Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quality Systems
Uploaded by
Christopher CooperCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quality Systems
Uploaded by
Christopher CooperCopyright:
Available Formats
Quality systems
101-shruti agarwal
114-shikha jain
142-avni shah
149-stuti shah
155-alisha
165-Naiya mehta
1
2
3
title
Topics covered under the presentation
Introduction
Six sigma
ISO
In the company the quality of the product is checked to
see the variations.the control variation with respect to the
design specification is an important task of the production
department.the more the variation,poorer the quality and
closer the variation better the quality.
International organisation
for standardization (ISO)
The ISO 9000 family of standards is related to quality
management systems designed to help organizations ensure that
they meet the needs of customers and other stakeholders while
meeting statutory and regulatory requirements related to a
product.
[1]
The standards are published by the International
Organization for Standardization (ISO) and available through
national standards bodies.
ISO 9000 deals with the fundamentals of quality management
systems, including the eight management principles upon which
the family of standards is based.ISO 9001 deals with the
requirements that organizations wishing to meet the standard
must fulfill.
[4]
Advantages
Implementing ISO often gives the following advantages:
Creates a more efficient, effective operation
Increases customer satisfaction and retention
Reduces audits
Enhances marketing
Improves employee motivation, awareness, and morale
Promotes international trade
Increases profit
Reduces waste and increases
productivity
Common tool for standardization
Overview of ISO content:
Management responsibility
Quality system
Contract review
Design control
Purchasing
Product identification
Process control
Inspection and testing
Training
Servicing
Quality records
Quality management framework of a company consists
of following principles:
Customer focused organisation
Leadership
Documentation and record keeping
Involvment of people
Process approach
Improvement as regular practise
Factual approach to decision making
Supplier relationship
There were several contestants which limited this
study:
1.The semester time frame was limited
2.The limitation of the resource and the body of
knowledge on the topic of total quality
management.
Past definitions of quality focused on
conformance to
Standards, as companies
strived to create products and services
that fell within certain specification
limits.
-Mikel
Harry and Richard Schroeder
Features that set Six Sigma apart from previous quality
improvement initiatives include:
A clear focus on achieving measurable and quantifiable
financial returns from any Six Sigma project.
An increased emphasis on strong and passionate management
leadership and support.
A special infrastructure of "Champions," "Master Black
Belts," "Black Belts," "Green Belts", etc. to lead and implement
the Six Sigma approach.
A clear commitment to making decisions on the basis of
verifiable data, rather than assumptions and guesswork.
Sigma is the Greek letter representing the standard
deviation of a population of data.
Sigma is a measure
of variation
(the data spread)
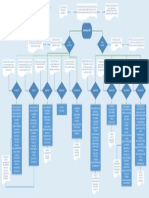
Two Methodologies:
DMAIC The
Improvement
Methodology
DMADV The
Design Methodology
Objective:
DEFINE the
opportunity
Objective:
MEASURE
current
performance
Objective:
ANALYZE the
root causes of
problems
Objective:
IMPROVE the
process to
eliminate root
causes
Objective:
CONTROL the
process
to sustain the gains.
Key Define Tools:
Cost of Poor
Quality (COPQ)
Voice of the
Stakeholder (VOS)
Project Charter
As-Is Process
Map(s)
Primary Metric
(Y)
Key Measure Tools:
Critical to
Quality
Requirements
(CTQs)
Sample Plan
Capability
Analysis
Failure Modes
and Effect
Analysis
(FMEA)
Key Analyze Tools:
Histograms,
Boxplots,
Multi-Vari
Charts, etc.
Hypothesis
Tests
Regression
Analysis
Key Improve Tools:
Solution
Selection
Matrix
To-Be Process
Map(s)
Key Control Tools:
Control
Charts
Contingency
and/or
Action
Plan(s)
Define Measure Analyze Improve Control
DMADV The Design Methodology
Uses
Design new processes, products, and/or services from scratch
Replace old processes where improvement will not suffice
Differences between DFSS and DMAIC
Projects typically longer than 4-6 months
Extensive definition of Customer Requirements (CTQs)
Heavy emphasis on benchmarking and simulation; less emphasis on base lining
Key Tools
Multi-Generational Planning (MGP)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Define Measure Analyze Develop Verify
Focus on customers.
Improved customer loyalty.
Reduced cycle time.
Less waste.
Data based decisions.
Time management
Sustained gains and improvements.
Systematic problem solving.
Employee motivation
Data analysis before decision making.
Faster to market.
Assure strategy planning.
Advantages
Thank You
You might also like
- Agile LatestDocument4 pagesAgile Latestgautham kamparaju33% (3)
- Iso 7 1 Pipe ThreadsDocument11 pagesIso 7 1 Pipe ThreadsSintha AidroosNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument53 pagesProject Quality ManagementEnsha AnwashNo ratings yet
- Tools and Quality Measurement and ImprovementDocument39 pagesTools and Quality Measurement and Improvementanishaharsh0% (1)
- What Is TQM?Document43 pagesWhat Is TQM?nimra100% (1)
- Supplier Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesSupplier Quality ManagementJossie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Audit Types Presentation - Sue Brewster PDFDocument45 pagesAudit Types Presentation - Sue Brewster PDFAnonymous WsEdGMIjmNo ratings yet
- Qms PPT FinalDocument13 pagesQms PPT FinalHaaMid RaSheedNo ratings yet
- Comparision ISO 9001 2018 & 2015Document8 pagesComparision ISO 9001 2018 & 2015manish100% (1)
- ISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group Guidance On:: ProcessesDocument6 pagesISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group Guidance On:: ProcessesJohn RajeshNo ratings yet
- ISO-TS 16949 AwarenessDocument117 pagesISO-TS 16949 AwarenessRavikumar PatilNo ratings yet
- Auditors Code of ConductDocument33 pagesAuditors Code of ConductSherwin MosomosNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 - QmsDocument110 pagesIso 9001 - QmsAjay GandhiNo ratings yet
- 2020 T2 MN601 Lecture 8 Quality Planning and KickoffDocument61 pages2020 T2 MN601 Lecture 8 Quality Planning and KickoffFavour Adenugba100% (1)
- APG InternalAudit2015 PDFDocument4 pagesAPG InternalAudit2015 PDFBulmaro SanchezNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards For ISODocument5 pagesQuality Standards For ISORaj kumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project Quality Planning: Saudi Arabian Parsons LTDDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Project Quality Planning: Saudi Arabian Parsons LTDAhmed ElhajNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument39 pagesProject Quality ManagementElloani Ross Arcenal Pitogo100% (1)
- LQMS 6Document76 pagesLQMS 6R C MathewNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 EPMDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 EPMWajiha JawwadNo ratings yet
- 2.2 QFD HoqDocument19 pages2.2 QFD HoqAayush KNo ratings yet
- 9.0 Performance EvaluationDocument5 pages9.0 Performance EvaluationShailesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Controlling Quality by Waqas Ali TunioDocument24 pagesControlling Quality by Waqas Ali TuniowaqasalitunioNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Iso: Envirotech Quality Management 1Document30 pagesAn Overview of Iso: Envirotech Quality Management 1bubun007No ratings yet
- Online Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANDocument10 pagesOnline Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANHehe HoNo ratings yet
- Balanced Score CardDocument19 pagesBalanced Score CardAamirx64No ratings yet
- MBA IInd SEM POM Chapter 04 Quality ManagementDocument62 pagesMBA IInd SEM POM Chapter 04 Quality ManagementPravie100% (5)
- Total Quality ManagementDocument97 pagesTotal Quality ManagementRodiemerNo ratings yet
- Issues in QualityDocument19 pagesIssues in QualityPappuRamaSubramaniamNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 - Quality ManagementDocument9 pagesISO 9000 - Quality ManagementVictor DharNo ratings yet
- Review Iso 9001 2015 PPMDocument27 pagesReview Iso 9001 2015 PPMAFDHAL PASANo ratings yet
- Iso 9000 & Total Quality ManagementDocument13 pagesIso 9000 & Total Quality Managementalifatehitqm100% (1)
- Management & Control of QualityDocument2 pagesManagement & Control of QualityDeepak Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of ISO 9000-2000 Quality System Standards, QS9000, IsO:TS 16949 and Baldrige CriteriaDocument10 pagesA Comparison of ISO 9000-2000 Quality System Standards, QS9000, IsO:TS 16949 and Baldrige CriteriaAfifNo ratings yet
- Construction Performance Management & Resource Optimization: Chapter Four Project Quality ManagementDocument41 pagesConstruction Performance Management & Resource Optimization: Chapter Four Project Quality ManagementhabtieNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance W15L30 Instructor: Saliha ZahoorDocument55 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance W15L30 Instructor: Saliha ZahoorygfdsgdgsdhdjkghkgjNo ratings yet
- ISO9001 OxfordDocument17 pagesISO9001 OxfordManigandan RNo ratings yet
- IRCA Auditor: Requirements For Certification As AnDocument61 pagesIRCA Auditor: Requirements For Certification As AnRiadh TaktakNo ratings yet
- Internal Quality Audit For ISO 9001 2008Document115 pagesInternal Quality Audit For ISO 9001 2008Srinivasan RadhaNo ratings yet
- 1dredging ITTxDocument273 pages1dredging ITTxAF Dowell MirinNo ratings yet
- 9 K TRGDocument96 pages9 K TRGRK ENTERPRISESNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety Aspects in HospitalsDocument11 pagesQuality and Safety Aspects in HospitalsMythily VedhagiriNo ratings yet
- TQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerDocument25 pagesTQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerJaga Deesh100% (1)
- Quality and InnovationDocument61 pagesQuality and InnovationahyaniluthfianasariNo ratings yet
- KerepeanDocument12 pagesKerepeansyeila_elmiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001Document97 pagesIso 9001GalkandaNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Quality MGMT - by SkanchiDocument44 pagesPMBOK Quality MGMT - by Skanchiksreddy58100% (2)
- Revised Auditing TechniquesDocument42 pagesRevised Auditing Techniquessaurabh choudhary100% (2)
- Iso 9000Document57 pagesIso 9000vinniieeNo ratings yet
- Process ImprovementDocument15 pagesProcess Improvementqwerty_123123No ratings yet
- Competence Vs QualificationDocument25 pagesCompetence Vs Qualificationjohnoo7No ratings yet
- Project Quality Management: - Quality Assurance Plan in Road ConstructionDocument30 pagesProject Quality Management: - Quality Assurance Plan in Road Constructionसुजन कार्कीNo ratings yet
- Auditor Training Module 2 - Audit ManagementDocument28 pagesAuditor Training Module 2 - Audit ManagementThant AungNo ratings yet
- BSI Internal Audit TipsDocument12 pagesBSI Internal Audit TipsAdrian AustinNo ratings yet
- Managing The Process Flow With ISO9000 FamilyDocument6 pagesManaging The Process Flow With ISO9000 FamilyVC100% (1)
- Presentation of Quality ControlDocument63 pagesPresentation of Quality ControlJohn YohansNo ratings yet
- 1fos - Call ManagementDocument53 pages1fos - Call Managementlourds rickson GementizaNo ratings yet
- EPRI Supplier Performance Base AuditDocument84 pagesEPRI Supplier Performance Base AuditixoteeNo ratings yet
- Section 2Document117 pagesSection 2باسل العدوانNo ratings yet
- MS5 and MS6.4 GBDocument65 pagesMS5 and MS6.4 GBnikodjole100% (4)
- Et Iso 12543 1 2011Document14 pagesEt Iso 12543 1 2011freddyguzman3471No ratings yet
- Tech Brief 101 Cannon Fenske ViscosimetersDocument5 pagesTech Brief 101 Cannon Fenske ViscosimetersHektor EktroposNo ratings yet
- Moxa Tech Note - What Is Turbo RingDocument4 pagesMoxa Tech Note - What Is Turbo RingDennis ZoisNo ratings yet
- Abb VFD Acs550 01Document320 pagesAbb VFD Acs550 01Anil SankhlaNo ratings yet
- T942we PDFDocument192 pagesT942we PDFLYF AndroidNo ratings yet
- Who HvacDocument22 pagesWho HvacAnas Abandeh100% (1)
- Selecting A SSD: Sata (2.5" or M.2) Nvme (Pcie M.2)Document1 pageSelecting A SSD: Sata (2.5" or M.2) Nvme (Pcie M.2)singenaadamNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic FeedersDocument5 pagesPneumatic FeedersKaramveer RatheeNo ratings yet
- Goods Lifts: 300 - 2000kg CapacityDocument14 pagesGoods Lifts: 300 - 2000kg CapacityAnton LyakhovNo ratings yet
- Ariston AVL-129Document72 pagesAriston AVL-129Birgitte Skanke BredeliNo ratings yet
- Cheatsheet GCP A4Document3 pagesCheatsheet GCP A4Anonymous kXqEoUHYCNo ratings yet
- Green Product Management - Wistron - ENDocument7 pagesGreen Product Management - Wistron - ENxtrayangNo ratings yet
- PCI Compliance - Best Practices For Securing Credit Card DataDocument3 pagesPCI Compliance - Best Practices For Securing Credit Card Datahalock100% (3)
- Org Seventeen: Serial Port Programming With Assembly and C#Document35 pagesOrg Seventeen: Serial Port Programming With Assembly and C#Nisargdesai91100% (2)
- Basic Airframe RepairDocument98 pagesBasic Airframe RepairBookMaggotNo ratings yet
- Steering Column: Section 6EDocument16 pagesSteering Column: Section 6Efrancisca19No ratings yet
- Manchester Encoding Using RS232Document4 pagesManchester Encoding Using RS232Izhar Rosli100% (1)
- Assignment of StrategicDocument6 pagesAssignment of StrategicbrahmantyoadiNo ratings yet
- ITG-Internal Control MatrixDocument14 pagesITG-Internal Control Matrixbladexdark67% (3)
- Defence Standard 22-48 (NES 2048)Document34 pagesDefence Standard 22-48 (NES 2048)Hattar MNo ratings yet
- Tempconversion PDFDocument6 pagesTempconversion PDFPravat TiadiNo ratings yet
- Brochure 4340 DensometerDocument1 pageBrochure 4340 DensometeranirudhbhokarikarNo ratings yet
- IECB Cie Pie Application Form 1022007Document2 pagesIECB Cie Pie Application Form 1022007Anonymous d6EtxrtbNo ratings yet
- HLT-1751 HLT-2051Document28 pagesHLT-1751 HLT-2051Pompei RusuNo ratings yet
- Katalog Magelis XBT N R RTDocument32 pagesKatalog Magelis XBT N R RTLASSAADNo ratings yet
- Key Terminology of The TOGAF 9 Standard PDFDocument8 pagesKey Terminology of The TOGAF 9 Standard PDFraghuNo ratings yet
- 3b Domestic Water Meter Installation in Meter Room GuidelinesDocument10 pages3b Domestic Water Meter Installation in Meter Room GuidelinesVinish HARIDAS NAIRNo ratings yet