0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views14 pagesDict Ssets
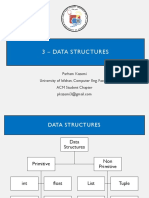
This document provides an overview of dictionaries and sets in programming, detailing their characteristics, methods, and usage. It explains how to create and manipulate sets and dictionaries, including operations like addition, intersection, and copying. Additionally, it includes a challenge to translate Spanish words to English using a dictionary.
Uploaded by
ammaryasser75211Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views14 pagesDict Ssets
This document provides an overview of dictionaries and sets in programming, detailing their characteristics, methods, and usage. It explains how to create and manipulate sets and dictionaries, including operations like addition, intersection, and copying. Additionally, it includes a challenge to translate Spanish words to English using a dictionary.
Uploaded by
ammaryasser75211Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd