Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teknik Las: Dr. Ario Sunar Baskoro, ST, MT, Meng
Uploaded by
MuhammadRiadyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teknik Las: Dr. Ario Sunar Baskoro, ST, MT, Meng
Uploaded by
MuhammadRiadyCopyright:
Available Formats
DTM-UI
Teknik Las
Dr. Ario Sunar Baskoro, ST, MT, MEng.
DTM-UI
Instructor and references
Instructor : Dr. Ario Sunar Baskoro, ST, MT, MEng. Office : Manufacturing Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Eng. UI Phone : 7270032 ext. 222 E-mail : ario@eng.ui.ac.id References : 3 Harsono W., T. Okumura, Teknologi Pengelasan Logam, PT Pradnya Paramita Jakarta Cetakan ke-10, 2008. 3 American Welding Society, AWS D1.1/D1.1M:2004, Structural Welding Code Steel, 19th edition, 2004.
DTM-UI
Course Evaluation
Course evaluation : Assignment, homework, quiz Project Mid Test Final Test 25% 30% 20% 25%
DTM-UI
The purpose of this course
Provide the knowledge, understanding of the theories, principles, design and assessment of the welding quality and applications.
DTM-UI
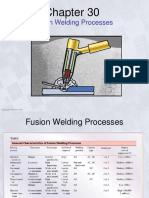
Topics
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Pendahuluan Istilah dan definisi, jenis-jenis proses pengelasan, standard Oxy-gas welding Shield Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) Resistance welding, Friction Stir Welding Other welding process: laser, electron beam, plasma Cutting and other edge preparation processes, surfacing and spraying 11. Brazing and soldering 12. Joining processes for plastics, ceramics and composites
DTM-UI
Topics
13. Testing materials and the weld joint, Non Destructive Examination (NDE), DT (Destructive Test) 14. Heat treatment of base materials and welded joints 15. Basic of welding design, Residual stresses and distortion 16. Welding Symbol 17. Behavior of welded structures under different types of loading, Design of welded structures under static and dynamic loading, welding defects 18. Design of welded pressure equipment 19. Welding Performance Qualification Record (WPQR) 20. Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) 21. Welding automation 22. Presentasi Tugas
DTM-UI
1. Introduction
DTM-UI
History
Nikolay Benardos
In 18811882, a Russian inventor Nikolai Bernardos created the electric arc welding method for steel known as carbon arc welding, using carbon electrodes.
DTM-UI
History (contd.)
Butt welds and sleeve welds were used in the fabrication of Philadelphia Electric Co.'s 2200ft-long steam line in 1922. Electric welding (shown left) was used on a 33 sleeve welds for the flange joints, while the 92 butt joints were made using oxy-acetylene welding. The entire line consisted of 12-in.-diameter steam line and a 3-in.-diameter water return line. The chemistry of the pipe included 0.0 percent 7 carbon, 0.30 percent manganese, 0.045 percent sulfur, and 0.100 percent phosphorus. The electrodes contained 0.011 percent carbon, 0.032 percent sulfur, and 0.025 percent oxygen. The sign speaks for itself in this gathering of welding people in 1924. This assemblage was about to board two buses for tours of three facilities in Cleveland. The first was the local utility where they witnessed the oxyacetylene welding of a 16-in.-diameter high-pressure steam line. The next stop was a tour of the Collingswood Shops of the New York Central Railroad. Third on the list was a visit to The Lincoln Electric Co. The editor of the November 1924 journal noted: "This plant is taking its own 'medicine' in that it is using welding wherever possible in the construction of its motors and generators."
DTM-UI
History (contd.)
At the annual convention of the American Institute of Steel Construction in 1930, an automatic welding machine was demonstrated which had been designed originally for "battledeck" steel construction. At the time, it was inferred that such equipment could also be used effectively in the fabrication of floors in building construction.
Regarded as a "first" at the time, three 10,000-ton cargo ships were launched simultaneously at Todd Shipbuilding Corp., South Portland, ME, in 1942. W.H. Hobart, vice president of Hobart Brothers Co., attributed the feat to three things. First, the steels did not have to be overlapped as they are when riveting is used, thus saving a great deal of steel. Second, he said, new welders could be trained much faster than new riveters. And third, welding lends itself more readily to production line assembly.
DTM-UI
Proses Penyambungan (Joining Processes)
Gambar :
DTM-UI
Alasan menggunakan Proses Penyambungan
1. Produk tidak mungkin di manufaktur dalam satu benda. 2. Produk lebih mudah dan ekonomis di manufaktur dan di kirim (transport) sebagian komponen-komponen yg kemudian di rakit (assembly). 3. Memungkinkan untuk mengambil komponen untuk perbaikan atau pemeliharaan thd bagian yg rusak. 4. Sifat material yg berbeda mungkin lebih diinginkan untuk tujuan fungsional dari produk.
DTM-UI
Joining Process & Equipment
Welding Adhesive Bonding Mechanical Fastening
Fusion
Brazing & Soldering
Solid State
Fastening
Chemical
Electrical
Electrical
Chemical
Mechanical
Seaming
Oxyfuel Gas
Arc
Resistance
Diffusion
Cold
Crimping
Thermit
Resistance
Explosion
Friction
Stitching
Laser beam
Ultrasonic
Electron beam
DTM-UI
Mesin Las
Mesin las listrik yang biasa kita temui di dalam dunia industri di antaranya Carbon Gas Arc Welding (GAW) Shielded Metal - Arc Welding (SMAW) Flux Core Arc Welding ( FCAW) Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) Gas Tungsten Arc welding (GTAW) Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) Stud Welding (SW) Friction Welding
DTM-UI
Cara Pemotongan
Pemotongan Gas
Pemotongan Busur Listrik
Pemotongan Gas Oksigen
Pemotongan Busur Karbon
Pemotongan Serbuk
Pemotongan Busur Logam
Pemotongan Sembur Api
Pemotongan Busur Plasma
Pemotongan Busur Udara
DTM-UI
Contoh Penyambungan dengan Welding
Gambar :
DTM-UI
Tiga Proses Penyambungan : Shielded Metal, Gas Metal, dan Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Kesamaan dari tiga proses :
1. Setiap proses menggunakan arus DC untuk menghasilkan arc antara electroda dan benda kerja. 2. Setiap proses menggunakan shielding untuk melindungi weld dari kontaminasi. 3. Setiap proses menggunakan material pengisi (filler), yang memiliki komposisi kimia yg sama dengan benda kerja.
DTM-UI
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
Dikembangkan pada awal abad ke 20. Penggunaan utamanya di dalam pengelasan baja (steel welding). Shielded metal arc welding dilaksanakan dengan membuat arc antara elektroda metal berlapis dan benda kerja. Sesaat arc terbentuk benda kerja menjadi cair pada titik lokasi arc. Batang elektroda memiliki dua fungsi Pertama : sebagai media utk arus listrik. Kedua : material pengisi digunakan untuk menghasilkan sambungan. Lapisan yg mengelilingi elektroda membentuk gas yg membantu melindungi lasan.
DTM-UI
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (contd)
DTM-UI
Gas Metal Arc Welding
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), juga dinamakan Metal Inert Gas (MIG) atau Metal Active Gas (MAG) welding, melindungi las-an dengan gas eksternal spt : argon, helium, carbon dioxide, atau campuran gas lain. GMAW digunakan untuk mengelas semua metal-metal komersial penting a.l. baja (steel), aluminum, tembaga (cooper), dan stainless steel. Pemilihan metal pengisi (filler metal) memiliki komposisi kimia yang sama dengan material yg di las. Proses dapat dilakukan dalam berbagai posisi : datar, horizontal, vertical, dan overhead.
DTM-UI
Gas Metal Arc Welding (contd)
DTM-UI
Proses GMAW
Panas dihasilkan oleh busur listrik (electric arc) antara elektroda dan benda kerja. Kedua metal, benda kerja dan pengisi, melebur. Area las-an dilindungi oleh gas inert (inert shiled gases).
Metal yg dapat di Las : -steel carbon - steel low-allow - steel stainless - aluminum - copper and its allows - nickel and its allows - magnesium - reactive metal (titanium, zirconium, tantalum)
Characteristics of the weld joint by GMAW (Modern Welding (p63))
DTM-UI
Parameter dalam proses GMAW
1. Ada empat metode pemindah metal : short circuit, globular, spray, dan pulsed spray. Setiap metode membutuhkan setting dan penggunaan yg berbeda. 2. Gas pelindung (shielding gas). 3. Ukuran elektroda (electrode size). 4. Parameter elektrik : Tegangan (voltage) dan Arus (current) (GMAW menggunakan arus kontinyu). 5. Laju pengumpanan (feed rate : kecepatan penyuplai-an pengisi). 6. Laju penge-las-an (travel speed).
DTM-UI
Perlengkapan Utama
1. 2. 3. 4. Torch Sumber daya elektrik (electric power source) Sumber gas pelindung (shielding gas source) wire spool with wire drive control
Peralaran yg dibutuhkan dlm GMAW (Modern Welding (p63))
DTM-UI
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
Dalam GTAW, elektroda tungsten digunakan sebagai pengganti elektroda metal dlm shielded metal arc welding. Gas inert yg bersifat kimia (chemically inert gas), spt argon, helium, atau hydrogen, digunakan utk melindungi metal dari oksidasi. Panas dari arc (busur) yg dibentuk oleh elektroda dan metal melebur bagian tepi metal. Proses ini dpt digunakan untuk hampir semua metal dan menghasilkan las-an dgn kualitas tinggi. Namun laju pege-las-an cukup lambat.
DTM-UI
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (contd)
DTM-UI
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (contd)
Elektroda Tungsten memiliki titik lebur yg tinggi hal ini membuat GTAW memiliki keuntungan spesifik : Pengelasan (Welding) dapat di lakukan dalam setiap posisi. Hasil las-an memiliki komposisi yg sama dengan metal benda kerja. Tidak digunakan Flux; sehingga, hasil las-an tidak membutuhkan pembersihan dari sisa las-an yg bersifat korosif. Tidak ada asap atau gas yg merusak penglihatan. Penyimpangan dari metal benda kerja adalah minim karena panas terkonsentrasi pada luasa yg kecil. Tidak ada cipratan api yg dihasilkan karena metal tidak di transfer melewati arc (busur).
DTM-UI
Faktor Keamanan dlm Pengelasan
Burn hazard Protection clothes and gloves
Eye protection against splatters and ultraviolet and infrared rays
Helmet or special glasses
Toxic gases: - carbon monoxide (CO) - ozone (O2) - phosgene gases produced with some metals when welded
Well ventilated area
DTM-UI
The ESAB CaB 600 installed at AB Martin Larsson in Plsboda, Sweden.
You might also like
- Welding and GmawDocument14 pagesWelding and GmawAl-hadi AliakbarNo ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- 13 Analysis of TIG Welding Process Parameters For Stainless Steel (SS202)Document5 pages13 Analysis of TIG Welding Process Parameters For Stainless Steel (SS202)IJAERS JOURNAL100% (1)
- Advanced welding techniques for shipbuildingDocument15 pagesAdvanced welding techniques for shipbuildingmadhan_kumar2000No ratings yet
- EML 2322L - Welding - MAE Design and Manufacturing LabDocument21 pagesEML 2322L - Welding - MAE Design and Manufacturing LabBhaiJan59No ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- 13 Analysis of TIG Welding Process Parameters For Stainless Steel (SS202) PDFDocument5 pages13 Analysis of TIG Welding Process Parameters For Stainless Steel (SS202) PDFAshemuNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsFrom EverandDie Casting Metallurgy: Butterworths Monographs in MaterialsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- WELDING PROCESSES GUIDEDocument52 pagesWELDING PROCESSES GUIDEIka Puspita NurainiNo ratings yet
- Workshop Case StudyDocument13 pagesWorkshop Case Study1071Vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Study On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelDocument8 pagesStudy On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelIJMERNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Welding - 1 GCDocument66 pagesIntroduction To Welding - 1 GCkr_abhijeet72356587No ratings yet
- CH 4Document63 pagesCH 4tariku seyoumNo ratings yet
- A Review of GTAW Gas Tungsten Arc Weldin PDFDocument8 pagesA Review of GTAW Gas Tungsten Arc Weldin PDFMarjorie ManukayNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument36 pagesWelding DefectsSunilNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Joining ProcessesDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Joining ProcessesNosta Silva100% (1)
- RCF KapurthallaDocument18 pagesRCF KapurthallaSudhir Kumar50% (2)
- 2 Joining ProcessDocument54 pages2 Joining ProcessIzzah Suhair Binti Sa'AbanNo ratings yet
- Welding and Cutting ProcessDocument60 pagesWelding and Cutting Processquiron2010100% (1)
- Mig Gmaw Welding 1Document26 pagesMig Gmaw Welding 1HAZEL BELLONo ratings yet
- Welding: Welding Is A Fabrication Process That Joins Materials, Usually Metals or Thermoplastics, byDocument6 pagesWelding: Welding Is A Fabrication Process That Joins Materials, Usually Metals or Thermoplastics, byTarun ChandraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process: Chapter 5 Joining ProcessesDocument53 pagesManufacturing Process: Chapter 5 Joining ProcesseshizanorhudaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes Lab WeldingDocument8 pagesManufacturing Processes Lab WeldingKhalid EwigNo ratings yet
- Welding MP-IDocument28 pagesWelding MP-IPIYUSH SHARMANo ratings yet
- Arc WeldingDocument42 pagesArc WeldingrkpnakNo ratings yet
- Welding: Philippine Society of Mechanical Engineers Professional Development CourseDocument30 pagesWelding: Philippine Society of Mechanical Engineers Professional Development CourseAngel Silva VicenteNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) - Review: January 2019Document7 pagesA Survey On Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) - Review: January 2019Radhi NurvianNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc WeldingDocument12 pagesGas Tungsten Arc WeldingPrasanth NairNo ratings yet
- Welding WorkshopDocument29 pagesWelding WorkshopAnonymous h5OeGoX3MTNo ratings yet
- Advanced Welding Process (Welding)Document58 pagesAdvanced Welding Process (Welding)Sk SamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Orbital-Welding Facts enDocument52 pagesOrbital-Welding Facts ene.vicente.caballeroNo ratings yet
- Study On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelDocument8 pagesStudy On Effect of Manual Metal Arc Welding Process Parameters On Width of Heat Affected Zone (Haz) For Ms 1005 SteelAngga Pamilu PutraNo ratings yet
- WELDING PROCESSES GUIDEDocument115 pagesWELDING PROCESSES GUIDEShanky BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Welding Processes and Safety PrecautionsDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Welding Processes and Safety PrecautionsRAMALAKSHMI SUDALAIKANNANNo ratings yet
- MRT-10-2 Arc Welding Principle and SSWDocument27 pagesMRT-10-2 Arc Welding Principle and SSW1026Aniket TankNo ratings yet
- Processes of WeldingDocument9 pagesProcesses of WeldingNaeemNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding, Shielded Metal Arc Welding, Metal Inert Gas WeldingDocument44 pagesArc Welding, Shielded Metal Arc Welding, Metal Inert Gas WeldingDinesh InavoluNo ratings yet
- Welder's Handbook (Air Products Co.)Document48 pagesWelder's Handbook (Air Products Co.)Patrick DominguezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Welding Handbook99 PDF TigDocument48 pagesEngineering Welding Handbook99 PDF TigSorin Stanescu100% (1)
- Study of Tig WeldingDocument11 pagesStudy of Tig WeldingChandan Srivastava100% (1)
- Metals 10 00099 v2 PDFDocument23 pagesMetals 10 00099 v2 PDFarjun prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Welding NPTEL Lecturers - Part4Document30 pagesWelding NPTEL Lecturers - Part4Sai ChaithanyaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Methods (Welding)Document84 pagesFabrication Methods (Welding)Karthikeyan MurugananthanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Tig Welding Weldment and Defect Identification Using Non Destructive Testing NDTDocument48 pagesAnalysis of Tig Welding Weldment and Defect Identification Using Non Destructive Testing NDTRebecca KelleyNo ratings yet
- Wielding Process Jayme 2 FinalDocument28 pagesWielding Process Jayme 2 FinalJAYME JOSWANo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc WeldingDocument15 pagesGas Tungsten Arc WeldingCarlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Welding Technologies in Shipbuilding IndustryDocument7 pagesWelding Technologies in Shipbuilding IndustryAravindh AkashNo ratings yet
- Case Study YayaDocument6 pagesCase Study YayaYayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document65 pagesLecture 4Ishtiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc Welding - WikipediaDocument10 pagesGas Tungsten Arc Welding - WikipediadevinfNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 5 SMAW Grade 9Document13 pagesLAS Week 5 SMAW Grade 9Hebe KamaNo ratings yet
- L31B Gmaw PDFDocument16 pagesL31B Gmaw PDFCrocodileNo ratings yet
- Gas Tungsten Arc WeldingDocument17 pagesGas Tungsten Arc WeldingMat SerabaiNo ratings yet
- Processes: Edit EditDocument8 pagesProcesses: Edit EditJenolan ChettyNo ratings yet
- Processes: Edit EditDocument4 pagesProcesses: Edit EditNgro Quinapaxi GonzalezNo ratings yet
- vtppt2016 170820040544Document19 pagesvtppt2016 170820040544Sk SajedulNo ratings yet
- MBDA Missile Test SuccessDocument2 pagesMBDA Missile Test SuccessMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Okamoto General Catalogue 2018 E PDFDocument25 pagesOkamoto General Catalogue 2018 E PDFMuhammadRiady100% (1)
- 2 2 Rules and Regulations 10Document1 page2 2 Rules and Regulations 10MuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Maintaining and repairing machineryDocument16 pagesMaintaining and repairing machineryMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- 04.technical Data 07.resharpeningDocument1 page04.technical Data 07.resharpeningMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- JadwalImsakiyahRomadlon1431H JakartaDocument1 pageJadwalImsakiyahRomadlon1431H JakartaAbu Hanif AssyathiryNo ratings yet
- 2008 Lancer Brochure PDFDocument14 pages2008 Lancer Brochure PDFMuhammadRiady100% (1)
- Okamoto General Catalogue 2018 E PDFDocument25 pagesOkamoto General Catalogue 2018 E PDFMuhammadRiady100% (1)
- J.M.J. Journée and W.W. Massie, "OFFSHORE HYDROMECHANICS - AppendixesDocument24 pagesJ.M.J. Journée and W.W. Massie, "OFFSHORE HYDROMECHANICS - Appendixespackya7191No ratings yet
- Maintaining and repairing machineryDocument16 pagesMaintaining and repairing machineryMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- 3a. Isi-B. Survey Dan Cara Pemeriksaan Kapal-31-55Document25 pages3a. Isi-B. Survey Dan Cara Pemeriksaan Kapal-31-55MuhammadRiady100% (1)
- Part I-Classification and Survey Requirements-Edition 2008Document81 pagesPart I-Classification and Survey Requirements-Edition 2008MuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Rheology, Ow Behaviour and Heat Transfer of Ice Slurries: A Review of The State of The ArtDocument13 pagesRheology, Ow Behaviour and Heat Transfer of Ice Slurries: A Review of The State of The ArtMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Maintaining and repairing machineryDocument16 pagesMaintaining and repairing machineryMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- HP Modular Power Distribution Unit Kit: Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesHP Modular Power Distribution Unit Kit: Installation InstructionsMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- HP Modular Power Distribution Unit Kit: Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesHP Modular Power Distribution Unit Kit: Installation InstructionsMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Operating Characteristics of An Agitator With A Draught TubeDocument6 pagesOperating Characteristics of An Agitator With A Draught TubeMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- HP Modular Power Distribution Unit Extension Bar Brackets and Core Universal MountingDocument2 pagesHP Modular Power Distribution Unit Extension Bar Brackets and Core Universal MountingMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Ballast ModelDocument1 pageBallast ModelMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Sensitization in Stainless SteelDocument8 pagesSensitization in Stainless SteelMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- K2 (Korean New Main Battle Tank)Document4 pagesK2 (Korean New Main Battle Tank)MuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Rheology, Ow Behaviour and Heat Transfer of Ice Slurries: A Review of The State of The ArtDocument13 pagesRheology, Ow Behaviour and Heat Transfer of Ice Slurries: A Review of The State of The ArtMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Brochure FabiaDocument17 pagesBrochure FabiaMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- Operating Characteristics of An Agitator With A Draught TubeDocument6 pagesOperating Characteristics of An Agitator With A Draught TubeMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- K1A1Document1 pageK1A1MuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument1 pageSurveyMuhammadRiadyNo ratings yet