Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amniotic Fluid Color Meanings
Uploaded by
geejei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9K views2 pagesAmniotic fluid can have different colors that provide information about the health of the fetus and mother. Pale straw is normal, while yellow or dark amber could indicate fetal hypoxia over 36 hours, hemolytic disease, or infection. Greenish fluid suggests meconium staining and fetal distress. Port wine color indicates abruptio placenta from a mixture of amniotic fluid and blood. Tests like the fern test under a microscope and checking pH levels can help determine if the amniotic membranes have ruptured.
Original Description:
Original Title
Amniotic Fluid Colors
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAmniotic fluid can have different colors that provide information about the health of the fetus and mother. Pale straw is normal, while yellow or dark amber could indicate fetal hypoxia over 36 hours, hemolytic disease, or infection. Greenish fluid suggests meconium staining and fetal distress. Port wine color indicates abruptio placenta from a mixture of amniotic fluid and blood. Tests like the fern test under a microscope and checking pH levels can help determine if the amniotic membranes have ruptured.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9K views2 pagesAmniotic Fluid Color Meanings
Uploaded by
geejeiAmniotic fluid can have different colors that provide information about the health of the fetus and mother. Pale straw is normal, while yellow or dark amber could indicate fetal hypoxia over 36 hours, hemolytic disease, or infection. Greenish fluid suggests meconium staining and fetal distress. Port wine color indicates abruptio placenta from a mixture of amniotic fluid and blood. Tests like the fern test under a microscope and checking pH levels can help determine if the amniotic membranes have ruptured.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Amniotic Fluid Colors
• a. pale straw color – normal
• b. yellow stained/ dark amber
• = fetal hypoxia that occurred 36 hours or more before the rupture of
membranes
• = fetal hemolytic disease (Rh or ABO incompatability, intrauterine infection)
• = Ominous sign of presence of Bilirubin, hemolytic disease
• Character – thick secretions with unpleasant odor = infection
• . Greenish: Meconium Stained / FETAL DISTRESS, Also if ph is less than 7.2
• greenish brown (meconium – sustained)
• = fetus had a hypoxic episode ---- relaxation of the anal sphincter ----
passage of meconium from the bowel
• = normal in breech presentation
• C If with odor: deliver within 24 hours, may indicate infection.
• d. Port Wine Color – admixture of amniotic fluid and blood - indication
abruptio placenta
Test for rupture of membranes
• Voiding by an incontinent woman and leukorrhea should be differentiated
from amniotic fluid.
• Spread a drop of the fluid on a clean slide. Dried amniotic fluid will show a
fern like crystalline pattern when viewed under the microscope (positive fern
test).
• Determine the pH of the vagina fluid. Amniotic fluid is slightly alkaline; urine
or pus is acidic.
• With sterile speculum, us sterile cotton swabs to take samples of vaginal
secretions at cervical os
• Test with pH paper (Nitrazine)
INTERPRETATION
• Yellow/Olive Yellow/Olive Green = pH5 to 6 (membrane probably intact)
• Blue green/blue gray/deep blue = pH 6.5 to 7.5 (ruptured membrane)
• Fetal lanugo or fetal squamous cell may be seen on the microscope
• Sudan III and Nile blue tests for detection of fetal fat particles and
desquamated fetal aft cells
You might also like
- Ob Part 2Document7 pagesOb Part 2gmik02No ratings yet
- Signs of increased ICP in infant with hydrocephalusDocument1 pageSigns of increased ICP in infant with hydrocephalusjamesNo ratings yet
- Obsterical Nclex QuesDocument14 pagesObsterical Nclex Quesms_m_r1082No ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Fetal Circulation and PrenatalDocument8 pagesQuiz 3 Fetal Circulation and PrenatalDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System and Childbirth ProcessesDocument64 pagesFemale Reproductive System and Childbirth ProcessesIvory SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Nur 2310 Maternal Exam Questions and AnswersDocument80 pagesNur 2310 Maternal Exam Questions and AnswersNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum ExamDocument4 pagesPost Partum ExamAhby Vitug de Luna100% (1)
- Maternal & Child NursingDocument25 pagesMaternal & Child NursingLilian FloresNo ratings yet
- Midwife 2Document65 pagesMidwife 2jancyraniJNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Postpartum Physiologic ChangesDocument10 pagesChapter 20 - Postpartum Physiologic ChangesJill Hill100% (2)
- Gynecology Test QuestionsDocument6 pagesGynecology Test Questionsdhodejun lizhaldeNo ratings yet
- 15 Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDocument14 pages15 Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Nursing QuestionsDocument11 pagesObstetrics Nursing Questionsurangel2214No ratings yet
- Care of The Woman During PregnancyDocument99 pagesCare of The Woman During PregnancyFrancr ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Maternal exam quiz: Key reproductive concepts and contraceptive methodsDocument11 pagesMaternal exam quiz: Key reproductive concepts and contraceptive methodsCherry Mae JasoNo ratings yet
- A4.Fundamentals - 25item With RationaleDocument4 pagesA4.Fundamentals - 25item With RationaleBlardy Falking You Benchod BlardyNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum PeriodDocument91 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing - Intrapartum Periodchuppepay20% (5)
- Maternal ReviewerDocument15 pagesMaternal ReviewerIvy DG100% (2)
- Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument36 pagesObstetrics and GynecologyLeiNo ratings yet
- Q&A 3ednDocument15 pagesQ&A 3ednrohitNo ratings yet
- Nclex Questions - Pediatric NursingDocument8 pagesNclex Questions - Pediatric NursingAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- Maternal NursingDocument130 pagesMaternal NursingChristine MatasNo ratings yet
- MEAL (Maternal and Child Nursing 1)Document6 pagesMEAL (Maternal and Child Nursing 1)Yucef Bahian-AbangNo ratings yet
- OB RNSG 2208 Mid-term OutlineDocument23 pagesOB RNSG 2208 Mid-term OutlineAnnissaLarnardNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test - Pedia With Answer 50 Items Without RatioDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Practice QuestionsDocument31 pagesObstetric Nursing Practice QuestionsCharles Gerard B. BeluanNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing NCLEX Questions Part 1Document9 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing NCLEX Questions Part 1Trisha ArizalaNo ratings yet
- Immaculate Conception College-Albay Daraga, Albay NCM 102Document2 pagesImmaculate Conception College-Albay Daraga, Albay NCM 102Paul Jhon Vergara100% (3)
- Normal Postpartum Changes Parameter First 24 H Clinical Heart RateDocument14 pagesNormal Postpartum Changes Parameter First 24 H Clinical Heart RatemiacajNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument8 pagesFamily PlanningAnonymous h2EnKyDbNo ratings yet
- Nursing OB Exam Q & ADocument173 pagesNursing OB Exam Q & Ajoerobinson8889323100% (8)
- NCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsDocument29 pagesNCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsAudi Kyle SaydovenNo ratings yet
- ComplicationsDocument22 pagesComplicationsLyra LoonNo ratings yet
- Jay ObDocument6 pagesJay ObJenxNo ratings yet
- OBS and GYN - HX TakingDocument3 pagesOBS and GYN - HX Takingboro1522No ratings yet
- MATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMATERNAL AND CHILD HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Comp ReDocument15 pagesComp ReROBERT C. REÑA, BSN, RN, MAN (ue)No ratings yet
- Fetal Positioning Leopold's Maneuver PMI LocationDocument3 pagesFetal Positioning Leopold's Maneuver PMI LocationDani Michaela100% (1)
- NCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Document113 pagesNCM 102 OB Abnormal 2Maria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IINo ratings yet
- Finals Part 1 (G&D)Document7 pagesFinals Part 1 (G&D)RandyNo ratings yet
- Power Git EndoDocument170 pagesPower Git Endoapi-3735995100% (1)
- Question 15Document8 pagesQuestion 15eloisa rabanes100% (1)
- OB Exam 1 ComboDocument82 pagesOB Exam 1 ComboHope RobersonNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for Postpartum Nursing QuestionsDocument6 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Postpartum Nursing QuestionsCharles Malcolm Dalugdug100% (1)
- Assessing Labor Stages and Postpartum ComplicationsDocument3 pagesAssessing Labor Stages and Postpartum ComplicationsAhwen 'ahwenism'100% (2)
- Pediatric NursingDocument3 pagesPediatric Nursingjegel23100% (1)
- MCN 1Document5 pagesMCN 1Aijem RyanNo ratings yet
- Assessing male infertility and significance of sperm motilityDocument94 pagesAssessing male infertility and significance of sperm motilityAnn Michelle Tarrobago100% (1)
- Q&ADocument45 pagesQ&AElba De Asis Manacob0% (1)
- Post-Partum Review Questions - Handout 2 With Answers /rationalesDocument9 pagesPost-Partum Review Questions - Handout 2 With Answers /rationalesnkuligowski100% (2)
- Peak age range for ALL and surgical risk factorsDocument12 pagesPeak age range for ALL and surgical risk factorsShantaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test MCNDocument36 pagesPractice Test MCNIriel NadongaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Test QuestionsDocument15 pagesAntepartum Test QuestionsMaria Estrella ImperioNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Amniocentesis Procedure and Sample AnalysisDocument10 pagesAmniocentesis Procedure and Sample AnalysisDane Orilla100% (1)
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument13 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineJannen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Skills Lab Results 1Document85 pagesNCM 107 Skills Lab Results 1Joseph DusichNo ratings yet
- PROMDocument3 pagesPROMعمر احمد شاكرNo ratings yet
- Abusing DrugsDocument1 pageAbusing DrugsgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Ca2 Mood Disorder Q&ADocument7 pagesCa2 Mood Disorder Q&AgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Normal ValuesDocument2 pagesNormal Valuesgeejei100% (1)
- Normal ValuesDocument2 pagesNormal Valuesgeejei100% (1)
- Filipino ScientistsDocument5 pagesFilipino ScientistsgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Complex Regional Pain SyndromeDocument10 pagesComplex Regional Pain SyndromegeejeiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Document21 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Richard Ines Valino100% (24)
- Map of AsiaDocument1 pageMap of AsiageejeiNo ratings yet
- Philippine Nursing LawsDocument2 pagesPhilippine Nursing Lawszelai0% (1)
- Intro COPDDocument2 pagesIntro COPDGemery Jade ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Last 24 HoursDocument6 pagesRizal's Last 24 Hoursgeejei100% (1)
- Nursing Care for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNursing Care for Impaired Gas ExchangegeejeiNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Human Growth and Development TheoriesDocument5 pagesHuman Growth and Development TheoriesgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Drug Tab YheDocument6 pagesDrug Tab YhegeejeiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Cancer Pathophysio WinjDocument4 pagesThyroid Cancer Pathophysio WinjgeejeiNo ratings yet
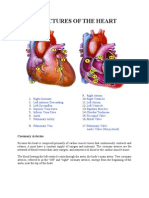
- Structures of The HeartDocument6 pagesStructures of The HeartgeejeiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Managemen T ServiceDocument12 pagesDisaster Managemen T ServicegeejeiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of StrokegeejeiNo ratings yet
- THE Digesti VE SystemDocument35 pagesTHE Digesti VE SystemgeejeiNo ratings yet
- PRAGYAN Vol 07 Issue 01Document92 pagesPRAGYAN Vol 07 Issue 01PRAGYAN,Tinsukia CollegeNo ratings yet
- Temperature Regulation Disorders: Hypothermia, Vasoconstriction, and Cold AcclimatizationDocument8 pagesTemperature Regulation Disorders: Hypothermia, Vasoconstriction, and Cold AcclimatizationDanielle Caryl SantosNo ratings yet
- Colorphobia in New YorkDocument3 pagesColorphobia in New Yorkapi-412124766No ratings yet
- Biological Control 178 (2023) 105145 M. Yousefvand Et AlDocument5 pagesBiological Control 178 (2023) 105145 M. Yousefvand Et AlGenaina CristofoliNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment FormDocument14 pagesPhysical Assessment FormHedda Melriz DelimaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Jurnal PaliatifDocument11 pagesTugas Jurnal PaliatifSiti Wahyuningsih100% (1)
- ConventionalDocument9 pagesConventionaltabbsum hussainNo ratings yet
- Boaz Gobera (NsambyaHospitalReport2021)Document62 pagesBoaz Gobera (NsambyaHospitalReport2021)GOBERA BOAZNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Tot - NR 6classid S.F.ADocument74 pagesPharmacology - Tot - NR 6classid S.F.AcorsairmdNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Jaundiced Cat - WSAVA 2015 Congress - VINDocument6 pagesApproach To The Jaundiced Cat - WSAVA 2015 Congress - VINdmantsioNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Care in Respiratory Disease: DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, K-GHDocument94 pagesNutritional Care in Respiratory Disease: DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, K-GHDesywinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Quarter 4 WK 1 Digestive ProcessDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Quarter 4 WK 1 Digestive ProcessmalouNo ratings yet
- Hand When You Need Them MostDocument9 pagesHand When You Need Them MostJim SchotterNo ratings yet
- JKNKLKLDocument10 pagesJKNKLKLCyntia AndrinaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests for Hemostasis EvaluationDocument5 pagesLaboratory Tests for Hemostasis EvaluationCMLNo ratings yet
- Reducing Waste in ICUDocument10 pagesReducing Waste in ICUzorbini69No ratings yet
- 2-Downer Cow and HypoMgDocument13 pages2-Downer Cow and HypoMgY.rajuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Introductory Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition by KlossnerJulieJacobsrkozw100% (84)
- ICMIDocument4 pagesICMIKim MingyuNo ratings yet
- Article Dietschi VeenersDocument18 pagesArticle Dietschi VeenersRoberto PucNo ratings yet
- CucumberDocument25 pagesCucumberDa Nie LNo ratings yet
- Influenza: CausesDocument2 pagesInfluenza: CausesMaui ShihtzuNo ratings yet
- Chapter II-Vocabulary ExerciseDocument3 pagesChapter II-Vocabulary ExerciseJessica KarinaNo ratings yet
- Upper FINAL 2Document5 pagesUpper FINAL 2Анна КоноваловаNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Dummy ReportDocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Dummy ReportVirat DaineNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument6 pagesPityriasis Versicolorh8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- AmavataDocument14 pagesAmavataSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by KisnerDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by Kisnera33085258962% (13)
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument14 pagesAbdominal ExaminationValeria Guerra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Guide To Environmental Microbiological MonitoringDocument29 pagesGuide To Environmental Microbiological MonitoringzyrtylNo ratings yet