance, blood pressure regulation, and hormone production. The kidney structure consists of stroma and parenchyma, with the parenchyma divided into the cortex and medulla, housing nephron components such as Bowman's capsule and glomerulus. The juxtaglomerular apparatus plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Uploaded by
Waqar AhmadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd