Eukaryotic Evolution: The Origin of
the Mitochondria
• Understanding the Powerhouse of the Cell
• By: Group Presentation (2 Members)
yone! Today we’ll talk about eukaryotic evolution — specifically the origin of the mitochondria and
� Objectives
• 1. To know what a mitochondria is and its
functions
• 2. To explain the origin of mitochondria and
the endosymbiotic theory
• 3. To discuss its significance today
tation has three goals — to understand what mitochondria are, how they originated, and why this d
� What is the Mitochondria?
• • Known as the 'Powerhouse of the Cell'
• • Found only in eukaryotic cells
• • Produces ATP — the cell’s energy currency
• • Also stores calcium and helps in heat
production and cell death
tes:
itochondria are the powerhouses of the cell because they produce ATP, the energy that drives all ce
� The Question: Where Did It Come
From?
• How did such a complex organelle evolve?
• → The answer lies in the Endosymbiotic
Theory.
Notes:
But have you ever wondered where mitochondria came from? Let’s find out through the Endosymb
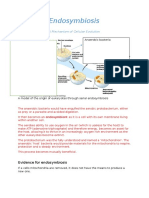
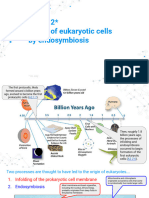
� The Endosymbiotic Theory (Part 1)
• • Early Earth had only prokaryotes
• • A large prokaryote engulfed smaller ones
• • Instead of digestion, they lived together
symbiotically
gulfed smaller bacteria, but instead of destroying them, they started working together — a partners
� The Endosymbiotic Theory (Part 2)
• • The oxygen-using bacteria became
mitochondria
• • Photosynthetic ones became chloroplasts
• • This led to modern eukaryotic cells (~1.5
billion years ago)
using bacteria became mitochondria, while the photosynthetic ones became chloroplasts in plants.
� Evidence Supporting the Theory
• 1. Mitochondria have their own circular DNA
• 2. Similar in size to bacteria
• 3. Reproduce by binary fission
• 4. Have double membranes
ound mitochondria have their own DNA and reproduce like bacteria — clear proof they were once in
� Why Is This Discovery Important
Today?
• • Provides energy for all life
• • Involved in calcium storage and metabolism
• • Helps explain evolution and diseases
rstanding mitochondria helps explain not only evolution but also many diseases and how our bodies
� Summary
• • Mitochondria = energy factory of the cell
• • Originated through endosymbiosis
• • Crucial for modern eukaryotic life
:
mmary, mitochondria’s story is one of cooperation and evolution — a small cell that powered the ris
� What We Learned
• 1. Mitochondria’s role and function
• 2. Its evolutionary origin via endosymbiosis
• 3. Its relevance in our world today
es:
’ve achieved our objectives — we now know what mitochondria are, how they evolved, and why the
� Thank You!
• That’s all! Thank you for listening 💡
tion Notes:
hank you so much for listening! We hope you enjoyed learning about the evolution of mitochondria