0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesClearing Process
The document discusses the clearing process in India. It explains that clearing houses are managed by the Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, or other public sector banks, and serve as the place where banks exchange instruments and settle claims. Each member bank is represented in the clearing house and presents instruments drawn on other banks for clearing. There are 860 clearing houses in India that facilitate the clearing process through steps like presenting cheques, payment if funds are available, returning unpaid cheques, and finally settling funds between banks through adjustments to their current accounts.
Uploaded by
Balajie PadmanabhanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesClearing Process
The document discusses the clearing process in India. It explains that clearing houses are managed by the Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, or other public sector banks, and serve as the place where banks exchange instruments and settle claims. Each member bank is represented in the clearing house and presents instruments drawn on other banks for clearing. There are 860 clearing houses in India that facilitate the clearing process through steps like presenting cheques, payment if funds are available, returning unpaid cheques, and finally settling funds between banks through adjustments to their current accounts.
Uploaded by
Balajie PadmanabhanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Clearing Process: An introduction to the clearing process within banking, setting the stage for detailed explanations.
- Clearing House: Defines the clearing house concept and its management under the bank's authority.
- Clearing Houses in India: Details the distribution and management of clearing houses across India.
- Clearing Process Steps: Outlines the sequential steps involved in the clearance of banking instruments.
- Settlement of Funds: Explains how funds are settled through clearing and the role of net settlements.
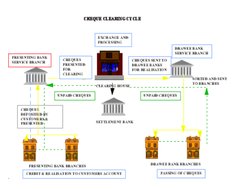
- Cheque Clearing Cycle: Visual representation of the complete cheque clearing cycle from submission to realization.
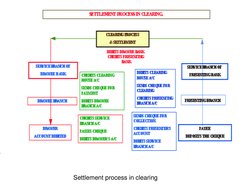
- Settlement Process in Clearing: Diagram demonstrating inter-bank settlement processes and flows.
- Collection of Outstation Instruments: Discusses the collection process of cheques from outstation branches including potential delays.