Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Biology Form 4) Stage in Meiosis
Uploaded by
geelatifOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Biology Form 4) Stage in Meiosis
Uploaded by
geelatifCopyright:
Available Formats
[Biology Form 4] Stage In Meiosis
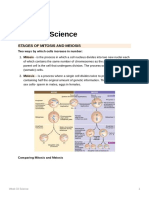
1. Anaphase II
o The sister chromatids are pulled apart and head towards opposite ends of
the cell.
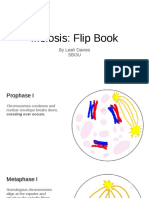
2. Prophase I
o The homologous chromosomes, which are visible under a microscope,
appear short, dense and thick. Each chromosome forms its own set of
sister chromatids. The homologous chromosomes exist as two tetrads
with a total of eight chromatids altogether. Crossing over may occur
between non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes.
3. Telophase I
o Spindle fibres disappear. The cell divides into two, each having two
chromosomes each. The sister chromatids for each homologous
chromosome are still present and attached to a common centromere.
4. Telophase II
o Each end of the cell now has two chromosomes. The nucleoli and nuclear
membranes re-form. This stage is followed by cytokinesis.
5. Anaphase I
o The homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite ends
of the cells
6. Prophase II
o There are now two chromosomes, each with their sister chromatids
present, in each of the two haploid cells. The chromatids thicken and
shorten. The nuclear membrane around them disappears again and the
chromatids are free to move.
7. Metaphase II
o The sister chromatids align themselves at the imaginary centre of the cell.
8. Metaphase I
o The homologous chromosomes, together with their chromatids, align
themselves at an imaginary line along the centre of the cell.
You might also like
- Handout MeiosisDocument4 pagesHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNo ratings yet
- Mitosis V MeiosisDocument5 pagesMitosis V MeiosisddaarrsshhiittNo ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Meiosis in Grasshopper TestisDocument7 pagesMeiosis in Grasshopper TestisRonisa100% (2)
- Meiosis Flipbook 1Document13 pagesMeiosis Flipbook 1Sara SNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Meiosis: 5 People Chapter 5: Cell DivisionDocument4 pages5.2 Meiosis: 5 People Chapter 5: Cell DivisionVivekananda MarieNo ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisDocument6 pages(Biology Form 4) Stage in MeiosisFuzieanna BakhtiarNo ratings yet
- What Is Meiosis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Meiosis?James DazNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument8 pagesMeiosisJohn Chiyu Garde-Labite Azuki100% (1)
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Pop BeadsDocument6 pagesMeiosis Pop BeadsKhadija PrescottNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: A. First Meiotic Division (Reductional Division)Document4 pagesMeiosis: A. First Meiotic Division (Reductional Division)Abbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis FactsDocument8 pagesMitosis and Meiosis FactsLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis I and IIDocument2 pagesMitosis, Meiosis I and IIYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Week 33 ScienceDocument3 pagesWeek 33 ScienceKittie EliseNo ratings yet
- Interphase IDocument3 pagesInterphase IJJAMPPONG PSNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionsDocument6 pagesCell DivisionsEuniceNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionCharlotte JalaNo ratings yet
- 7) Mitosis and Meiosis Summary 9744 - 2018Document3 pages7) Mitosis and Meiosis Summary 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Document16 pagesBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic - Lab-2Document12 pagesHuman Genetic - Lab-2dhoha alawsiNo ratings yet
- What Is Mitosis & MeiosisDocument7 pagesWhat Is Mitosis & MeiosisMuhammad VaizNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument17 pagesMeiosisSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Document34 pagesChapter Four.. 2022-10-12 11 - 31 - 55Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (OrganelleDocument7 pagesMitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (Organelleazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleRenzdy MejillaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NotesDocument5 pagesMitosis Meiosis NotesnicoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 HWDocument24 pagesChapter 10 HWJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Gummy Worm Meiosis LabDocument4 pagesGummy Worm Meiosis Labtheograph361No ratings yet
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument7 pages4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNo ratings yet
- Meiosis IIDocument3 pagesMeiosis IIArdhiansyah BaskaraNo ratings yet
- Tdn°2 103019Document9 pagesTdn°2 103019selmi bouzidNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual ReproductionDocument48 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproductionerdayu86100% (1)
- Module-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisDocument88 pagesModule-2-Meiosis-and-MitosisSevdred CadelinaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument33 pagesMeiosisShrawani DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Cell CycleDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer - Cell CycleCarlieseNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Illustration: How a Single Parent Cell Divides to Produce Four Daughter CellsDocument4 pagesMeiosis Illustration: How a Single Parent Cell Divides to Produce Four Daughter CellsJikah JiKiNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Draw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesDraw The Process of Mitosis and MeiosisTang Tiong Min 郑中铭No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis II - Group 2Document15 pagesMeiosis II - Group 2Yoongi MinNo ratings yet
- Copia de Meiosis Gummy Worm LabDocument8 pagesCopia de Meiosis Gummy Worm Labgopan629No ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument12 pagesMEIOSISDave BoocNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Document21 pagesLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument1 pageCell Divisionapi-237427942No ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sci 8Document33 pagesWeek 2 Sci 8Joseph Gabriel Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Class 9Document4 pagesCell Division Class 9pillapandurangapatruduNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument48 pagesCell DivisionMichaelNo ratings yet
- "Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9Document7 pages"Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9kylevNo ratings yet
- Binary Fission, Mitosis and Meiosis ProcessesDocument4 pagesBinary Fission, Mitosis and Meiosis ProcessesMarielle GeronimoNo ratings yet
- The Life of A Cell From Its Origin in The Division of A Parent Cell Until Its Own Division Into TwoDocument27 pagesThe Life of A Cell From Its Origin in The Division of A Parent Cell Until Its Own Division Into TwoMENWER ALJOHANINo ratings yet
- Part II-Meiosis ActivityDocument2 pagesPart II-Meiosis ActivityChristian LabisNo ratings yet
- Mitosis y MeiosisDocument20 pagesMitosis y MeiosisSusana JimenezNo ratings yet
- To Understand What Is Needed To Achieve Effective CleaningDocument5 pagesTo Understand What Is Needed To Achieve Effective CleaninggeelatifNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesFinancial ManagementgeelatifNo ratings yet
- 2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W AnsDocument93 pages2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- Malayan Sun Bear OverviewDocument5 pagesMalayan Sun Bear OverviewgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme P2 (Essay)Document5 pagesMark Scheme P2 (Essay)Rozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Short StoriesDocument3 pagesShort StoriesgeelatifNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Personal Cleanliness Date Back To PrehistoricDocument5 pagesThe Origins of Personal Cleanliness Date Back To PrehistoricgeelatifNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductiongeelatifNo ratings yet
- Rich PoorDocument2 pagesRich PoorgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Najihah Abd. Latif (4 SAGA) : Prepared byDocument5 pagesNajihah Abd. Latif (4 SAGA) : Prepared bygeelatifNo ratings yet
- Cations N AnionsDocument1 pageCations N AnionsgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Ulbs English 2Document4 pagesUlbs English 2geelatifNo ratings yet
- Most People in Our Society Generally HaveDocument3 pagesMost People in Our Society Generally HavegeelatifNo ratings yet
- Media ViolenceDocument2 pagesMedia ViolencegeelatifNo ratings yet
- To Understand What Is Needed To Achieve Effective CleaningDocument5 pagesTo Understand What Is Needed To Achieve Effective CleaninggeelatifNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Personal Cleanliness Date Back To PrehistoricDocument5 pagesThe Origins of Personal Cleanliness Date Back To PrehistoricgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Biologi k3 Percubaan SBP 2007Document11 pagesBiologi k3 Percubaan SBP 2007geelatifNo ratings yet
- Short StoriesDocument3 pagesShort StoriesgeelatifNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 3Document9 pagesSkema Kertas 3Sitinorsyahidah Jantan100% (1)