Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By: Jesús Cullell Óscar Güell Guillermo Martínez
Uploaded by
Natalie GreenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Jesús Cullell Óscar Güell Guillermo Martínez
Uploaded by
Natalie GreenCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Jess Cullell scar Gell Guillermo Martnez
When people eat more calories than they burn off, their bodies store the extra calories as fat. A couple of pounds of extra body fat are not a health risk for most people. But when people keep up a pattern of eating more calories than they burn, more and more fat builds up in their bodies. Eventually, the body gets to a point where the amount of body fat can have a negative effect on a person's health. Doctors use the terms "overweight" or "obese" to describe when someone is at greatest risk of developing weightrelated health problems. As you've probably heard, more people are overweight today than ever before. Experts are calling this an "obesity epidemic." This health problem affects young people as well as adults one third of all kids between the ages of 2 and 19 are overweight or obese. So younger people are now developing health problems that used to affect only adults, like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and type 2 diabetes.
Obesity tends to run in families. Some people have a genetic tendency to gain weight more easily than others because they burn calories more slowly. During times when food was scarce, this was a real advantage. But now that food is available 24/7 in most industrialized countries, an efficient metabolism that once ensured our survival now works to our disadvantage.
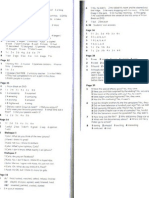
75% 70% 65% 60% - - - Past projection New data points
Rate of overweight
55% 50% 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 1970 France Korea 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 USA Spain Italy Canada
England
Year
The problem of childhood obesity in the United States has grown considerably in recent years. Between 16 and 33 percent of children and adolescents are obese. Obesity is among the easiest medical conditions to recognize but most difficult to treat. Unhealthy weight gain due to poor diet and lack of exercise is responsible for over 300,000 deaths each year. The annual cost to society for obesity is estimated at nearly $100 billion. Overweight children are much more likely to become overweight adults unless they adopt and maintain healthier patterns of eating and exercise.
poor eating habits overeating or binging lack of exercise (i.e., couch potato kids) family history of obesity medical illnesses (endocrine, neurological problems) medications (steroids, some psychiatric medications) stressful life events or changes (separations, divorce, moves, deaths, abuse) family and peer problems low self-esteem depression or other emotional problems
The consequences of obesity can be split into two groups, physical and social. Coronary heart disease High blood pressure Strokes Type 2 diabetes Some cancers Experiencing fertility problems Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
You might also like
- How To Save Your TeethDocument193 pagesHow To Save Your TeethTanon Jaturonnatee100% (2)
- Obesity & Diabetes - FINALDocument8 pagesObesity & Diabetes - FINALLisa Tackett MurphyNo ratings yet
- Teens, Youngsters and Weight Loss: The Art Of Slimming For The Typical TeenagerFrom EverandTeens, Youngsters and Weight Loss: The Art Of Slimming For The Typical TeenagerNo ratings yet
- Cause and EffectDocument5 pagesCause and EffectNiaDamaNo ratings yet
- Implant Failure and ManagementDocument59 pagesImplant Failure and ManagementDrIbrahimShaikh0% (1)
- What Causes Obesity? The Main FactorsDocument20 pagesWhat Causes Obesity? The Main FactorsgheorghesimedrumaxxNo ratings yet
- Excerpt: "Fat Chance" by Robert LustigDocument3 pagesExcerpt: "Fat Chance" by Robert Lustigwamu885067% (3)
- Effects of ObesityDocument48 pagesEffects of ObesityFairuz KangNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Care Nursing Table of ContentsDocument2 pagesMaternal & Child Care Nursing Table of Contentsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- How to Lose 8 Pounds in 7 Days: Amazing tips to weight loss without struggle.From EverandHow to Lose 8 Pounds in 7 Days: Amazing tips to weight loss without struggle.No ratings yet
- Homeopathy Medicine For Obesity.Document11 pagesHomeopathy Medicine For Obesity.Tayyab Tahir MinhasNo ratings yet
- User's Guide to Preventing & Reversing Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandUser's Guide to Preventing & Reversing Diabetes NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Obesity Research PaperDocument10 pagesObesity Research PaperPaige-Hill88% (16)
- Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 2 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 2Document409 pagesStem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 2 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 2ArtanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Case Study NDDocument11 pagesCardiac Case Study NDapi-313165458No ratings yet
- 1-Equine Digestion PowerPointDocument15 pages1-Equine Digestion PowerPointMazhar FaridNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Guided Bone Regeneration: A Literature ReviewDocument16 pagesReview Article: Guided Bone Regeneration: A Literature ReviewGonçalo Gomes SanchesNo ratings yet
- AGada TantraDocument3 pagesAGada TantraGuru Prasad100% (1)
- Informative EssayDocument4 pagesInformative Essayapi-491520138No ratings yet
- Psychological and Social Effects of ObesityDocument7 pagesPsychological and Social Effects of Obesityاحمد زينل محمدNo ratings yet
- Longevity Decoded: The Miracle Plant Based Diet That Can Save Your LifeFrom EverandLongevity Decoded: The Miracle Plant Based Diet That Can Save Your LifeNo ratings yet
- "Obesity": How Common Is Obesity?Document7 pages"Obesity": How Common Is Obesity?Jericho Dimaano Arago ﭢNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument4 pagesObesityOscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity Effects and SolutionsDocument3 pagesChildhood Obesity Effects and SolutionsHappy SmileNo ratings yet
- How Obesity Affects Our Health?Document6 pagesHow Obesity Affects Our Health?Mark PadernalNo ratings yet
- Research Paper FinalDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Finalapi-312560435No ratings yet
- FinalDocument65 pagesFinalapi-3722454100% (2)
- Running Head: Diabetes Continues To Climb 1Document8 pagesRunning Head: Diabetes Continues To Climb 1TigreoeilNo ratings yet
- The Fat DivideDocument6 pagesThe Fat DivideFran MolloyNo ratings yet
- Overweight and Obesity in AmericaDocument10 pagesOverweight and Obesity in Americamzvette234No ratings yet
- Obesity Biology Folio: Name: Collage Number: Class: DateDocument11 pagesObesity Biology Folio: Name: Collage Number: Class: DateJazlyn JongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionWan Nur Nabilah100% (1)
- OBESITYDocument3 pagesOBESITYfemeritusconsultNo ratings yet
- GGGGGGGGDocument5 pagesGGGGGGGGapi-315832979No ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of Stunting, Underweight, Obesity and OverweightDocument4 pagesCauses and Effects of Stunting, Underweight, Obesity and OverweightLordkaiser VasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapters1 5Document75 pagesChapters1 5api-3722454100% (2)
- What Is Obesity and How Does It Affect The UDocument10 pagesWhat Is Obesity and How Does It Affect The UavahajNo ratings yet
- Causes, Health Risks and Measures of ObesityDocument2 pagesCauses, Health Risks and Measures of ObesityKarenLópezAragónNo ratings yet
- Obesity in America: Understanding the Growing Health CrisisDocument6 pagesObesity in America: Understanding the Growing Health CrisisAshna WaseemNo ratings yet
- The Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You byDocument6 pagesThe Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You bySam YoussefNo ratings yet
- Maximum Fat Loss: You Don't Have a Weight Problem! It's Much Simpler Than That.From EverandMaximum Fat Loss: You Don't Have a Weight Problem! It's Much Simpler Than That.No ratings yet
- Obesity Debate: Public or Private IssueDocument10 pagesObesity Debate: Public or Private Issueesi333No ratings yet
- Obesity statistics and causes: Understanding the obesity epidemicDocument4 pagesObesity statistics and causes: Understanding the obesity epidemicBryan Andrés AnguloNo ratings yet
- Tic2 - PiaDocument19 pagesTic2 - PiaVane ValdesNo ratings yet
- Devjourn Science-FeatureDocument4 pagesDevjourn Science-Feature20-1-00816No ratings yet
- Obesity in AmericaDocument6 pagesObesity in AmericapnupnNo ratings yet
- Globalisation and ObesityDocument2 pagesGlobalisation and ObesityDavid WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1-5 FINALDocument55 pagesChapters 1-5 FINALGwen NamNo ratings yet
- Home/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleDocument5 pagesHome/health & Living Health Center/diet & Weight Management A-Z List/obesity Weight Loss Center /obesity (Weight Loss) ArticleHannah LNo ratings yet
- The Caloric Balance EquationDocument3 pagesThe Caloric Balance EquationGlenda WestNo ratings yet
- Pain Dysfunction Distress Social Problems DeathDocument4 pagesPain Dysfunction Distress Social Problems Deathapi-280291806No ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Research Paper ExampleDocument5 pagesType 2 Diabetes Research Paper Examplexdhuvjrif100% (1)
- Inactivity. Unhealthy Diet and Eating Habits. GeneticsDocument3 pagesInactivity. Unhealthy Diet and Eating Habits. GeneticsChristopher EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Higher Risks of Cancer, Type 2 Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, Respiratory Disorders, and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesHigher Risks of Cancer, Type 2 Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, Respiratory Disorders, and Cardiovascular DiseaseJuveria nsNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On American ObesityDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On American Obesityafnkhujzxbfnls100% (1)
- Ingles II - ObesidadDocument8 pagesIngles II - ObesidadBigAlexito 16No ratings yet
- Body of Childhood Obesity Informative SpeechDocument2 pagesBody of Childhood Obesity Informative SpeechJOEL O. UDTOHANNo ratings yet
- Obesity in USADocument10 pagesObesity in USASalman TahirNo ratings yet
- KeriobeseDocument7 pagesKeriobeseapi-285517124No ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesityapi-298240070No ratings yet
- Obesity Research Paper IntroductionDocument4 pagesObesity Research Paper Introductionafnkcjxisddxil100% (1)
- Physical FitnessDocument1 pagePhysical FitnessjoãoNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Effects of ObesityDocument7 pagesMental Health Effects of ObesityMohd FaizNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument14 pagesObesityюрий локтионов100% (1)
- Top 10 Contributing Factors To ObesityDocument2 pagesTop 10 Contributing Factors To ObesityKu Meng ChuNo ratings yet
- Oral Criteria 1501 - HolisticDocument1 pageOral Criteria 1501 - HolisticNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- India Project by JésusDocument9 pagesIndia Project by JésusNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Scones RecipeDocument1 pageScones RecipeNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela Project by The GirlsDocument7 pagesNelson Mandela Project by The GirlsNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Stonehenge Project by Artur, Martí and JésusDocument7 pagesStonehenge Project by Artur, Martí and JésusNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela Power Point by Óscar, Guille and JésusDocument10 pagesNelson Mandela Power Point by Óscar, Guille and JésusNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- London: Project Conducted By: Marta Lorena and MonicaDocument6 pagesLondon: Project Conducted By: Marta Lorena and MonicaNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- India Project by LorenaDocument7 pagesIndia Project by LorenaNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Scotland ProjectDocument6 pagesScotland ProjectNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- SconesDocument1 pageSconesNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Cheescake For KidsDocument1 pageRaspberry Cheescake For KidsNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Nelson Mandela Power Point by Artur and MartíDocument7 pagesNelson Mandela Power Point by Artur and MartíNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Homemade Bread RollsDocument1 pageHomemade Bread RollsNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Homemade Bread RollsDocument1 pageHomemade Bread RollsNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- ESo5 Workbook AnswersDocument2 pagesESo5 Workbook AnswersNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- WB Answers ESO2U8Document1 pageWB Answers ESO2U8Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- WB Answers Units 4 & 5Document2 pagesWB Answers Units 4 & 5Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Strawberry CheesecakeDocument1 pageStrawberry CheesecakeNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Delias Simplified Pancake RecipeDocument1 pageDelias Simplified Pancake RecipeNatalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Answers Unit 3 English Explorer 2Document1 pageAnswers Unit 3 English Explorer 2Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Workbook Answers 1C1DVocGR1Document8 pagesWorkbook Answers 1C1DVocGR1Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercises Unit 1Document6 pagesRevision Exercises Unit 1Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Correction Eng Explorer 4Document3 pagesCorrection Eng Explorer 4Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercises Unit 1Document6 pagesRevision Exercises Unit 1Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Correction Eng Explorer 4Document3 pagesCorrection Eng Explorer 4Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- ESO 2 - Term 2 & 3 Plan 2010-11Document2 pagesESO 2 - Term 2 & 3 Plan 2010-11Natalie GreenNo ratings yet
- Asama PosterDocument1 pageAsama Postershuvojit moulikNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Procedures: Tracheal Intubation PreparationDocument46 pagesRespiratory Procedures: Tracheal Intubation PreparationRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Predictions Using Data Mining and Case Based Reasoning A Case Study For RetinopathyDocument4 pagesPredictions Using Data Mining and Case Based Reasoning A Case Study For RetinopathyBiraj kumar BholNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseJohn SammutNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacology Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument19 pagesNephritic SyndromesangheetaNo ratings yet
- Intubasi Sulit: Nur Hajriya BrahmiDocument26 pagesIntubasi Sulit: Nur Hajriya BrahmiFathiah HusainNo ratings yet
- The Privacy Isuues of AppleDocument7 pagesThe Privacy Isuues of Applephysicser15No ratings yet
- MOH, DHA and HAAD recalls from 2017 WhatsApp groupDocument32 pagesMOH, DHA and HAAD recalls from 2017 WhatsApp groupshahzadNo ratings yet
- Pflipsen Anaphylaxis Recognition and ManagementDocument10 pagesPflipsen Anaphylaxis Recognition and ManagementOlivia McCuskerNo ratings yet
- RENBUT BHN LAB 2022 SD Agt 2023Document3 pagesRENBUT BHN LAB 2022 SD Agt 2023ajisNo ratings yet
- Rohini 59284010117Document21 pagesRohini 59284010117narasimmanbiomedicalNo ratings yet
- IMCI - For PakistanDocument35 pagesIMCI - For Pakistanerajkhan100% (1)
- EMT Training at Mansion Mandiri HotelDocument4 pagesEMT Training at Mansion Mandiri Hotelyuna triazNo ratings yet
- SRJI 4-3-2015 Historical Roots of Acupressure Pillows PatentsDocument4 pagesSRJI 4-3-2015 Historical Roots of Acupressure Pillows PatentsDr. Krishna N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- MBBS - General Medicine Reg Id: KMC - 142105 RX ID: 406824261Document1 pageMBBS - General Medicine Reg Id: KMC - 142105 RX ID: 406824261Dipam HalderNo ratings yet
- ODC Nursing FormsDocument5 pagesODC Nursing Formsgyds_17No ratings yet
- Instructions For Use: Home Sperm Test For Male FertilityDocument2 pagesInstructions For Use: Home Sperm Test For Male FertilityRAVAN ZJNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityAngelika VeluzNo ratings yet
- Precision Attachment: Retained OverdentureDocument4 pagesPrecision Attachment: Retained OverdentureSudhanshu Kumar KashyapNo ratings yet
- Presented by DR Rahul D AgrawalDocument64 pagesPresented by DR Rahul D AgrawalRahul AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Assessment ChecklistDocument27 pagesPreoperative Assessment ChecklistHairina MazlanNo ratings yet