0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesMMT
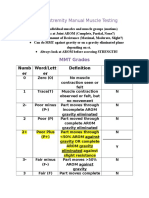
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) evaluates muscle function and strength against gravity and resistance, with limitations including neurological disorders and central nervous system lesions. The testing involves break tests and active resistance tests, focusing on muscle mechanics and positioning. Precautions and contraindications must be considered, such as open wounds, severe pain, and specific pathological conditions.
Uploaded by
skarthika2506Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views3 pagesMMT
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT) evaluates muscle function and strength against gravity and resistance, with limitations including neurological disorders and central nervous system lesions. The testing involves break tests and active resistance tests, focusing on muscle mechanics and positioning. Precautions and contraindications must be considered, such as open wounds, severe pain, and specific pathological conditions.
Uploaded by
skarthika2506Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd