0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views32 pagesLecture 5n
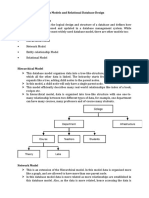
The document outlines the steps in developing a database, including requirements analysis and conceptual design using the Entity Relationship (ER) model. It explains key concepts such as entities, relationships, attributes, and the types of keys used to uniquely identify entities. Additionally, it discusses participation constraints and cardinality in relationships, providing examples and references for further reading.
Uploaded by
sagarbungla13Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views32 pagesLecture 5n
The document outlines the steps in developing a database, including requirements analysis and conceptual design using the Entity Relationship (ER) model. It explains key concepts such as entities, relationships, attributes, and the types of keys used to uniquely identify entities. Additionally, it discusses participation constraints and cardinality in relationships, providing examples and references for further reading.
Uploaded by
sagarbungla13Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd