Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIDAS SteelCompositeCurvedBridgeTutorial
Uploaded by
Oscar MendozaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIDAS SteelCompositeCurvedBridgeTutorial
Uploaded by
Oscar MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
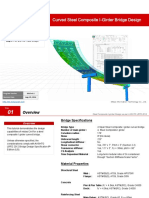
Curved Steel I-Girder Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
Overview
1. The bridge geometry is made.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Materials and sections are defined. Geometry is made from scratch. Crossbeam/ diaphragm modeling. Boundary conditions are applied. Loading is applied. (Self weight and SIDL)
2.
Live Loads are applied as per AASHTO LRFD.
1. 2. Two lanes is defined. The lane can carry vehicles in both directions.
3.
Analysis
1. 2. Response Spectrum Live load
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
1. Introduction
30 ft 200 ft
8 in
6 ft
32 ft 1.5 ft
4
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
1. Introduction
FEA Modeling of Steel Bridges
1. Beam Element (Composite Section)
2. Beam & Plate Elements
3. Plate Elements
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
2. Materials
Properties> Material > Add
Steel:
2 3
5 6 7
1. Select Steel under type of design. 2. Select ASTM09(S) under Steel Standard. 3. Select A709-50W type from DB. 4. Click Apply. Concrete: 5. Select Concrete under type of design.
6. Select ASTM(RC) under Concrete Standard.
7. Select C5000 (for pier and pier table). 8. Click Apply. Concrete for Crossbeam: 9. Select C5000 from DB, then Standard as None.
10. Enter Name as Crossbeams.
11. Set Weight density as Zero. 12. Click OK.
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
3. Sections
Properties > Section > Add > select DB/User tab 1. Select I-section 2. Select User 3. Plug in dimensions as provided 4. Click Change Offset 5. Select Center-Top 6. OK 7. OK
5 3 6
midas Civil
Steel Composite Girder Ramp
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
Sections
1 3 2 4
Properties > Section > Add > DB/User Diaphragm: 1. Select BD/User tab. 2. Select I-Section, and DB 3. Select AISC(US) under Steel Standard. 4. Enter name Diaphragm, as W16X45 from DB. 5. Change Offset to Center Top.
6. Click Apply
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
3. Sections
1 2 3 4 10 9
Properties> Section > Add
7 8
Bracing: 1. Select DB/User tab. 2. Select Angle Section, and DB. 3. Select AISC(US) under Steel Standard. 4. Enter name as Bracing, and L- 4X4X3/8 from DB.
11
5. Set Offset as Center-Center.
6. Click Apply. Pier : 7. Select DB/User tab. 8. Select Solid Round. 9. Select User.
5 6 12
10. Enter name as Pier. 11. Enter Diameter as 72 in. 12. Click Apply. Pier Cap Center: 13. Select Solid Rectangle. 14. Name as Pier Cap Center. 15. Enter H as 72 and B as 72. 16. Set Offset as Center Top. 17. Click OK.
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
3. Sections
Define Tapered Section properties (For Pier Cap) Properties> Section
1 2 3 4
Add Section Pier Cap: (P_L) 1. Select Tapered Section Tab. 2. Select Solid Rectangle section for the ends of Pier Cap. 3. Enter name as P_L for left end. 4. Enter values for i and j . 5. Apply y and z axis variation for linear. 6. Set Offset Center Top. 7. Click Apply Repeat above step s again for the other end of cap(P_R) (i and j end interchanged) Dummy Crossbeams: 1. Select DB/User tab. 2.Select Solid Rectangle 3. Enter name as Dummy Crossbeams. 4. Select User.
6 7
5. Enter the H as 8 and B as 60. (Note: Thickness of beam = deck thickness) 6. Set Offset as Center-Bottom. 7. Click OK.
10
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
3. Sections
1 2 3 4
Properties > Thickness 1. In-plane & Out-of-plane: 8 in 2. Check Plate offset 3. Value: 4 in 4. OK
6 7
11
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Node/Element > Nodes > Create nodes. Create nodes at (0,0,0) and copy once. 2. Create node at (100,30,0) 3. Select all by clicking and translate (Nodes>Translate) along Y axis to make the nodes for edge girders
12
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Node/Element > Nodes > Rotate Nodes. Rotate nodes at abutment 1 (left side)by 30 first. 2. Then abutment 2 (right side) by - 30.
13
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Node/Element > Elements > Create Line Elements on Curve. Create Line Elements on Curve by using Arc by 3 Points methods. Enter 40 for Number of Segments. Click in field P1 and then click on nodes from left to right (like nodes 1, 2, 3)
2.
Repeat for the other four girders.
14
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. 2. Select beam element of two exterior girders, be aware that only beams elements should be selected not any nodes Hit Delete key from your keyboard. The nodes should remain in place
15
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Create diaphragms for Abutment 1. Click in nodal connectivity field and click on nodes 7,1,4. 2. Repeat step 1 for diaphragm over Pier Cap and Abutment 2.
3. Repeat Step 1 for every 4th node (diaphragm at pier cap) on inner edge girder with section as Bracing as shown.
Diaphragm Sections Toggle off Hidden
Over Pier cap
Abut. 1
Abut. 2
16
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - End Diaphragm
1. Right click on Diaphragm section from Works Tree Menu and select Active. Then Select All and translate (Node/Element > Nodes>Translate) along Z axis by (0,0,-76.8), to make the nodes for Bottom chords of diaphragms at abutments. 2. Node/Element > Elements Create Elements. Create bottom chords by connecting the translated nodes using bracing sections.
Change units to inch
17
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - End Diaphragm
3. Change element type to Truss and create inverted K- bracings for end diaphragms by snapping nodes at the mid points of the bottom chord.* 4. Click in Nodal connectivity. Click node at top and then move down to the bottom chord, the cursor will automatically be placed at its mid point, and click there.* 5. Repeat for all end-diaphragms. (i.e. at pier cap and abutment 2)
At bottom-right corner of midas CIVIL window
* 2 signifies that nodes will be snapped automatically to divide the element into . It can be changed to 3,4,5,,,,, to divide element by snapping nodes at 1/3 , ,1/5 ,.of 18 element length.
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - End Diaphragm
6. Boundary>Rigid Links. Create Rigid Link between top and bottom nodes on the girder webs at Abutment 1 diaphragm; the bottom node as Master node and top node as Slave node. 7. Click in Master node field and then click on bottom node in Model View window. 8. Use Select Single Slave node. to select the node directly above Master node as
9. Click on typical type as Rigid Body. 10 Click Apply. 11. Repeat for other girder webs at Abutment 1 diaphragm, and then for Abutment 2 diaphragm.
Slave Node
8 Rigid links 9
Cross Bracings Master Node 10
7 19
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - Intermediate Diaphragm
1. Activate All and right click on Bracing section from Works Tree Menu and select Active. Then Select by Window member corresponding to intermediate diaphragm. the
2. Click Activate(F2). Select All and Translate nodes (Node/Element > Nodes>Translate) along Z axis by (0,0,-74.4) , to make the nodes for the bottom chords of intermediate diaphragms.
3. Node/Element > Elements > Create Elements. Create bottom chords by connecting the translated nodes using bracing sections.
1 2
20
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - Intermediate Diaphragm
4. Change element type to truss and check off intersect Node and Element and create cross bracings for intermediate diaphragms. 5. Click in Nodal Connectivity. Click node at top and then move down diagonally to the bottom chord.
6. Repeat for all intermediate diaphragms.
Cross Bracing 4
Bottom Chord
Intermediate Diaphragm 21
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - Intermediate Diaphragm
7. Boundary > Rigid Links. Create Rigid Link between top and bottom nodes on the girder webs at intermediate diaphragms. The top node as Master node and bottom node as Slave node. 8. Click in Master node field and then click on top node in Model View window. 9. Use Select Single Slave node. to select the node directly below Master node as
10. Click on typical type as Rigid Body. 11. Click Apply. 12. Repeat for other girder webs at intermediate diaphragm, and then for other intermediate diaphragm.
Master Node
8 Rigid links 10
Cross Bracings 11 Slave Node 9 22
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling Concrete Deck
Node/Element > Elements >Auto Mesh 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Select Nodes Type: Quadrilateral Select Material 1 Select Thickness 1 Click the box to turn to green Select nodes one by one in clockwise direction starting from left top node to create an enclosed area (so the 1st node and the last node should be the same) When all nodes selected > Click Apply
1 5 2
6.
7.
3 4
23
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling Concrete Deck
24
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling - Pier
1. Activate All . Switch to Top-View over pier cap. (Box A) 2. Click Activate(F2) Select by Window Select member corresponding to end diaphragm
and switch to Left-View
A 1
25
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. 2. Use Select Single and select the bottom nodes of the girders.
Translate by (0,0,-12.4). Node/Element > Nodes>Translate
3.
Select node A using select single, and translate through unequal distance along y axis by -36,-138,210,138.
3 1 Girder bottom Nodes 3
Node A
26
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. 2. 3. 4. Node/Element > Elements>Create Elements. Set material as C5000. Create Pier Cap left end using Section as P_L ,click in nodal connectivity and click on nodes along a to c . Change Section to Pier Cap Center, click in nodal connectivity and then click nodes c to e. Change Section to P_R , click in nodal connectivity and then click on nodes e to g.
1 2 3 4
27
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Properties>Tapered Section Group. Select by window the right end of pier cap. Enter name as P_Right . Z-Axis variation as Polynomial (2) with Symmetric plane from J end. Y Axis variation being Linear. Click Add. Select by Window the left end of Pier Cap.
2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
8.
Name as P_Left and Z axis symmetric plane from I-end.
Click Add.
9.
Left End 7
Right End 2
9 28
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. 2. 3. Node/Element > Nodes>Translate. Translate node a by (0,0,-72 in). Using Select Single, select the translated node Node/Element > Elements>Extrude. Extrude Node into line element to create pier as shown in dialog box.
Node a
2 Newly Translated node
29
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
4. Modeling
1. Boundary > Elastic Link. 2. Select Rigid Type. 3. Click in 2 Nodes field and then click at nodes a and b. 4. Check on Copy Elastic link and copy along Y axis as shown 5. Click on nodes c and d. 6. Click on d and e.
e 6 d a 3 b c 5
4 30
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
6. Boundary Conditions: Supports
Model > Boundary> Supports 1. Select the support nodes. 2. Select Support type. 3. Click Apply. Repeat for abutment nodes.
Interior girder node
1 3
Exterior girder node
31
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads
Load>Static Load Cases 1. Enter SW, SIDL as Dead Loads.
32
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Self Weight and SIDL
Load>Self Weight
1. Load case name as SW and group name as default. 2. Z = -1 3. Click Add. SIDL: 4. . Select the elements to be loaded. For example, for Girders, double click on girder section from Works Tree. 5. Load>Element Beam Load. Load case name as SIDL. 6. Enter element beam loads as UDL in z direction. -0.5 kips/ft (Change units from in to ft). 7. Click Apply.
3 7
33
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Structure Groups
1. Click on Groups tab under Tree menu. 2. Right click on Structure group and click on New 3. Enter name as Girder, click add. 4. Enter name as Crossbeams + Diaphragms, click add, click close. 5. Click on Select by Plane Close. 6. Click Activate. 7. Double click on Girder under section in Works tree to select all girders. 8. Go to groups tab, click on Girder under structure group and drag and drop it over the Model View window. (to assign the girder members to the structure group.) 9. Right click on Girder structure group and select Inactive. 10. Click on Select All and drag and drop the Crossbeam + Diaphragm structure group on Model View window to assign the diaphragms and crosbeams to the structure group. and select XY plane with Z=0 ft. and click
34
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Live Loads (Define Lane)
1
Load > Moving >Moving Load Code. 1. Select AASHTO LRFD from the moving load code. Load > Moving Load Analysis > Traffic Surface Lanes. 1. Lane Name : Lane 1
2 3 4
2. Lane width: 12 ft 3. Wheel spacing:6ft 4. Offset: -7 ft 5. Selection by: Picking. 6. Select all exterior nodes in bottom one by one starting from left bottom corner.
7. Apply
8. Repeat the process for Lane 2. Only change Eccentricity to -23 ft
6 35
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Live loads (Vehicles and Load cases)
5
Load > Moving Load Analysis Data> Moving Load case. 5. Enter a Load case name: MVL 6. Check or modify Multiple Presence Factor. 7.Select loading effect for sub load case as Independent . 8. Add Sub-Load case. 9. Select one of the vehicles.. 10. Scale factor as 1, and min. number of loaded lane as 1 and max. as 2.
11. Select lanes L1 and L2. 12. Click OK. 13. Similarly create load case for HL-93 Tandem Vehicle.
8
Load > Moving Load Analysis Data> Vehicles.
9 10
1. Click Add Standard
2. Click on Vehicle load type 3. Select HL-93 TRK as first vehicle load type., DLA = 33%,Click Apply 4. Select HL-93 TDM as second vehicle load type. Click OK
11
12 36
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Moving Load analysis Control
Analysis> Moving Load Analysis Control Data 1. Set the analysis control as specified in the dialog box.
37
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Loads: Conversion of Loads to masses for seismic analysis.
Load > Static Loads > Masses > Loads to masses. 1. Select the Mass direction :X,Y,Z 2. Load type: Nodal, Beam, Floor, Pressure 3. Select the Load case (SIDL) to be converted and scale factor.
1 2
4. Click Add. 5. Click OK. Model> Structure type 6. Check on Convert Self Weight into Masses.
38
midas Civil
Steel Composite Curved Bridge
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
8. Response Spectrum Analysis
1 4 2 3
Load> Response Spectrum analysis data > Response spectrum functions
1. Enter the Function Name. 2. Import the response spectrum coordinates as obtained from RS.spd file, [AASHTO LRFD , Soil type E site.]. 3. Response spectrum is generated simultaneously. 4. Enter the Damping Value and acceleration due to gravity.
39
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
7. Seismic Load case / Eigenvalue Analysis Control
Load> Response Spectrum analysis data > Response spectrum load cases
1 2
1. Enter the Load case name. RS-X 2. Select Direction and Excitation angle as 0 deg. 3. Select Function name. 4. Click Add. And repeat with Load case name as RS-Y and Excitation angle as 90 deg 5. Click Eigenvalue Analysis Control.
6 7
4
6.Select Lancoz Vectors as type of Analysis. 7. Enter no. of frequencies as 10.
40
midas Civil
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
9. Perform analysis
Analysis > Perform Analysis
41
Bridging Your Innovations to Realities
You might also like
- Midas Civil Training - 0220-Edit-Final PDFDocument48 pagesMidas Civil Training - 0220-Edit-Final PDFgundulp100% (2)
- Composite Girder - Tutorial Midas CivilDocument59 pagesComposite Girder - Tutorial Midas CivilAndiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Steel Composite BridgeDocument31 pages4 - Steel Composite BridgeNabeel Ahmad100% (1)
- Curved SLab Bridge - FINALDocument32 pagesCurved SLab Bridge - FINALSuman DharaNo ratings yet
- Curved Steel Composite I-Girder Bridge Design PDFDocument46 pagesCurved Steel Composite I-Girder Bridge Design PDFSindhu BharathiNo ratings yet
- MIDAS 2013 Indonesia Workshop - Cable Stayed BridgeDocument85 pagesMIDAS 2013 Indonesia Workshop - Cable Stayed BridgeDanang Rahadian100% (1)
- PSC Design (Aashto-Lrfd Tyu07) TutorialDocument44 pagesPSC Design (Aashto-Lrfd Tyu07) TutorialMohammad Tawfiq WaraNo ratings yet
- PSC Box Girder Design Aashto LRFDDocument29 pagesPSC Box Girder Design Aashto LRFDkdb92uceNo ratings yet
- Midas CatalogueDocument38 pagesMidas CatalogueChaudharyShubhamSachanNo ratings yet
- Slab Bridge Using Midas CivilDocument57 pagesSlab Bridge Using Midas CivilPratap JadhavNo ratings yet
- 2-Span PSC Composite Girder BridgeDocument51 pages2-Span PSC Composite Girder BridgeNabeel Ahmad100% (2)
- Vol.02 - Complete Guide To PrestressingDocument14 pagesVol.02 - Complete Guide To PrestressingShadiNo ratings yet
- MIDAS 2013 Indonesia Workshop Cable Stayed Bridge PDFDocument85 pagesMIDAS 2013 Indonesia Workshop Cable Stayed Bridge PDFdwi yantoNo ratings yet
- Bowstring Steel Bridge - ModifiedDocument44 pagesBowstring Steel Bridge - Modifiedpratap jadhavNo ratings yet
- PSC Box Girder Bridge With Abutment & Pier Design in AASHTO-LRFDDocument197 pagesPSC Box Girder Bridge With Abutment & Pier Design in AASHTO-LRFDSANDIPNo ratings yet
- Optimize MIDASDocument31 pagesOptimize MIDASMario FrankistaNo ratings yet
- Extradosed Bridge MidasDocument49 pagesExtradosed Bridge MidasTarun Kant Goyal100% (6)
- PSC Composite I Integral BridgeDocument94 pagesPSC Composite I Integral BridgeADITYA DATTATRAYA GAITONDENo ratings yet
- 2-Span PSC Composite Girder FinalDocument51 pages2-Span PSC Composite Girder FinalSuman DharaNo ratings yet
- Midas Civil - Advanced - Prestressed Box Girder Design (FCM, FSM)Document77 pagesMidas Civil - Advanced - Prestressed Box Girder Design (FCM, FSM)mdkmlNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cantilever Bridge Analysis Day 3Document15 pagesBalanced Cantilever Bridge Analysis Day 3Isidro P. BuquironNo ratings yet
- Substructures - Solutions - MidasbridgeDocument14 pagesSubstructures - Solutions - Midasbridgechao liuNo ratings yet
- PSC Box Girder Design PDFDocument93 pagesPSC Box Girder Design PDFRavi Chandra Ivp100% (1)
- S05 - Balanced Cantilver Segmental Bridge - Engr. PatrickDocument60 pagesS05 - Balanced Cantilver Segmental Bridge - Engr. Patrickomar42170No ratings yet
- SPC Manual PDFDocument11 pagesSPC Manual PDFNgiuyen Viet TienNo ratings yet
- Midas Civil - Detail AnalysisDocument34 pagesMidas Civil - Detail Analysiswilfred100% (2)
- 05-Multi-Cell Prestressed Box Girder Bridge Design As Per AASHTO PDFDocument36 pages05-Multi-Cell Prestressed Box Girder Bridge Design As Per AASHTO PDFJeong Woon KangNo ratings yet
- International Workshop Bridges Integral Abutments LTU-TR-0614-SEDocument157 pagesInternational Workshop Bridges Integral Abutments LTU-TR-0614-SEJc WongNo ratings yet
- Integral Bridge Midas SeminarDocument36 pagesIntegral Bridge Midas Seminarlamkinpark3373100% (1)
- MIDAS Civil Advanced Webinar PresentationDocument49 pagesMIDAS Civil Advanced Webinar PresentationNecmi HocaNo ratings yet
- Design of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDDocument32 pagesDesign of Dingley Bypass Integral Bridges: Dr. Kabir Patoary - Principal Engineer - Bridges - GHDkevin_au18No ratings yet
- Steel Bridge Design Using FEM Analysis: Peter Reeves-Toy Director, UAEDocument47 pagesSteel Bridge Design Using FEM Analysis: Peter Reeves-Toy Director, UAEROHANNo ratings yet
- 2-Span PSC Composite GirderDocument79 pages2-Span PSC Composite Girderbhagwat Singh RautelaNo ratings yet
- Workshop Midas Civil FSMDocument87 pagesWorkshop Midas Civil FSMAkhmad Ilham RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Integral Bridges Skew EffectsDocument32 pagesIntegral Bridges Skew EffectsSuryaNo ratings yet
- Tendon Template PDFDocument27 pagesTendon Template PDFGeorge LazarNo ratings yet
- En1992 2 ManualDocument86 pagesEn1992 2 ManualMarian Dragos100% (1)
- Single Span Composite Precast Beam and Deck Bridge Design ManualDocument26 pagesSingle Span Composite Precast Beam and Deck Bridge Design Manualani4576100% (1)
- Midas Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesMidas Practice ProblemsAbc ZyxNo ratings yet
- Slab ModellingDocument15 pagesSlab ModellingRajesh Pawar LallaNo ratings yet
- Single Span Steel Composite Plate Girder Bridge PDFDocument42 pagesSingle Span Steel Composite Plate Girder Bridge PDFNeeta RautelaNo ratings yet
- Moving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2Document30 pagesMoving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2tyukgombaNo ratings yet
- Moving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2 PDFDocument30 pagesMoving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2 PDFRay GongNo ratings yet
- MIDAS BRIDGE To BRIDGES #3 Training Material - Prestressed Concrete Girder TutorialDocument43 pagesMIDAS BRIDGE To BRIDGES #3 Training Material - Prestressed Concrete Girder TutorialEddy BongNo ratings yet
- 2016 FAQ Midas CivilDocument67 pages2016 FAQ Midas Civillamkinpark3373No ratings yet
- 2-Span PSC Composite AASHTODocument49 pages2-Span PSC Composite AASHTOSuman DharaNo ratings yet
- Cable Force TuningDocument23 pagesCable Force TuningBarben Group CorpNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Three Span Continuous Integral Bridge (Balanced Cantilever) PDFDocument181 pagesAnalysis of Three Span Continuous Integral Bridge (Balanced Cantilever) PDFMaitrabarun KarjeeNo ratings yet
- Bridge Design Report - Final-SadaDocument294 pagesBridge Design Report - Final-SadaSadatcharaMoorthi NNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesFrom EverandFinite Element Analysis and Design of Steel and Steel–Concrete Composite BridgesNo ratings yet
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignFrom EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bridging the Strait: The Story of The Confederation Bridge ProjectFrom EverandBridging the Strait: The Story of The Confederation Bridge ProjectRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Innovative Bridge Design Handbook: Construction, Rehabilitation and MaintenanceFrom EverandInnovative Bridge Design Handbook: Construction, Rehabilitation and MaintenanceAlessio PipinatoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Tutorial of MidasDocument41 pagesTutorial of MidasChaudharyShubhamSachan100% (1)
- Unwedge Getting Started CompressedDocument4 pagesUnwedge Getting Started CompressedJuan Carlos Rosas San AgustinNo ratings yet
- Unwedge Getting StartedDocument4 pagesUnwedge Getting StartedAnonymous iWaBM6P9V6No ratings yet
- Underground Ring Design PDFDocument49 pagesUnderground Ring Design PDFАнхбаяр БатболдNo ratings yet
- Portada - Atrás-Manual de Instrucciones Estación Total TOPCON GPT 2006Document1 pagePortada - Atrás-Manual de Instrucciones Estación Total TOPCON GPT 2006Juan PabloNo ratings yet
- AU09 Optimize The Performance of Civil 3D CV308 2Document27 pagesAU09 Optimize The Performance of Civil 3D CV308 2Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- ProLINK ConversionsDocument12 pagesProLINK ConversionsOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cadlearning Autocad Civil 3d 2011 OutlineDocument3 pagesCadlearning Autocad Civil 3d 2011 OutlineOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- C3D Cadalyst-47-05 1Document3 pagesC3D Cadalyst-47-05 1Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Serie GTS-220: Estación Total Electrónica Estación Total ElectrónicaDocument2 pagesSerie GTS-220: Estación Total Electrónica Estación Total ElectrónicaOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Publishing Geoprocessing Services TutorialDocument16 pagesPublishing Geoprocessing Services TutorialOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- ProLINK Comms Quick Start GuideDocument17 pagesProLINK Comms Quick Start GuideOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- TPS800 Manual V1 0 EnglishDocument158 pagesTPS800 Manual V1 0 EnglishOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Hydrographs Extension - User's GuideDocument106 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Hydrographs Extension - User's GuideericfgNo ratings yet
- ProLINK Reference ManualDocument378 pagesProLINK Reference ManualOscar Mendoza0% (2)
- AU09 Optimize The Performance of Civil 3D CV308 2Document27 pagesAU09 Optimize The Performance of Civil 3D CV308 2Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- TPS800 QuickStart EnglishDocument4 pagesTPS800 QuickStart EnglishOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Hydrographs Extension - User's GuideDocument106 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Hydrographs Extension - User's GuideericfgNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Survey ExposedDocument22 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D Survey ExposedSajid Hussain100% (1)
- US Corridor EZY BrochureDocument1 pageUS Corridor EZY BrochureOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Autocad Sheet Sets in Civil 3d 2008 SMDocument14 pagesAutocad Sheet Sets in Civil 3d 2008 SMCarlos Sánchez-MendietaNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: Autocad Civil 3D 2010Document10 pagesQuestions and Answers: Autocad Civil 3D 2010Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- C3 DStock Subassembly HelpDocument614 pagesC3 DStock Subassembly HelpKatty Lorena Chapilliquen GuarnizoNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Express Extension - User's GuideDocument84 pagesAutoCAD Civil 3D Hydraflow Express Extension - User's Guideericfg0% (1)
- Moviendo de Land Destopk A Civil 3DDocument130 pagesMoviendo de Land Destopk A Civil 3DIng Ignacio Rojo GastelumNo ratings yet
- Manual XlstatproDocument230 pagesManual Xlstatprogintex3937No ratings yet
- Manual de Vigas HP 50GDocument9 pagesManual de Vigas HP 50GamadoromanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ArcscanDocument20 pagesTutorial ArcscanALFONSOVR89No ratings yet
- 03.04 - General Design - Tack Welding of Reinforcing Bars - BD 40-93Document16 pages03.04 - General Design - Tack Welding of Reinforcing Bars - BD 40-93Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- 03.13 - General Design - Bracing Systems & Use of U-Frames in Steel BridgesDocument18 pages03.13 - General Design - Bracing Systems & Use of U-Frames in Steel BridgesOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- G Section 08Document42 pagesG Section 08Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Observables Sof. TitoDocument6 pagesObservables Sof. TitoOscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- 03.12 - General Design - Design of Integral BridgesDocument15 pages03.12 - General Design - Design of Integral BridgesOscar Mendoza100% (1)
- 14.01 - General Design - Structures in Areas of Mining Subsidence - BD-10-97Document31 pages14.01 - General Design - Structures in Areas of Mining Subsidence - BD-10-97Oscar MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cable Trench Installation GuideDocument12 pagesCable Trench Installation Guideecruz_yhwhNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 4 Design Composite Steel Concrete StructuresDocument245 pagesEurocode 4 Design Composite Steel Concrete Structuresfritzstrobl100% (6)
- SANS1200MMDocument15 pagesSANS1200MMKyle MoolmanNo ratings yet
- Corerosion - Thomasnet Navigator - Com Asset AWWA D103 97 Guide SpecificationDocument12 pagesCorerosion - Thomasnet Navigator - Com Asset AWWA D103 97 Guide Specificationnespak06No ratings yet
- Elevator Chapter 6Document65 pagesElevator Chapter 6Pedro AmorsoloNo ratings yet
- Painting System 20000E02Document142 pagesPainting System 20000E02prabha221No ratings yet
- Design of Anchor Bolt - Rev.ADocument8 pagesDesign of Anchor Bolt - Rev.AcivilaskarNo ratings yet
- Bridges Spanish HSRLDocument13 pagesBridges Spanish HSRLVelugoti VijayachandNo ratings yet
- RAM Steel Column Design Tutorial - Structural Analysis and Design - Wiki - Structural Analysis and Design - Be Communities by Bentley PDFDocument9 pagesRAM Steel Column Design Tutorial - Structural Analysis and Design - Wiki - Structural Analysis and Design - Be Communities by Bentley PDFRron de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ep-Gis 46-040Document31 pagesEp-Gis 46-040GorakhNo ratings yet
- QC System Manual PDFDocument41 pagesQC System Manual PDFwhitebros100% (1)
- QNBN Tech Spec For F& C Rev August 2014Document21 pagesQNBN Tech Spec For F& C Rev August 2014raghebom100% (1)
- Structure Calculation Warehouse 19 Mei'14Document28 pagesStructure Calculation Warehouse 19 Mei'14Su NarkoNo ratings yet
- Esp. NDS 15Document202 pagesEsp. NDS 15Javier CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Shear Steel ConnectionDocument3 pagesShear Steel ConnectionНемања Караклајић100% (1)
- Rules For The Classification of Ships, Pt. 2, 2013 PDFDocument203 pagesRules For The Classification of Ships, Pt. 2, 2013 PDFMilitza PerezNo ratings yet
- Repair Cases PaperDocument22 pagesRepair Cases PaperKatyogleNo ratings yet
- DNVGL Ru Ship Pt3ch3Document94 pagesDNVGL Ru Ship Pt3ch3DeonNo ratings yet
- Connections I V2.0.6b FinalDocument71 pagesConnections I V2.0.6b FinalNick Andrews50% (2)
- Sampling Procedure For Impact Testing of Structural SteelDocument5 pagesSampling Procedure For Impact Testing of Structural Steeljoy gultomNo ratings yet
- 0302 Corp Standard, Furnishing of Steel Structures Rev 5 - (44557493) PDFDocument31 pages0302 Corp Standard, Furnishing of Steel Structures Rev 5 - (44557493) PDFrpazbNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slabs Design ExampleDocument31 pagesConcrete Slabs Design ExampleandinumailNo ratings yet
- BS5507-3 1982Document11 pagesBS5507-3 1982surangaNo ratings yet
- Steel Design CE 408Document23 pagesSteel Design CE 408gundulpNo ratings yet
- Wood Express ManualDocument36 pagesWood Express ManualgertjaniNo ratings yet
- Foreword: Steel Detailers' ManualDocument1 pageForeword: Steel Detailers' ManualCarlos Gallardo LagosNo ratings yet
- JSPL - Structural - Steel - JINDALDocument6 pagesJSPL - Structural - Steel - JINDALMISBAH UL HAQUENo ratings yet
- Structural Steel in Housing - 3rd Edition PDFDocument32 pagesStructural Steel in Housing - 3rd Edition PDFscooba84No ratings yet
- Product Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Document48 pagesProduct Catalogue - (SP-NEW)Turoy100% (1)