Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2106 Uti
Uploaded by
shimi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOriginal Title
2106 UTI
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pages2106 Uti
Uploaded by
shimiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
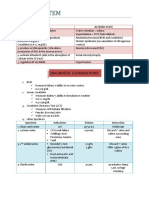
Incontinence Retention
Loss of voluntary control of bladder Inability to empty bladder
Stress incontinence May accompany with overflow incontinence
-Increase in intra-abdominal pressure /occur after anesthesia
-Forces urine through the sphincter Spinal cord injury at the sacral level
Laughing, Coughing, Females weakened -Catheter: tube inserted in urethra
Spinal cord injuries, brain damage --Drains urine from bladder to collecting bag
Common source of UTI
Urinalysis
Constituents, characteristics of urine vary with dietary intake, drugs, care of specimen
Normally clear, straw-colored; pH 4.5-8.0
Abnormal Cloudy large amounts protein, blood cells, bacteria, pus
appearance Dark color Hematuria (blood), excessive bilirubin, high
concentration of urine
Unpleasant, unusual odor infection
Abnormal Blood (hematuria) Small, microscopic amounts: Infection, inflammation,
constituents tumors of UT
(high in Large no. of RBC: Increased glomerular permeability or
numbers) hemorrhage in tract
Protein (Proteinuria) Leakage of albumin into the filtrate
Inflammation, increased glomerular permeability
Bacteria (Bacteriuria) Indicates UTI
Pus (Pyuria)
Urinary casts Microscopic mold of tubules: 1+ cells, bacteria, protein
Inflammation of tubules
Specific gravity Ability of tubules to concentrate urine
Low = renal failure
Blood tests
High serum urea (BUN) & Indicate failure to excrete nitrogen wastes due to low GFR
creatinine
Metabolic acidosis Indicates low GFR, failure of tubules to control acid/base balance
Anemia Indicates low erythropoietin secretion and/or bone marrow depression
Due to accumulating wastes
Antibody level Antistreptolysin O (ASO) or antistreptokinase (ASK)
-Use to diagnose the poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
Renin level Indicates a cause of hypertension
Other test
Culture and sensitivity tests Urine specimens: identify organism and select drug treatment
Clearance tests used to asses GFR
creatinine, insulin clearance
Radiologic tests used to visualize structures and abnormalities
Intravenous pyelography (IVP)
Angiography
Ultrasound
CT, MRI
Cytoscopy visualize lower UT
Can be used to perform biopsy or remove kidney stones
Biopsy Acquire tissue specimen for microscopic analysis
Dialysis Provides “artificial kidney”
-Sustains life after kidney fails
For acute renal failure or end-stage renal failure (those waiting for a transplant)
Two forms: Hemodialysis & Peritoneal dialysis
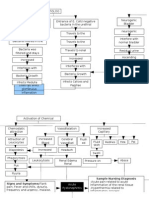
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)
Urine: excellent medium for microorganismal growth (e.g. Escherichia coli)
-ascending: Perineal cavity mucosa bladder ureters kidneys
etiology female Proximity to anus
Short urethra
Frequent irritation to tissues: bubble bath, sexual activity
Older male with prostatic hypertrophy and retention of urine prone to UTI
-Male reproductive tract shares some of the structures of the urinary tract
Children Congenital abnormalities
Elderly Incomplete emptying
Reduced fluid intake
Impaired blood supply to bladder
Immobility
You might also like
- Hematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesFrom EverandHematuria, (Blood in Urine) A Simple Guide to The Condition, Related Diseases And Use in Diagnosis of DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Urinary Symptoms and InvestigationsDocument16 pagesUrinary Symptoms and Investigationsمبدر حامدNo ratings yet
- Abnormal UrineDocument28 pagesAbnormal UrinemujeebNo ratings yet
- Ginjal PatofisiologiDocument49 pagesGinjal PatofisiologiJonovSelfNo ratings yet
- 313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsDocument8 pages313 - Disorders of Renal and Urinary SystemsChrissy Mendoza100% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorDocument62 pagesUrinary Tract Infections: Dr. Shweta Naik Assistant ProfessorMeenakshisundaram CNo ratings yet
- Grand Case StudyDocument13 pagesGrand Case StudyLaica A. LunetaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument71 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionsdayibon499No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionTom Mallinson100% (1)
- Referat - Syifa Firza UtiDocument28 pagesReferat - Syifa Firza Utimiir ikbalNo ratings yet
- Storing A Urine SampleDocument8 pagesStoring A Urine SampleMarz DempseyNo ratings yet
- Uti in AdultsDocument11 pagesUti in AdultsThabang ThaboNo ratings yet
- C5. Renal Disorders FileDocument38 pagesC5. Renal Disorders Filecoco brillqnteNo ratings yet
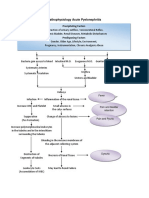
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- UTI (Esparagoza & Delos Reyes BSN2E)Document11 pagesUTI (Esparagoza & Delos Reyes BSN2E)EYANAH DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections Definition: ClassificationDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Definition: Classificationjishu baruaNo ratings yet
- Canine Prostatic Diseases: Reproduction and Periparturient CareDocument13 pagesCanine Prostatic Diseases: Reproduction and Periparturient CareSatria Adi MarhendraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in PregnancyDocument49 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in PregnancyBALMERA, DANIELLA B.No ratings yet
- Obstruksi Uropati IrfanDocument43 pagesObstruksi Uropati IrfanirfanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsGeethika GummadiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument30 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionLeo Mar MakilanNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 1Document2 pagesAubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 1Hannah KateNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Glossary - Ana SanchezDocument3 pagesUrinary System Glossary - Ana SanchezAna S.No ratings yet
- RLE Urinary Tract InfectionDocument13 pagesRLE Urinary Tract InfectionAliza AlyyNo ratings yet
- 8.urinary Tract Infections-1Document82 pages8.urinary Tract Infections-1fikirjohn8No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionDRANo ratings yet
- UrologyDocument30 pagesUrologyNikita KumariNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument10 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionMira Mariana UlfahNo ratings yet
- Acterial Yelonephritis: Jennifer Good, DVM Mark P. Rondeau, DVM, DACVIM (SAIM)Document5 pagesActerial Yelonephritis: Jennifer Good, DVM Mark P. Rondeau, DVM, DACVIM (SAIM)Phương Liên Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Urinary Disorders 2Document19 pagesUrinary Disorders 2ula mdiNo ratings yet
- 6 UtiDocument18 pages6 UtiMahesh RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument35 pagesUrinalysisAbdulelah MurshidNo ratings yet
- Management of Patient With Urinary Disorder1Document14 pagesManagement of Patient With Urinary Disorder1eighkheideeNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument24 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsTom TsouNo ratings yet
- INFEKSI SALURAN KEMIH (ISK) PADA ANAK Blok 14Document26 pagesINFEKSI SALURAN KEMIH (ISK) PADA ANAK Blok 14Siti Shaihany YustikawariNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTI)Document58 pagesUrinary Tract Infections (UTI)afdaliaNo ratings yet
- Disease of Prostate Tutorial-Dec-2014Document49 pagesDisease of Prostate Tutorial-Dec-2014marina_shawkyNo ratings yet
- 6 Genitourinary Dise 2020 Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectioDocument8 pages6 Genitourinary Dise 2020 Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectioThaiz P.SNo ratings yet
- LP BPH HasanuddinDocument21 pagesLP BPH Hasanuddinahmad yusufNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Is A BenignDocument4 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Is A BenignZeinab SrourNo ratings yet
- Renal System: Diagnostic ExaminationsDocument8 pagesRenal System: Diagnostic Examinationsjoan olanteNo ratings yet
- GenitoUrinary Tract PresentationDocument60 pagesGenitoUrinary Tract PresentationJaezee RamosNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument27 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionNaseem Bin Yoosaf100% (1)
- UTI Microbiology and DiagnosisDocument11 pagesUTI Microbiology and Diagnosisoxford_commaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017Document51 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017NinaNo ratings yet
- Suspected Site Symptoms/signs Initial Microbiologic EvaluationDocument2 pagesSuspected Site Symptoms/signs Initial Microbiologic EvaluationprobowurNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Renal and Urinary Tract Syatems NewDocument27 pagesAssessment of The Renal and Urinary Tract Syatems NewMay LindaNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument13 pagesMicroscopic Examination of UrineMark Raymund Galvez Nava100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrDocument20 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Pharmacotherapeutics II YrpawannnnNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisjohndelfinmNo ratings yet
- CH 49 MedsurgDocument18 pagesCH 49 MedsurgJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- CystitisDocument10 pagesCystitisJeffNo ratings yet
- Isolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument3 pagesIsolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionleozdmNo ratings yet
- (2020) Goldman-Cecil Medicine - Approach To The Patient With Urinary Tract InfectionDocument23 pages(2020) Goldman-Cecil Medicine - Approach To The Patient With Urinary Tract InfectionMiftahurrohmat AlmaasahNo ratings yet
- Emergency in Urology - Edit241021Document76 pagesEmergency in Urology - Edit241021Alverina Ode Nifaki100% (1)
- UTI, HSC With QuestionsDocument43 pagesUTI, HSC With QuestionsAlex MatthewNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanDocument24 pagesPatofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- PYELONEPHRITISDocument1 pagePYELONEPHRITISgreskpremium8No ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument39 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument11 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-582875150No ratings yet
- Galay1 1 1 1Document2 pagesGalay1 1 1 1Glynne AlmadenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Result Report: Requested Test Result Units Reference Value Method ImmunologyDocument1 pageLaboratory Result Report: Requested Test Result Units Reference Value Method ImmunologyYaya ZakariaNo ratings yet
- PBHCI - Mental Health ScreeningDocument2 pagesPBHCI - Mental Health ScreeningRoshin Tejero0% (1)
- SUPW SrimukhDocument15 pagesSUPW SrimukhsrimukhsaiNo ratings yet
- AAP ASD Exec SummaryDocument7 pagesAAP ASD Exec SummaryCatherine AgustinNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership Towards The Star Rating Evaluation of Malaysian Seni Gayung Fatani Malaysia Organization PSGFMDocument10 pagesEffective Leadership Towards The Star Rating Evaluation of Malaysian Seni Gayung Fatani Malaysia Organization PSGFMabishekj274No ratings yet
- Significance of HACCP and SSOP in Food Processing EstablishmentsDocument7 pagesSignificance of HACCP and SSOP in Food Processing EstablishmentselfiraNo ratings yet
- A Novel Technique For Pudendal Nerve BlockDocument4 pagesA Novel Technique For Pudendal Nerve Blockmohs2007100% (1)
- Good Knight 420 GPatien ManualDocument30 pagesGood Knight 420 GPatien ManualJose Antonio AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Contentdamdiagnosticsusenproductsaaccu Chek Inform IitoolkitOS0130802 Accu Chek Inform IIDocument264 pagesContentdamdiagnosticsusenproductsaaccu Chek Inform IitoolkitOS0130802 Accu Chek Inform IIRose LeanoNo ratings yet
- Playlist AssignmentDocument7 pagesPlaylist AssignmentTimothy Matthew JohnstoneNo ratings yet
- 7th Edition NRP Brings Big Changes For NRP Instructors: Instructor UpdateDocument12 pages7th Edition NRP Brings Big Changes For NRP Instructors: Instructor UpdateJoev SaquinNo ratings yet
- WBC DisordersDocument45 pagesWBC DisordersyalahopaNo ratings yet
- Activity Design (Summer League 2022)Document6 pagesActivity Design (Summer League 2022)Yubert ViosNo ratings yet
- Formularium 2018 ADocument213 pagesFormularium 2018 Asupril anshariNo ratings yet
- GP Panel ClinicsDocument9 pagesGP Panel ClinicsKoh WYhowNo ratings yet
- De Anisya Tri Ab - CBD - 30101507419 - FixDocument198 pagesDe Anisya Tri Ab - CBD - 30101507419 - FixFarah UlyaNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 - 8 - FisheryDocument17 pagesTle 7 - 8 - FisheryRey JavierNo ratings yet
- ApproachPerformance 01 PDFDocument6 pagesApproachPerformance 01 PDFAdam MazurekNo ratings yet
- Hazop PDFDocument18 pagesHazop PDFLuiz Rubens Souza Cantelli0% (1)
- The Dandenong Dossier 2010Document243 pagesThe Dandenong Dossier 2010reshminNo ratings yet
- Mastertile A 200 Msds PDFDocument11 pagesMastertile A 200 Msds PDFyaswanth reddy mummadiNo ratings yet
- Normative Data For A Spanish Version of The Rey Auditory-Verbal Learning Test in Older PeopleDocument12 pagesNormative Data For A Spanish Version of The Rey Auditory-Verbal Learning Test in Older PeopleeastareaNo ratings yet
- Therapy Is For Everybody: Black Mental HealthDocument22 pagesTherapy Is For Everybody: Black Mental HealthIresha Picot100% (2)
- IELTS 1 Test IntroDocument1 pageIELTS 1 Test IntromichaelNo ratings yet
- Ramsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItDocument10 pagesRamsay Sedation Scale and How To Use ItAdinda Putra PradhanaNo ratings yet
- Amy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of HomeopathyDocument295 pagesAmy L. Lansky - Impossible Cure - The Promise of Homeopathybjjman88% (17)
- PECFASDocument2 pagesPECFASNunik KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- DrFuhrmans Super Immunity FactsheetDocument2 pagesDrFuhrmans Super Immunity FactsheetPerrela Perrela100% (1)