0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views8 pagesAndroid Activity Lifecycle
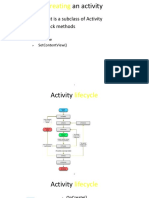
The Android Activity Lifecycle outlines the stages an activity undergoes from creation to destruction, emphasizing the importance of lifecycle methods for resource management and user experience. Key methods include onCreate(), onStart(), onResume(), onPause(), onStop(), and onDestroy(), each serving specific roles in managing state and user interaction. Developers must also handle configuration changes effectively and follow best practices for resource management and state preservation to ensure robust application performance.
Uploaded by
sarmadrehan91Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views8 pagesAndroid Activity Lifecycle
The Android Activity Lifecycle outlines the stages an activity undergoes from creation to destruction, emphasizing the importance of lifecycle methods for resource management and user experience. Key methods include onCreate(), onStart(), onResume(), onPause(), onStop(), and onDestroy(), each serving specific roles in managing state and user interaction. Developers must also handle configuration changes effectively and follow best practices for resource management and state preservation to ensure robust application performance.
Uploaded by
sarmadrehan91Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd