0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views9 pagesDbms
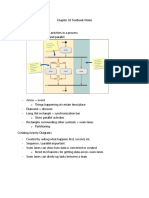
The document provides an introduction to Entity-Relationship (ER) diagrams in Database Management Systems (DBMS), detailing core components such as entities, attributes, and relationships. It outlines various types of entities and attributes, as well as relationship types like one-to-many and many-to-many. Additionally, it includes design principles, notations, and steps for creating an ER diagram, exemplified by a library database scenario.
Uploaded by
yashik kakkarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views9 pagesDbms
The document provides an introduction to Entity-Relationship (ER) diagrams in Database Management Systems (DBMS), detailing core components such as entities, attributes, and relationships. It outlines various types of entities and attributes, as well as relationship types like one-to-many and many-to-many. Additionally, it includes design principles, notations, and steps for creating an ER diagram, exemplified by a library database scenario.
Uploaded by
yashik kakkarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd