Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Uploaded by
Aldrin Ian Oraza Alpe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
936 views1 pagepathophysiology
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpathophysiology
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
936 views1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis
Uploaded by
Aldrin Ian Oraza Alpepathophysiology
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
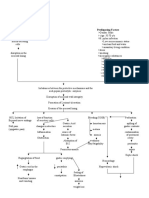
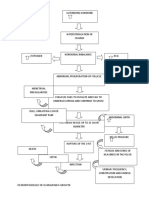
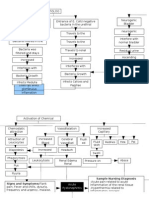
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of NEPHROLITHIASIS
AGENT - Excessive Intake of Ca (milk) / Hypercalcemia - Male
HOST
ENVIRONMENT - Family history of renal disease
- Low intake of H2O
Supersaturation of urine with increased calcium
Low urinary flow
May produce excess amounts of mucoprotein in the bladder or the kidney
Allowing crystallites to be deposited and trapped forming calculi or stones
Urine (upon voiding) moves tiny stones to the ureter
Large stones
Tiny stones
Blocks the ureter Causes spasm Makes urines turbidity cloudy
Becomes nidus for bacteria
Low urine output or dysuria Painful urination or dysuria
Injures the wall of the ureter
Urinary Tract Infection
Blood or RBCs combine with urine or hematuria
Hgb count Causes WBC count
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of UTIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of UTIKeannepotz80% (5)
- SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 pageSCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceJan Niño EstrellaNo ratings yet
- VII. Pathophysiology of PUDDocument1 pageVII. Pathophysiology of PUDJehmima Gloriani100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of NephrolithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasisanreilegarde80% (5)
- NEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesNEPHROLITHIASIS - PathophysiologyJon Corpuz Aggasid100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrolithiasis, Struvites Stone (Staghorn Calculi)Floyd100% (2)
- Etiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument5 pagesEtiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJanelle NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans For Renal CalculiRaveen mayi77% (22)
- IV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)Document3 pagesIV. The PATIENTS ILLNESS (Nephrolithiasis) Pathophysiology (Book-Based)wapakalypseNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocument84 pagesCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisSteph BulanNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDocument31 pagesNephrolithiasis Case StudyL.a.Zumárraga67% (3)
- Nephrolithiasis - PathoDocument1 pageNephrolithiasis - PathoAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis Case StudyDocument41 pagesNephrolithiasis Case StudyRachel Semilla50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of UrolithiasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of UrolithiasisNavjot Brar100% (2)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocument9 pagesPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- NephrolithiasisDocument2 pagesNephrolithiasisDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDocument8 pagesMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethergine Drug StudyMarlet N. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyJanica Marinas100% (3)
- Case Presentation On NephrolithiasisDocument25 pagesCase Presentation On NephrolithiasisBarbara Detaro50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 pagesPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Ovarian New GrowthDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Ovarian New Growthhaniellan100% (5)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoNo ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument5 pagesCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- NCP NephrolithiasisDocument1 pageNCP NephrolithiasisDonna Cabal AmogNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisDocument85 pagesCase Study On Bilateral NephrolithiasisShoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Gouty ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Gouty ArthritiskyawNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- CholelithiasisDocument11 pagesCholelithiasisSugar Capule - Manuel100% (1)
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology OsteosarcomaVernadeth Dumagat50% (2)
- Etiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisDocument3 pagesEtiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations of CholecystitisGerriNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infectio Case StudyDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract Infectio Case Studyjunex123No ratings yet
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Myoma PathoniixDocument1 pageMyoma PathoniixRendel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis / Renal Calculi: Clinical Manifestation: Stones in The Renal PelvisDocument3 pagesUrolithiasis / Renal Calculi: Clinical Manifestation: Stones in The Renal PelvisErika ArceoNo ratings yet
- B. Pathophysiology Diagram: A Case Study On UreterolithiasisDocument5 pagesB. Pathophysiology Diagram: A Case Study On UreterolithiasisIan Mizzel A. DulfinaNo ratings yet
- UrolithiasisDocument31 pagesUrolithiasisRatih Kusumaning MumpuniNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument39 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Vesicolithiasis BSHDocument24 pagesVesicolithiasis BSHDurian ArmsNo ratings yet
- IV PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesIV PathophysiologyJanedear Pasal100% (1)
- Vesicolithiasis BSHDocument24 pagesVesicolithiasis BSHBobby Faisyal RakhmanNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing FactorsDocument4 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factorselfera09No ratings yet
- Urinary Stone DiseaseDocument11 pagesUrinary Stone DiseaseAdelia Maharani DNo ratings yet
- Neprolithiasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageNeprolithiasis PathophysiologyMyka Silang Mendoza100% (1)
- 4 Accesory Organ DisordersDocument14 pages4 Accesory Organ DisordersNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract StoneDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract StoneWilko WilliamNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Kidney StoneDocument36 pagesCase Study On Kidney Stonemanojkumar200624No ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisjohndelfinmNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (kidney ppt 자료)Document5 pagesPathophysiology (kidney ppt 자료)tnwls4031No ratings yet
- 2106 UtiDocument2 pages2106 UtishimiNo ratings yet