Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercice2 Structural Chemistry-V20130911
Uploaded by
Gramoz CubreliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercice2 Structural Chemistry-V20130911
Uploaded by
Gramoz CubreliCopyright:
Available Formats
Monabiphot Fundamental Chemistry
2. Structural Chemistry Exercises for Training
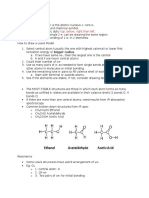
General Method for e!is Structure "ra!ing# 1/ Sum the number of electrons on the outer shell for each atom (add 1 e for a negatively charged ion, subtract 1e for a positively charge ion) Ex: atoms Ex: */ +dd other e (usually several ,e-is structure can be obtained) Ex: $% e!is Structure and &SE'( !" : # $ " (%) $ 1 & 1' e "/ (lace the less electronegative atom at the center ( usually), and lin) it by a single bond to other
1/ .rite the ,e-is structure (including non/bonding electron pairs and/or vacant orbitals) for the follo-ing ions or molecules (central atom is bold): 0"), *1*, +0*, C02, S!", S!"3l", $3l*, '!3l*, (C!*)", (+!")$ (this requires the determination of the outer shell configuration for each element involved) "/ 4ra- the geometry of these molecules using 5SE(6 theory $$% $mplicit Electrons, Electron 'airs and Empty )rbitals 7dentify single electrons, bonding and non/bonding electron pairs, or bonds and vacant orbitals for these compounds: 0"S, 81*, 30*$, 3l30&30", 0*3!0 , 0"3&3030"$, !" $$$% (esonance ,et9s consider 3! (carbon monoxide), !* (nitrate ion), 3l!2 (perchlorate ion): 1/ 4ra- the ,e-is structure -ith the appropriate geometry "/ 7f several reasonant forms are possible, specify -hich is the ma;or one */ Specify the geometry of the molecule/ion by applying 5SE(6 theory
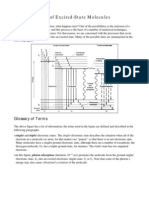
$&% Molecular orbital energy le-el diagram# )2 1/ 4ra- the <! energy level diagram (only consider valence orbitals): "/ Explain -hy dioxygen is often =ualified as a >biradical?: */ .hich magnetic property can you expect for this molecule @ 2/ 3alculate the bond order: &% Molecular orbital energy le-el diagram# C) Ahe <! energy diagram is given belo-:
1/ .hat is the electronic configuration of the molecule @ "/ .hat is the meaning of , , x and y @ */ .hich atomic orbitals are used in the construction of molecular orbitals #, 1x and 1y @ 2/ 4ra- a schematic representation of 1x:
"
You might also like
- Chemical BondingDocument12 pagesChemical Bondingrockworld009No ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry ReviewDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry ReviewPatrick Jay ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument9 pagesElectron ConfigurationShuganthi MasilamanyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure MethodsDocument71 pagesElectronic Structure MethodsAnonymous jByA78No ratings yet
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewFrom EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Review - Dec 13Document16 pagesChemistry Review - Dec 13JaredNo ratings yet
- How To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementDocument8 pagesHow To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any Elementdamz allidemNo ratings yet
- Introduction On Electron ConfigurationDocument1 pageIntroduction On Electron ConfigurationjoleeNo ratings yet
- Complete Unit 2 Notes ChemDocument81 pagesComplete Unit 2 Notes ChemJack jacksonNo ratings yet
- VSEPR ShortcutDocument3 pagesVSEPR ShortcutSubhojyotiDasNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument9 pagesElectron ConfigurationAngel SuicoNo ratings yet
- 3 Electronic Structure of Atoms 1Document28 pages3 Electronic Structure of Atoms 1Dummy BunnNo ratings yet
- Products From Oil: Double Bond Alkene Isomer Pentene Butane PentaneDocument5 pagesProducts From Oil: Double Bond Alkene Isomer Pentene Butane Pentanejojialleppey1No ratings yet
- Lewis Structures - VSEPR - Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument14 pagesLewis Structures - VSEPR - Molecular Orbital TheorytbalunNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q3 Week7Document20 pagesScience8 Q3 Week7Kathrina De SenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical BondingDocument10 pagesChapter 4: Chemical BondingdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Chem EOC1Document2 pagesChem EOC1Kimberly MawhineyNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Handout q2 Weeks 2 4Document20 pagesGen Chem 1 Handout q2 Weeks 2 4Keyaru HealerNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 Simulation ActivityDocument12 pagesProblem Set 3 Simulation Activityapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument23 pagesElectron ConfigurationJenny Claire CrusperoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (AP MC)Document4 pagesAtomic Structure (AP MC)Nyxas IoannisNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, IonsDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecules, IonsRohanulIslamNo ratings yet
- A Level Notes On Electronic Structure On AtomsDocument9 pagesA Level Notes On Electronic Structure On Atomskmoiz427No ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Electrons in Atoms - 2.1 Atomic Orbitals and Electronic ConfigurationDocument41 pagesUNIT 2 Electrons in Atoms - 2.1 Atomic Orbitals and Electronic ConfigurationSahana KumarNo ratings yet
- Ikatan IonikDocument15 pagesIkatan IonikAniesa FithriaNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Chapter 10 - Drawing Lewis Dot Structures and VSEPR ModelsDocument8 pagesHandout 2 - Chapter 10 - Drawing Lewis Dot Structures and VSEPR ModelsValentinaClavijoNo ratings yet
- Ab Initio and Semiempirical MethodsDocument58 pagesAb Initio and Semiempirical MethodsElisha Niña75% (4)
- Continuation of Week 1 - Quarter 2Document8 pagesContinuation of Week 1 - Quarter 2Ann DayritNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding: Valence Electrons and Valence Shell OrbitalsDocument20 pagesBonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding: Valence Electrons and Valence Shell OrbitalsrizkiwaNo ratings yet
- Electronic StructureDocument9 pagesElectronic StructuresimNo ratings yet
- How To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementDocument6 pagesHow To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementRemartin MaglantayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Part 2Document12 pagesChapter 05 Part 2Dana CapbunNo ratings yet
- II. Electronic Structure of Atoms and Peridioc Table of ElementsDocument16 pagesII. Electronic Structure of Atoms and Peridioc Table of ElementsHania ABDULNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry (Vsepr Theory) : For Chemistry 1 Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 4Document15 pagesMolecular Geometry (Vsepr Theory) : For Chemistry 1 Grade 12 Quarter 2 / Week 4ariinnggg onichaNo ratings yet
- Review For FinalsDocument54 pagesReview For FinalsChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- How To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementDocument8 pagesHow To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms of Any ElementTania Louise Pioquinto AbuanNo ratings yet
- Lewis Dot Procedure, KDocument2 pagesLewis Dot Procedure, KTachelle JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document16 pagesCH 02Joanna QuintoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital Theory: Luis Bonilla Abel Perez University of Texas at El Paso Molecular Electronics, Chem 5369Document26 pagesMolecular Orbital Theory: Luis Bonilla Abel Perez University of Texas at El Paso Molecular Electronics, Chem 5369viraivil9417No ratings yet
- Soal Konfigurasi ElektronDocument3 pagesSoal Konfigurasi ElektronZuliJamiatiNo ratings yet
- Write An Electron Configurations of ElementDocument10 pagesWrite An Electron Configurations of ElementMiccarina Fablina SatirNo ratings yet
- 2b. Shapes of MoleculesDocument78 pages2b. Shapes of MoleculesKareem MckenzieNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument6 pagesElectron ConfigurationJignasa ShahNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document38 pagesCH 8MoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chem Target Sheet U 1Document7 pagesEdexcel Chem Target Sheet U 1Ruwan BandaraNo ratings yet
- Electron Practice Combined Sp10Document7 pagesElectron Practice Combined Sp10Lara Greyjoy100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3John Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument26 pagesMolecular Orbital TheoryYuni RahmaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry Lab 12 6 12 Tenure PortfolioDocument5 pagesMolecular Geometry Lab 12 6 12 Tenure Portfolioapi-249441006No ratings yet
- Drawing Lewis Structures Using Formal ChargeDocument6 pagesDrawing Lewis Structures Using Formal Chargemeg megNo ratings yet
- Affan Telek - Chemistry Unit Test 1 Ver - 1Document14 pagesAffan Telek - Chemistry Unit Test 1 Ver - 1Affan TelekNo ratings yet
- 141 Tro CH 8Document16 pages141 Tro CH 8Haley HamillNo ratings yet
- Atoms First Chapter 6 Lewis StructuresDocument58 pagesAtoms First Chapter 6 Lewis StructuresJaya Chitra Degala Ramalu100% (1)
- Iniern T Ohd Journd of Spectromet&and Ion P&y&Document9 pagesIniern T Ohd Journd of Spectromet&and Ion P&y&Rudolf KiraljNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Benjamin Ratin - 1.6 Photoelectron Spectroscopy StudentDocument3 pagesKami Export - Benjamin Ratin - 1.6 Photoelectron Spectroscopy StudentBenjamin RatinNo ratings yet
- Top, Below, Right Then LeftDocument4 pagesTop, Below, Right Then LeftTrinh Tat-TranNo ratings yet
- The Slavic LanguagesDocument4 pagesThe Slavic LanguagesGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Russian GrammarDocument141 pagesRussian GrammarMichael Sturgeon, Ph.D.100% (55)
- Compgrammar PolishDocument114 pagesCompgrammar Polish420100% (4)
- Romanian and Albanian Common Vocabulary-LibreDocument16 pagesRomanian and Albanian Common Vocabulary-LibreGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- RepProgPh70 - Pitarke Theory SPSPPDocument87 pagesRepProgPh70 - Pitarke Theory SPSPPGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- MIT6 094IAP10 Lec04Document34 pagesMIT6 094IAP10 Lec04Happy2021No ratings yet
- EndosDocument7 pagesEndosGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- The Synchrotron: Longitudinal Focusing & The Gamma TransitionDocument13 pagesThe Synchrotron: Longitudinal Focusing & The Gamma TransitionGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Ar Ni Er: Av. M Illie Mathy SDocument1 pageAr Ni Er: Av. M Illie Mathy SGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Biases and Information Systems: KeywordsDocument11 pagesDecision-Making Biases and Information Systems: KeywordsGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oDocument12 pagesValence Bond Theory: Hybridization: o o o o o oGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Unit 11aDocument45 pagesUnit 11aGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument28 pagesNutritionGramoz Cubreli100% (1)
- StereoisomersDocument17 pagesStereoisomersGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Molecular FluorescenceDocument7 pagesMolecular FluorescenceGramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Document38 pagesStereoisomerism: AH Chemistry Unit 3 (C)Gramoz CubreliNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthFrom EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (197)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeFrom EverandProof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the AfterlifeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (165)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsFrom EverandThe Game: Penetrating the Secret Society of Pickup ArtistsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (131)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet