Algorithm design and
Problem-solving
�Program development life
cycle
➜ Consists of four main stages
analysis
design
coding
Testing
�Analysis
Before any problem can be solved, it needs to
be clearly defined and set out so anyone
working on the solution understands what is
needed.
Abstraction: Removal of unnecessary details
and identification of the key elements of the
problem
Decomposition: Breaking down a complex
problem into smaller, easier-to-solve parts
Identification of the problem and
requirements
�Design
The program specification from the analysis
stage is used to show to how the program
should be developed
Pseudocode
Flowcharts
Structure diagrams
How the problem is to be solved, what tasks
are required for it and how they work with
each other, and the order of those tasks is
found out in this stage
�Coding and iterative testing
Program code is written using a
programming language
Iterative testing of the separate modules of
the program is carried out, ensuring they
work as they are meant to
Most amendments to the code are carried out
in this stage
�Testing
The completed program or set of programs is
run many times with different sets of test
data. This ensures that all the tasks
completed work together as specified in the
program design.
The completed program is tested with test
data to spot any errors
�Computer systems
A computer system is made up of software,
data, hardware, communications and people;
each computer system can be divided up into a
set of sub-systems.
Each sub-system can be further divided into sub-
systems and so on until each sub-system just
performs a single action.
The alarm program is a very small computer
system but when you check the weather
forecast, you obtain the information you need
from one of the largest computer systems in the
world.
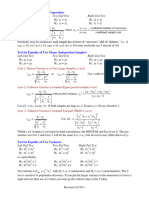
�The computer system and its sub-
systems
In order to understand how a computer
system is built up and how it works it is often
divided up into sub-systems.
How each sub-routine works can be shown by
using flowcharts or Pseudocode
Top-down design is the decomposition of a
computer system into a set of subsystems,
then breaking each sub-system down into a
set of smaller sub-systems, until each sub-
system just performs a single action.
� This is an effective way of designing a computer
system to provide a solution to a problem, since
each part of the problem is broken down into
smaller more manageable problems.
The process of breaking down into smaller sub-
systems is called stepwise refinement.
When larger computer systems are being
developed this means that several programmers
can work independently to develop and test
different sub-systems for the same system at the
same time. This reduces the development
and testing time.
�Decomposing a problem