Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of PTB (Myrc)
Uploaded by
Rj Magpayo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
623 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of tuberculosis infection through airborne droplets. It describes how the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria are inspired into the lungs, lodge in the upper lobes and migrate to lymph nodes where they proliferate, causing inflammation of the lungs. The immune system responds by activating macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytose the bacteria, sealing them off in tubercles that develop caseous necrosis, becoming dormant within collagenous scar tissue in the bronchi.
Original Description:
PTB patho
Original Title
Pathophysiology of Ptb (Myrc)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of tuberculosis infection through airborne droplets. It describes how the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria are inspired into the lungs, lodge in the upper lobes and migrate to lymph nodes where they proliferate, causing inflammation of the lungs. The immune system responds by activating macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytose the bacteria, sealing them off in tubercles that develop caseous necrosis, becoming dormant within collagenous scar tissue in the bronchi.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
623 views2 pagesPathophysiology of PTB (Myrc)
Uploaded by
Rj MagpayoThe document summarizes the pathophysiology of tuberculosis infection through airborne droplets. It describes how the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria are inspired into the lungs, lodge in the upper lobes and migrate to lymph nodes where they proliferate, causing inflammation of the lungs. The immune system responds by activating macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytose the bacteria, sealing them off in tubercles that develop caseous necrosis, becoming dormant within collagenous scar tissue in the bronchi.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
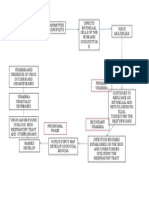
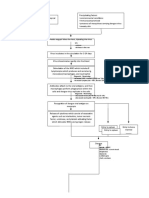
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (Book Based)
Airborne/Droplets
Inspiration of bacteria (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) to the lungs
Bacilli lodge to the upper lobe Migration to the lymph nodes
Proliferation of bacilli
Inflammation of the lungs (Pneumonitis)
Initiation of immune response
Activation of alveolar macrophages and neutrophils
Phagocytosis of the bacilli
Sealing of the colonies of bacilli
Formation of tubercle
Formation of caseous necrosis
Collagenous scar tissue grows tubercle
Complete isolation of the bacilli in the bronchi
Bacilli becomes dormant
Impairment of the immune system
Bacilli escape from the bronchi
Endogenous reactivation of dormant bacilli
Active bacteria spread through blood and lymphatic organs
You might also like
- NCP MyomaDocument6 pagesNCP MyomaIzza Mae Ferrancol PastranaNo ratings yet
- NCP GastroenteritisDocument1 pageNCP GastroenteritisFranchesca PaunganNo ratings yet
- NCP For PCAPDocument4 pagesNCP For PCAPDianeNo ratings yet
- Measles PathoDocument1 pageMeasles PathoAin JamelaNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument14 pagesCellular AberrationjinahyangNo ratings yet
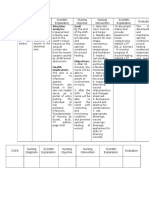
- VI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesVI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Dengue Case StudyDocument23 pagesDengue Case Studycutie_0023No ratings yet
- Book Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument7 pagesBook Based: Etiology: Tubercle Bacilli Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- NCP For FeverDocument2 pagesNCP For FeverDominises Jade Corpuz82% (17)
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PTB (Myrc)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of PTB (Myrc)Rj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology TBDocument2 pagesPathophysiology TBJhen DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- H MoleDocument7 pagesH MoleRaymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Case StudyDocument28 pagesBronchitis Case Studyroselyn valdezNo ratings yet
- Dermatomyositis NCPDocument3 pagesDermatomyositis NCPMakki MarcosNo ratings yet
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationWyeth Earl Padar EndrianoNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomyKadulum100% (1)
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocument5 pagesCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- NCP LatestDocument6 pagesNCP LatestThirdy AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Case NCPDocument25 pagesCase NCPJoher Bolante Mendez100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Raynauds Disease-Acute PainEerie EraNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan MeaslesDocument1 pageDischarge Plan MeaslesInosanto May AnnNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AmoebiasisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AmoebiasisCathy AcquiatanNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- NCP CholeraDocument2 pagesNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxyai19100% (2)
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- Case Study OpdDocument35 pagesCase Study OpdMicah MagallanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FeverDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan Feverbharat singhNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNo ratings yet
- NCP'SDocument10 pagesNCP'SEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- Ecologic ModelDocument2 pagesEcologic Modelluis_chubeeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- Cap MRDocument4 pagesCap MRKit BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- NCP For DengueDocument6 pagesNCP For DengueSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute PainDocument1 pageNCP - Acute PainjsthrNo ratings yet
- 2nd Case Scenario BronchitisDocument5 pages2nd Case Scenario BronchitisKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument4 pagesDengueKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesPeptic Ulcerdanica100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPmimingdot33No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For InflammationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For InflammationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- CASE Study PTBDocument52 pagesCASE Study PTBbennettchuaNo ratings yet
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 LUMBAR PUNCTURE - Students PDFDocument78 pagesNCM 109 LUMBAR PUNCTURE - Students PDFChristine Cabbigat100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Pa ThoDocument1 pagePa ThoVema Andea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Causative Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis/ Mycobacterium Bovis/ Tubercle Bacilli/ Mode of Transmission: Airborne Droplets PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCausative Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis/ Mycobacterium Bovis/ Tubercle Bacilli/ Mode of Transmission: Airborne Droplets Pathophysiologydwyane0033No ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologydwyane0033No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Primary ComplexPong's Teodoro SalvadorNo ratings yet
- LP Anak Ni Nyoman SekariniDocument30 pagesLP Anak Ni Nyoman Sekarinihendrapartha8No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Pneumoniapallavi100% (2)
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Exam Name Result Unit Normal Value AnalysisDocument1 pageExam Name Result Unit Normal Value AnalysisRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Case StudyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Case StudyRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- CHD AsthmaDocument20 pagesCHD AsthmaRj MagpayoNo ratings yet