Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluorescent Light Incandescent Bulb: Fluorescent Starters Are Used in
Uploaded by
Roga29Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluorescent Light Incandescent Bulb: Fluorescent Starters Are Used in
Uploaded by
Roga29Copyright:
Available Formats
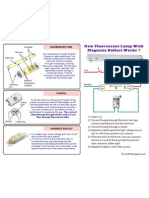
A fluorescent light does not have the usual glowing filament of an incandescent bulb, but instead contains a mercury
vapor that gives off ultraviolet light when ionized. The ultraviolet light makes particles that coat the inside of the tube, and these particles glow or fluoresce (see How Fluorescent Lamps ork for details!. Fluorescent starters are used in several t"pes of fluorescent lights. The starter is there to help the lamp light. hen voltage is applied to the fluorescent lamp, here#s what happens$ %. The starter (which is simpl" a timed switch! allows current to flow through the filaments at the ends of the tube. &. The current causes the starter#s contacts to heat up and open, thus interrupting the flow of current. The tube lights. '. (ince the lighted fluorescent tube has a low resistance, the ballast now serves as a current limiter. hen "ou turn on a fluorescent tube, the starter is a closed switch. The filaments at the ends of the tube are heated b" electricit", and the" create a cloud of electrons inside the tube. The fluorescent starter is a time-delay switch that opens after a second or two. hen it opens, the voltage across the tube allows a stream of electrons to flow across the tube and ionize the mercur" vapor. ithout the starter, a stead" stream of electrons is never created between the two filaments, and the lamp flickers. ithout the ballast, the arc is a short circuit between the filaments, and this short circuit contains a lot of current. The current either vaporizes the filaments or causes the bulb to e)plode. According to (am#s F*Lamp FA+$ The most common fluorescent starter is called a ,glow tube starter, (or -ust starter! and contains a small gas (neon, etc.! filled tube and an optional radio fre.uenc" interference (/F0! suppression capacitor in a c"lindrical aluminum can with a & pin base. hile all starters are ph"sicall" interchangeable, the wattage rating of the starter should be matched to the wattage rating of the fluorescent tubes for reliable operation and long life. The glow tube incorporates a switch which is normall" open. hen power is applied, a glow discharge takes place which heats a bimetal contact. A second or so later, the
contacts close and provide current to the fluorescent filaments. (ince the glow is e)tinguished, there is no longer an" heating of the bimetal and the contacts open. The inductive kick generated at the instant of opening triggers the main discharge in the fluorescent tube. 0f the contacts open at a bad time, there isn#t enough inductive kick and the process repeats.
You might also like
- Chord Progressions Money ChordsDocument116 pagesChord Progressions Money ChordsEmma Sinclair80% (5)
- Ultimate Fingerpcking Patterns PDFDocument11 pagesUltimate Fingerpcking Patterns PDFRoga2980% (5)
- Carla L Rueckert - A Wanderers HandbookDocument566 pagesCarla L Rueckert - A Wanderers Handbookanon-207295100% (35)
- Klasicna Gitara Dnevni Raspored +++Document7 pagesKlasicna Gitara Dnevni Raspored +++Roga29100% (1)
- Abb HD4Document52 pagesAbb HD4Saurav Sirkeck100% (2)
- Scorpions - Guitar Tabs - Wind of Change TabDocument2 pagesScorpions - Guitar Tabs - Wind of Change TabRoga29No ratings yet
- How to Wire a Doll's House for Electricity - An Illustrated GuideFrom EverandHow to Wire a Doll's House for Electricity - An Illustrated GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ten Week Self Improvement Plan 1Document15 pagesTen Week Self Improvement Plan 1Roga29No ratings yet
- Ten Week Self Improvement Plan 1Document15 pagesTen Week Self Improvement Plan 1Roga29No ratings yet
- Planted AquariumDocument2 pagesPlanted Aquariumadrianb7100% (1)
- Astm 5453 - Stantard Test Method For Determination of Total SulfurDocument9 pagesAstm 5453 - Stantard Test Method For Determination of Total Sulfurgaso99No ratings yet
- Deep Purple - Guitar Tabs - Smoke On The Water TabDocument3 pagesDeep Purple - Guitar Tabs - Smoke On The Water TabRoga29No ratings yet
- Beinsa Douno The Beauty of Life Lectures PDFDocument203 pagesBeinsa Douno The Beauty of Life Lectures PDFIrma MonsalveNo ratings yet
- Astm E415-2008Document9 pagesAstm E415-2008Syamsul AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Lighting FixtureDocument17 pagesFluorescent Lighting FixtureelyNo ratings yet
- Planting Your Tank: Tropical FishDocument10 pagesPlanting Your Tank: Tropical FishRoga29No ratings yet
- Microwave TubesDocument23 pagesMicrowave TubesElisha NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Drive A CFL From 6v or 12vDocument1 pageDrive A CFL From 6v or 12vJohn ApostleNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities Summary PDFDocument6 pagesBuilding Utilities Summary PDFGallardo Nixon100% (2)
- Schema Pentru Tub NeonDocument2 pagesSchema Pentru Tub Neondanydymary100% (1)
- Slayer Exciter CircuitDocument2 pagesSlayer Exciter CircuitRalph VaronNo ratings yet
- Sylvania Engineering Bulletin - Fluorescent Lamps 1985Document26 pagesSylvania Engineering Bulletin - Fluorescent Lamps 1985Alan Masters100% (1)
- Electron GunDocument44 pagesElectron Gungo2smanju5857No ratings yet
- Driver Lamparas Fluorescentes 12 VoltsDocument7 pagesDriver Lamparas Fluorescentes 12 VoltsDiego García MedinaNo ratings yet
- Bilge Alarm Monitor OMD 11Document22 pagesBilge Alarm Monitor OMD 11Lucian Iftemie100% (3)
- How Does A Fluorescent Starter WorkDocument4 pagesHow Does A Fluorescent Starter Workhardmanperson100% (1)
- Fluoroscent Lamp EditDocument11 pagesFluoroscent Lamp EditchandraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Use of Choke in Florescent TubesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Use of Choke in Florescent Tubessumanta1981100% (2)
- Tube Light WordDocument21 pagesTube Light WordMuniyasamyNo ratings yet
- US Iran ConflictDocument6 pagesUS Iran ConflictIhsaan GulzarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestionsAmber PreetNo ratings yet
- Working of TubelightDocument2 pagesWorking of Tubelightjsrilakshmi42720% (2)
- ECNG Design Project - Year 1Document38 pagesECNG Design Project - Year 1kurmakkNo ratings yet
- A Fuse Tubelight Glower Without Any Electric ChokeDocument25 pagesA Fuse Tubelight Glower Without Any Electric ChokePrints BindingsNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Fluorescent LampDocument13 pagesParts and Functions of Fluorescent LampJayson Deocareza Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent LampDocument3 pagesFluorescent LampReign Nard AuzamakiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.10213Document6 pagesExperiment No.10213nithinNo ratings yet
- Operation of Pre-Heat Type Fluorescent Lamp The Tube Filaments, Starter (Glow Switch), and Ballast Are All in Series, Which Constitute A Complete Circuit Once TheDocument4 pagesOperation of Pre-Heat Type Fluorescent Lamp The Tube Filaments, Starter (Glow Switch), and Ballast Are All in Series, Which Constitute A Complete Circuit Once TheAnonymous urcRjigzNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Arc LampDocument8 pagesWorking Principle of Arc LamphimNo ratings yet
- Tle 9Document3 pagesTle 9Lilian Laurel Cariquitan50% (2)
- Working Principle of A Tube LightDocument3 pagesWorking Principle of A Tube LightYassir ButtNo ratings yet
- The Light Bulb: The Concept of LighteningDocument15 pagesThe Light Bulb: The Concept of LighteningOmar Reda Abdel Hakim El saaedNo ratings yet
- Emailing AC - Exp - 05 - StudentDocument8 pagesEmailing AC - Exp - 05 - StudentNafiul BariNo ratings yet
- GSC Subject EnrichmentDocument8 pagesGSC Subject EnrichmentAbhinav BhargavNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever Wondered How A Fluorescent Light Works? Even Though They're Nearly AsDocument4 pagesHave You Ever Wondered How A Fluorescent Light Works? Even Though They're Nearly AsMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Compact Florescent Lamp-2Document5 pagesCompact Florescent Lamp-2AdhiNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 5.1 Fluorescent Lighting FixturesDocument17 pagesInformation Sheet 5.1 Fluorescent Lighting FixturesJhobhel Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- BEE Lab Manual - Exp-4-NewDocument11 pagesBEE Lab Manual - Exp-4-NewImchaulNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent LampDocument1 pageFluorescent LampKaitlin MamarilNo ratings yet
- Mod 11 Book 21 LightsDocument49 pagesMod 11 Book 21 Lightsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Compact Fluorescent Lighting CFL Construction and Working and ComparisonDocument23 pagesCompact Fluorescent Lighting CFL Construction and Working and ComparisonAnimesh Verma100% (7)
- B. The Small Glass Tube Is Filled With Neon or Argon and Contains A Bi-Metallic PlateDocument2 pagesB. The Small Glass Tube Is Filled With Neon or Argon and Contains A Bi-Metallic PlateDhaha RoohullaNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Lamp and Working Principle of Fluorescent Lamp - Electrical4UDocument9 pagesFluorescent Lamp and Working Principle of Fluorescent Lamp - Electrical4Udassujoy312No ratings yet
- Artificial Sources of LightDocument3 pagesArtificial Sources of LightjdipbhadraNo ratings yet
- TLE 9 Aristotle Group 2Document7 pagesTLE 9 Aristotle Group 2mariviebuendia777No ratings yet
- How Fluorescent Lamps Work: Let There Be LightDocument9 pagesHow Fluorescent Lamps Work: Let There Be Lightlahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- FluorescentDocument2 pagesFluorescentruel_spideyNo ratings yet
- FluorescentDocument2 pagesFluorescentruel_spideyNo ratings yet
- FluorescentDocument2 pagesFluorescentruel_spideyNo ratings yet
- FluorescentDocument2 pagesFluorescentruel_spideyNo ratings yet
- How To Drive A Drive CFLDocument1 pageHow To Drive A Drive CFLJohn ApostleNo ratings yet
- Ships LightingDocument8 pagesShips LightingjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember - ElectricityDocument4 pagesPoints To Remember - ElectricityafaqueNo ratings yet
- Resistance: ConductorsDocument6 pagesResistance: ConductorsKokoArdNo ratings yet
- AN1543/D Electronic Lamp Ballast Design: Application NoteDocument35 pagesAN1543/D Electronic Lamp Ballast Design: Application NoteprovolissimaNo ratings yet
- Camera Flash WorkDocument10 pagesCamera Flash WorkajgoluNo ratings yet
- 1 5 ResistanceDocument7 pages1 5 ResistancetestyNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent LAMPSDocument23 pagesFluorescent LAMPSKevin NdetiNo ratings yet
- Iiiumination4 Tube LightDocument11 pagesIiiumination4 Tube LightPushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- How Flourescent Lamp WorkDocument1 pageHow Flourescent Lamp WorkJoebenson JjNo ratings yet
- J. Electrochem. Soc. 1948 Kroll 1 20Document10 pagesJ. Electrochem. Soc. 1948 Kroll 1 20Jairo Silva CoreaNo ratings yet
- RelayDocument2 pagesRelayAnuj KumarNo ratings yet
- How Inductors WorkDocument3 pagesHow Inductors WorkAlex PortilloNo ratings yet
- How Do Incandescent Lamps Work?: AdvantagesDocument18 pagesHow Do Incandescent Lamps Work?: Advantagesjayho haraNo ratings yet
- Metal Detector Parts ListDocument4 pagesMetal Detector Parts ListAlex AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Lighting MaterialsDocument35 pagesElectrical Lighting MaterialsPaulo ValerioNo ratings yet
- Christmas Lights and How To Fix ThemDocument8 pagesChristmas Lights and How To Fix ThemtwinscrewcanoeNo ratings yet
- How to Install Electric Bells, Annunciators, and AlarmsFrom EverandHow to Install Electric Bells, Annunciators, and AlarmsNo ratings yet
- Good Hobby Is A MustDocument1 pageGood Hobby Is A MustRoga29No ratings yet
- Positive Vs Negative Inputs ChecklistDocument1 pagePositive Vs Negative Inputs ChecklistRoga29No ratings yet
- Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesChecklist PDFRoga29No ratings yet
- 10 Weeks ChecklistDocument2 pages10 Weeks ChecklistRoga29No ratings yet
- Good Hobby Is A MustDocument1 pageGood Hobby Is A MustRoga29No ratings yet
- MET Standards For Electro-Technical Officers PDFDocument4 pagesMET Standards For Electro-Technical Officers PDFRoga29No ratings yet
- Finished Plan: Hyundai Heavy Industries H1748 EcdisDocument1 pageFinished Plan: Hyundai Heavy Industries H1748 EcdisRoga29No ratings yet
- Strangers in The NightDocument2 pagesStrangers in The NightblueveinsNo ratings yet
- Re 54 OperENnDocument48 pagesRe 54 OperENnVivek KhedgaonkarNo ratings yet
- 2icp 4025 Ug R2 enDocument49 pages2icp 4025 Ug R2 enMichael J. SchillNo ratings yet
- 06-01 - New Trends and InnovationsDocument69 pages06-01 - New Trends and InnovationsRoga29No ratings yet
- Datasheet Solenoid ValveDocument43 pagesDatasheet Solenoid ValveRoga29No ratings yet
- Manual Calibracion Fluke 725Document76 pagesManual Calibracion Fluke 725Luis Carlos GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Heitor Villa-Lobos - Etude No.1Document4 pagesHeitor Villa-Lobos - Etude No.1cirruscirrus100% (1)
- 17.5 MM DIN Rail Mounting MAR1 Part Number 88826115: Functions Timing Output Nominal Rating Connections Supply VoltageDocument3 pages17.5 MM DIN Rail Mounting MAR1 Part Number 88826115: Functions Timing Output Nominal Rating Connections Supply VoltageRoga29No ratings yet
- Tesla The Strange Life of Nikola TeslaDocument47 pagesTesla The Strange Life of Nikola TeslajajelenaNo ratings yet
- Yesterday - Beatles Tabs-Tablatures-Lyrics-Chords - Guitar-Bass - Tab PowerDocument2 pagesYesterday - Beatles Tabs-Tablatures-Lyrics-Chords - Guitar-Bass - Tab PowerRoga29No ratings yet
- Marley Bob - Guitar Tabs - Roots Rock Reggae TabDocument2 pagesMarley Bob - Guitar Tabs - Roots Rock Reggae TabRoga29No ratings yet
- LS6000AT ControllerDocument24 pagesLS6000AT ControllerTrung Hiếu CamNo ratings yet
- PUHY P200 250YREM A Service HandbookDocument124 pagesPUHY P200 250YREM A Service HandbookGingubaNo ratings yet
- AJDocument39 pagesAJBazin TsegayeNo ratings yet
- 560 PM gb9 142891044Document106 pages560 PM gb9 142891044DintcherIssoufNo ratings yet
- Coils For Solenoid Valves: 1 DescriptionDocument5 pagesCoils For Solenoid Valves: 1 DescriptionAnonymous Xz3PgZR8No ratings yet
- 1942 Siemens Sql33 Sqk33 Sql83Document8 pages1942 Siemens Sql33 Sqk33 Sql83rachman hardianNo ratings yet
- Catalogo HispaniaDocument58 pagesCatalogo Hispaniapiscobar67% (6)
- Sony kv-sw292m50 sw292m61 sw292m80 sw292n60 Chassis bx1l Ver.2.0Document189 pagesSony kv-sw292m50 sw292m61 sw292m80 sw292n60 Chassis bx1l Ver.2.0mrcrypto223No ratings yet
- The Story of Electricity by John MunroDocument105 pagesThe Story of Electricity by John Munrortchavali100% (1)
- Est Reading ClassifiedDocument29 pagesEst Reading ClassifiedMakram AliNo ratings yet
- Toro 760 & 780 Series SprinklersDocument12 pagesToro 760 & 780 Series SprinklersLuca Riccardi100% (1)
- Ans: Ans:: Column I Column II Column I Column IIDocument6 pagesAns: Ans:: Column I Column II Column I Column IIGeneric nameNo ratings yet
- Government Approved Test Laboratory: Ia CertificateDocument13 pagesGovernment Approved Test Laboratory: Ia CertificatecisyabNo ratings yet
- MC 275 MK 4Document20 pagesMC 275 MK 4Ray GreeneNo ratings yet
- Radiation DetectorsDocument14 pagesRadiation DetectorsaisyahNo ratings yet
- Goldline Solar ControllerDocument12 pagesGoldline Solar ControllerJeff KirschNo ratings yet
- Audio Transformer InductanceDocument8 pagesAudio Transformer InductanceCharles AustinNo ratings yet
- Biosan Catalog Eng 11 LQDocument92 pagesBiosan Catalog Eng 11 LQAnca IacobNo ratings yet
- BSNL Report - 1 - NBADocument10 pagesBSNL Report - 1 - NBAkhadarbasha.n nNo ratings yet
- Magnetron - Thesis - LiliMADocument192 pagesMagnetron - Thesis - LiliMASergej KaunNo ratings yet
- Radio Transmitter DesignDocument12 pagesRadio Transmitter DesignMarian MarianNo ratings yet
- Valve Amplifier For Proportional Pressure Valves: FeaturesDocument12 pagesValve Amplifier For Proportional Pressure Valves: FeaturesInbanesan AkNo ratings yet
- Apu Troubleshoot Tree: Abbreviations & DefinitionsDocument8 pagesApu Troubleshoot Tree: Abbreviations & DefinitionsAde YahyaNo ratings yet
- S - 26 @dynamic ResponseDocument48 pagesS - 26 @dynamic Responseknightfelix12No ratings yet