Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) : 5-Minute Guide
Uploaded by
OmniSkills, LLCOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) : 5-Minute Guide
Uploaded by
OmniSkills, LLCCopyright:
Available Formats
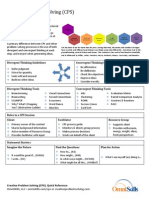
Creative Problem Solving (CPS): The 5‐Minute Guide
What
is
Creative
Problem
Solving?
CPS
is
a
structured
process
for
solving
problems
or
finding
opportunities,
used
when
you
want
to
go
beyond
conventional
thinking
and
arrive
at
creative
(novel
and
useful)
solutions.
A
key
point:
although
the
process
is
depicted
as
linear,
in
practice
it
is
more
organic.
Depending
on
the
situation,
you
may
not
use
all
the
stages,
and
may
not
use
them
in
the
order
shown.
Facilitate
Goal
of
this
stage:
at
the
beginning
of
the
process,
to
determine
the
problem
space
you
are
working
in;
throughout
the
process,
to
make
process
decisions.
Description:
a
meta‐process
step
used
throughout
CPS
to
make
process‐related
decisions:
where
to
enter,
which
tools
to
use,
and
when
to
move
to
the
next
step.
This
oversight
is
the
responsibility
of
the
problem's
owner
and
the
CPS
facilitator,
who
is
usually
a
neutral
third
party.
Useful
tools:
SWOT
(Strengths,
Weaknesses,
Opportunities,
Strengths),
or
any
diagnostic
tool.
Imagine
the
Future
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
created
a
broad,
brief,
beneficial
statement
beginning
with
"I
wish..."
or
"Wouldn't
it
be
great
if...".
Description:
this
stage
defines
a
desired
future
condition,
and
sets
the
stage
for
“clarifying
the
problem.”
Useful
tools:
Brainstorming,
Brainwriting,
Web
of
Abstraction,
and
Excursions
for
divergent
thinking;
Hits,
Clustering,
and
Restating
Clusters
for
convergent
thinking.
Find
the
Questions
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
identified
one
or
more
problems
you
wish
to
work
on,
in
the
form
of
concise
problem
statements
that
begin
with
"How
to...",
"How
might...",
"In
what
ways
might...",
and
"What
might
be
all
the...."
Description:
identify
the
problems
that
must
be
solved
if
you
are
to
realize
the
goal/wish/challenge
identified
in
previous
stage.
Useful
tools:
Brainstorming,
Brainwriting,
Web
of
Abstraction,
and
Word
Dance
for
divergent
thinking;
Hits,
Clustering,
and
Restating
Clusters
for
convergent
thinking.
Generate
Ideas
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
generated
many
ideas
that
would
solve
the
problems
identified
in
the
previous
stage,
and
you
would
have
selected
those
that
are
worth
carrying
forward.
Description:
imagine
many
solutions,
alternatives,
and
opportunities
for
the
problem
statement
you
selected
in
the
previous
step.
Then,
evaluate,
judge,
strengthen,
and
finally
decide
which
to
carry
forward.
Useful
tools:
Idea
Box,
Brainwriting,
Brainstorming,
SCAMPER,
Forced
Connections,
Visual
Connections,
and
Excursions
for
divergent
thinking;
Hits,
Clustering,
and
Restating
Clusters
for
convergent
thinking.
Craft
Solutions
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
refined
and
decided
on
the
solution(s)
you
will
implement.
One
way:
create
a
solution
statement,
an
extended
description
of
what
you
plan
to
do,
that
begins
with:
"What
I
see
myself
(us)
doing
is...".
Description:
After
generating
ideas
in
the
previous
step,
you
will
have
one
or
more
ideas
that
you
wish
to
pursue.
In
this
step,
you
select
the
ones
you
have
the
time
are
resources
to
pursue,
and
you
strengthen
them
‐
you
make
them
better.
Useful
tools:
when
strengthening,
any
divergent
thinking
tools
(see
Generating
Ideas);
when
evaluating,
POINt,
Card
Sort,
Evaluation
Matrix,
and
Paired
Comparison
Analysis
for
convergent
thinking.
Explore
Acceptance
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
identified
those
who
will
assist
your
solution,
those
who
will
resist,
and
what
to
do
with
each.
Description:
Make
a
list
of
people
and
groups
who
will
assist
you,
then
generate
ideas
for
how
they
can
help
you
advance
your
solution.
Make
a
list
of
people
and
groups
who
will
resist
your
solution,
then
generate
ideas
for
how
you
can
overcome
or
mitigate
the
resistance.
Plan
for
Action
At
the
end
of
this
stage:
you
will
have
created
an
action
plan
that
identifies
what
is
to
be
done,
by
when,
and
by
whom.
Description:
create
an
action
plan
that
identifies
the
discrete
and
concrete
steps
you
will
follow,
and
who
is
involved
in
the
implementation.
Useful
tool:
RACI
chart,
which
lists
the
action
steps
and,
for
each
step,
the
person
Responsible
to
do
it;
the
person
who
is
Accountable
for
it
being
done;
the
person(s)
who
can
be
Consulted
for
help
and
guidance;
and
the
person(s)
who
need
to
be
Informed
when
done.
Creative
Problem
Solving
(CPS):
The
5‐Minute
Guide
OmniSkills,
LLC
▪
omniskills.com/cps
or
creativeproblemsolving.com
You might also like
- Decision Making SkillsDocument40 pagesDecision Making Skillsanna_blonde16No ratings yet
- Problem Solving ModelDocument7 pagesProblem Solving ModelKerrnaz PanthakiNo ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques of Decision MakingDocument11 pagesTools and Techniques of Decision Makingpavankrishna930% (1)
- Unit DevelopmentDocument4 pagesUnit Developmentapi-193614660No ratings yet
- Johari Window: A Model For Self-Awareness, Personal Development, Group Development and Understanding RelationshipDocument33 pagesJohari Window: A Model For Self-Awareness, Personal Development, Group Development and Understanding RelationshipImran HassanNo ratings yet
- Certification Roadmap 11-30-16Document1 pageCertification Roadmap 11-30-16Cristian Gavilanes MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Call Center ActivityDocument3 pagesCall Center ActivityAlexandra MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Community Integration Questionnaire Testing FormDocument4 pagesCommunity Integration Questionnaire Testing FormriddhiNo ratings yet
- Agustin Career Plan WorksheetDocument5 pagesAgustin Career Plan WorksheetElijah Jade AgustinNo ratings yet
- A705F Schematic Circuit Diagram HALABTECHDocument11 pagesA705F Schematic Circuit Diagram HALABTECHbcscneg0% (1)
- Creative Problem Solving (CPS) : One-Page SummaryDocument1 pageCreative Problem Solving (CPS) : One-Page SummaryOmniSkills, LLCNo ratings yet
- Team Importance & Management: Presentation By: Deepthi. P Jinesh Jain Gheerdhardhini. M Bindu Thushara. NDocument14 pagesTeam Importance & Management: Presentation By: Deepthi. P Jinesh Jain Gheerdhardhini. M Bindu Thushara. NNB Thushara HarithasNo ratings yet
- D4530Document5 pagesD4530rimi7al100% (1)
- Self-Discovery Reflection QuestionsDocument1 pageSelf-Discovery Reflection QuestionsSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Logic Models A Practical GuideDocument10 pagesLogic Models A Practical GuideGatot hadiwijoyo100% (1)
- New Teacher Orientation: Administrative InformationDocument14 pagesNew Teacher Orientation: Administrative Informationtsoxxx100% (1)
- Function of Management: Jahid Hasan Assistant Professor Department of IPE, SUSTDocument54 pagesFunction of Management: Jahid Hasan Assistant Professor Department of IPE, SUSTফারহান আহমেদ আবীরNo ratings yet
- What Is TeamworkDocument9 pagesWhat Is TeamworkKOwh ArEa Jae-panessEs100% (1)
- Understanding Complexity: Having Good Strong Problem Solving Skills Can Make A Huge Difference To Your CareerDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Complexity: Having Good Strong Problem Solving Skills Can Make A Huge Difference To Your CareerSolo Jugar ParaNo ratings yet
- Jastram Rudder Feedback UnitDocument21 pagesJastram Rudder Feedback UnitGary Gouveia100% (3)
- Brochure Exterior LightingDocument49 pagesBrochure Exterior Lightingmurali_227No ratings yet
- Sample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Document31 pagesSample CBAP Elicitation Scenario Based Questions Set 01Rubab Javaid100% (1)
- Map The Stakeholders - Interaction Design FoundationDocument8 pagesMap The Stakeholders - Interaction Design FoundationAluísio MartellNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Good EmployeeDocument17 pagesWhat Makes A Good EmployeeAngelika QuevedoNo ratings yet
- Midterms HCI 1Document43 pagesMidterms HCI 1I_am_just_a_kidNo ratings yet
- Parents Teachers Asociation-Pta CP Goenka International School, ThaneDocument8 pagesParents Teachers Asociation-Pta CP Goenka International School, ThaneRakshit GhadigaonkarNo ratings yet
- Project of Business Ethics FinalDocument20 pagesProject of Business Ethics FinalMarwah YaseenNo ratings yet
- Human Computer InteractionDocument13 pagesHuman Computer InteractionMarie AshleyNo ratings yet
- Workshop One - Work-Life BalanceDocument3 pagesWorkshop One - Work-Life Balanceapi-319898057No ratings yet
- Kthorell StoryboardDocument11 pagesKthorell Storyboardapi-309975933No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Models of CommunicationEuwella GloriaNo ratings yet
- PM BasicsDocument153 pagesPM BasicssNo ratings yet
- RsharpeeqstoryboardDocument27 pagesRsharpeeqstoryboardapi-359215472No ratings yet
- GCDocument198 pagesGCapi-240425191No ratings yet
- Made EasyDocument24 pagesMade EasykzulNo ratings yet
- Forging Success Through Better Presos: Doyle FreemanDocument20 pagesForging Success Through Better Presos: Doyle FreemanyampdchaulagainNo ratings yet
- Promoting Health and Wellness of ChildrenDocument41 pagesPromoting Health and Wellness of ChildrenLeonard AloyanNo ratings yet
- 575 StoryboardDocument11 pages575 Storyboardapi-299766271No ratings yet
- Secretarial and Administrative Skills Public ProgramDocument2 pagesSecretarial and Administrative Skills Public ProgramiTrainingExpertNo ratings yet
- SMART Goal SettingDocument5 pagesSMART Goal SettingblakeloganNo ratings yet
- Sample Training BriefDocument1 pageSample Training BriefFatima Jabeen0% (1)
- Recruitment and Selection ProcessDocument29 pagesRecruitment and Selection Processapi-3709921100% (1)
- Get Fully Solved Assignment. PLZ Drop A Mail With Your Sub CodeDocument206 pagesGet Fully Solved Assignment. PLZ Drop A Mail With Your Sub CodeProjectHelpForuNo ratings yet
- Student Handbook Complete 1306FDocument48 pagesStudent Handbook Complete 1306Fkamal anish yanduriNo ratings yet
- Effective Fact-Finding TechniquesDocument65 pagesEffective Fact-Finding Techniquest0ck9243No ratings yet
- Personality and LifestyleDocument23 pagesPersonality and LifestyleVinod JoshiNo ratings yet
- YS Events Pvt. LTD.: Presenter Satish SinghDocument15 pagesYS Events Pvt. LTD.: Presenter Satish SinghSatish Singh ॐNo ratings yet
- Addie Presentation - Sharin 1Document15 pagesAddie Presentation - Sharin 1api-510028688No ratings yet
- Understanding Generalist Practice, 8E: Karen K. Kirst-Ashman Grafton H. Hull, JRDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Generalist Practice, 8E: Karen K. Kirst-Ashman Grafton H. Hull, JRmaniiNo ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving - 5 Min Guide PDFDocument1 pageCreative Problem Solving - 5 Min Guide PDFsushumcastle6546No ratings yet
- 6 Step Problem Solving ProcessDocument9 pages6 Step Problem Solving ProcessLalitha VbNo ratings yet
- Concept of Decision MakingDocument12 pagesConcept of Decision MakingLeilani JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Planning CycleDocument10 pagesPlanning CycleMuqaddas TasneemNo ratings yet
- ProblemsolvingmodelDocument5 pagesProblemsolvingmodelnizam.ramlanNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Science Module 3 AmityDocument2 pagesBehaviour Science Module 3 AmityishanNo ratings yet
- Creative Problem Solving 1 Running Head: Model For Creative Problem SolvingDocument12 pagesCreative Problem Solving 1 Running Head: Model For Creative Problem SolvingRishabh OswalNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Model - 207Document6 pagesProblem Solving Model - 207Cristina GomezNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument4 pagesCritical Thinking20h4030101No ratings yet
- Generalidades - DT - GPSDocument73 pagesGeneralidades - DT - GPSJavier GusmanNo ratings yet
- Simon's Model of Decision-Making: Intelligence PhaseDocument2 pagesSimon's Model of Decision-Making: Intelligence PhaseVani GangilNo ratings yet
- Planning Cycle: Stage 1. Analysis of OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesPlanning Cycle: Stage 1. Analysis of OpportunitiesZel VilleNo ratings yet
- 6Zdr7Ve2Eemplgpfqc6zSA Tag Reading 1 PDFDocument3 pages6Zdr7Ve2Eemplgpfqc6zSA Tag Reading 1 PDFtarunNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decision MakingDocument7 pagesManagerial Decision MakingJaya Mae ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- Basic Steps Involved in ThinkingDocument5 pagesBasic Steps Involved in Thinkinggodofwar5601No ratings yet
- The 5 Stages in The Design Thinking ProcessDocument5 pagesThe 5 Stages in The Design Thinking Processhervehirwa25No ratings yet
- Simon's Model of Decision MakingDocument1 pageSimon's Model of Decision MakingAbhisek SarkarNo ratings yet
- CPS: Divergent Tools Quick ReferenceDocument1 pageCPS: Divergent Tools Quick ReferenceOmniSkills, LLCNo ratings yet
- CPS Tools: Stakeholder Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesCPS Tools: Stakeholder Analysis WorksheetOmniSkills, LLCNo ratings yet
- CPS Tools: Brainwriting WorksheetDocument1 pageCPS Tools: Brainwriting WorksheetOmniSkills, LLCNo ratings yet
- CPS Tools: Word Dance WorksheetDocument1 pageCPS Tools: Word Dance WorksheetOmniSkills, LLCNo ratings yet
- Lock Maiolo Savonarola MachiavelliDocument22 pagesLock Maiolo Savonarola MachiavelliHeliogabolusNo ratings yet
- Product-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Document4 pagesProduct-Oriented Learning Competencies: (Beginner)Kri S ELNo ratings yet
- Bibliografi 3Document3 pagesBibliografi 3Praba RauNo ratings yet
- Briefing Evaluation: Yes / No High / Low Yes / No High / Low Good / Inferior Yes / NoDocument4 pagesBriefing Evaluation: Yes / No High / Low Yes / No High / Low Good / Inferior Yes / NoAmmarah AzharNo ratings yet
- Strain GaugeDocument7 pagesStrain GaugefahadarizkiNo ratings yet
- BUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation ScheduleDocument7 pagesBUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation SchedulePaulina Arti WilujengNo ratings yet
- Headworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargDocument29 pagesHeadworks & Barrage: Chapter # 09 Santosh Kumar GargUmer WaheedNo ratings yet
- Semantic SearchMonkeyDocument39 pagesSemantic SearchMonkeyPaul TarjanNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - A Closer Look 2Document3 pagesUnit 8 - A Closer Look 2Trần Linh TâmNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Is The Backbone of ResearchDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Is The Backbone of Researchafmzweybsyajeq100% (1)
- Preview - ISO+8655 6 2022Document6 pagesPreview - ISO+8655 6 2022s7631040No ratings yet
- (LS 1 English, From The Division of Zamboanga Del SurDocument17 pages(LS 1 English, From The Division of Zamboanga Del SurKeara MhieNo ratings yet
- CS221 - Artificial Intelligence - Search - 4 Dynamic ProgrammingDocument23 pagesCS221 - Artificial Intelligence - Search - 4 Dynamic ProgrammingArdiansyah Mochamad NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Al Kindi AssingmentDocument9 pagesAl Kindi AssingmentMuhammad Sirajuddin MazlanNo ratings yet
- KaranDocument4 pagesKarancristioronaldo90No ratings yet
- Amanuel MekonnenDocument125 pagesAmanuel Mekonnenabata yohannesNo ratings yet
- Straightforward Pre-Intermediate Progress Test 4: Language Section VocabularyDocument8 pagesStraightforward Pre-Intermediate Progress Test 4: Language Section VocabularyStrange BrawlerNo ratings yet
- 翻译件 2021 The - Early - Life - of - Marx's - "Mode - 【彩云小译】Document61 pages翻译件 2021 The - Early - Life - of - Marx's - "Mode - 【彩云小译】James BNo ratings yet
- Loading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperDocument2 pagesLoading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperRJNo ratings yet
- Problems 1Document2 pagesProblems 1Andoy Don M.No ratings yet
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- BP KWN RPM W KGW KGW KGW KG SFC GM KWHR Caloricfivalue MJ KGDocument3 pagesBP KWN RPM W KGW KGW KGW KG SFC GM KWHR Caloricfivalue MJ KGHoàng Khôi100% (1)
- Project Scheduling: Marinella A. LosaDocument12 pagesProject Scheduling: Marinella A. LosaMarinella LosaNo ratings yet
- Bachelors - Project Report 1Document43 pagesBachelors - Project Report 1divyaNo ratings yet