0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views35 pagesSources of Finance
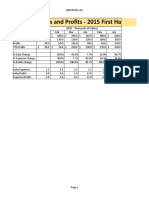
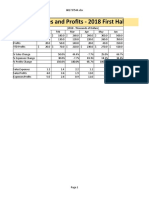
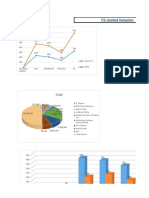
The document outlines various sources of finance, including equity capital, internal accruals, preference capital, term loans, and debentures, along with their advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses working capital management, emphasizing the importance of managing current assets and liabilities to maintain liquidity. Additionally, it covers working capital financing methods such as accruals, trade credit, and commercial bank loans.
Uploaded by
tanushree9663Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views35 pagesSources of Finance
The document outlines various sources of finance, including equity capital, internal accruals, preference capital, term loans, and debentures, along with their advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses working capital management, emphasizing the importance of managing current assets and liabilities to maintain liquidity. Additionally, it covers working capital financing methods such as accruals, trade credit, and commercial bank loans.
Uploaded by
tanushree9663Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd