Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeed
Uploaded by
ianecunarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeed
Uploaded by
ianecunarCopyright:
Available Formats
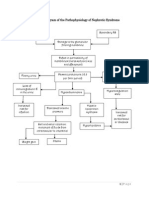
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
ETIOLOGIES: SECONDARY:
PRIMARY: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Hepatitis
Infection: Pyelonephritis Diabetes Mellitus Malaria
Glomerulopnephritis Allergic Responses Cyanotic Heart Disease
Sickle Cell Anemia Tuberculosis
Anaphylactoid Purpura Infected Vedntriculojugular shunts
Renal Vein Throimbosis Stings/Venoms
Drug Toxicity: TRIMETHADIONE
IgG Level Falls Endothelial lining and basement membranes damaged (Renal Glomeruli Damage) Steroids
Altered Immunity Increase permeability to [plasma CHON / leak of Albumin
HYPERLIPEDEMIA
CHON excreted in urine
Increase serum cholesterol and
Risk for infection related to depression of
immunologic defenses triglyceride level PROTEINURIA Foamy Urine
Stimulates Production of lipoprotein in liver (attempt Reduced serum albumin level
Risk for decreased cardiac output related to fluid
deficit to make for lost protein)
HYPOALBUMINEMIA DIET: high Protein and Low Sodium
Decrease fluid gradient pressure changes /
Monitor Intake and Decrease Urine Output HYPOVOLEMIA Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements
decrease colloidal osmotic pressure in capillary related to dietary restrictions as evidenced by a
Output
decreased in food and fluid intake
Production of Antidiuretic Hormone Decrease renal blood flow Decrease GFR Increase hydrostatic pressure
Diuretics
Activates Renin-Angiotensin Fluid level accumulates in interstitial spaces and body cavities Albumin IV Transfusion
System Hypertension Weight Gain
EDEMA Abdomen Ascites
Antihypertensive Drugs
Adrenal Secretion of Aldosterone Eyes Periorbital Edema
Monitor BP Weigh Daily and dietary
Scrotum
Impaired skin integrity restrictions
related to the Increase RBC and Platelet
Vasoconstriction presence of edema as Excess fluid volume related to compromised renal
evidenced by perfusion as evidenced by decreased urine output
Lack of knowledge of the mother Clots Form and edema
reddened or taut skin
Increase absorption of Sodium and
about the disease entity or actual breaks in the
water in distal tubules skin Blood flow slows Acute pain related to presence LEGENDS:
of edema as evidence by Classical Signs
Knowledge deficit regarding condition, prognosis, complaints of pain, and wincing Physiology changes
treatment, self-care, and discharge needs related to Clotting Problem Arise on movement Clinical Manifestations
lack of exposure
Treatment or Nursing
Decrease blood flow to kidneys Interventions
Nursing Diagnoses
End Stage Renal Failure Dialysis
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of GooDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of GooTania Noviza100% (1)
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyDocument1 pageNephrotic Syndrome PathophysiologyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CHFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CHFLance MarquezNo ratings yet
- Bladder CancerDocument1 pageBladder CancerCarmina AguilarNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument4 pagesConcept MapChelsyann FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Nephrotic Syndromejoyshe111No ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyDimple BlancoNo ratings yet
- GERD Pathophysiology Cleveland ClinicDocument17 pagesGERD Pathophysiology Cleveland ClinicMavisNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverDocument3 pagesPathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverCyrus De AsisNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument27 pagesHemorrhagic StrokeMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure PathoDocument4 pagesAcute Renal Failure PathoGlenn Asuncion Pagaduan100% (1)
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument34 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiamtyboyNo ratings yet
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Case StudyDocument87 pagesParoxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Case Studyrachael100% (4)
- Vii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmDocument2 pagesVii. Pathophysiology A. AlgorithmJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 pagesConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- POTTs Disease PathoDocument3 pagesPOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Intracerebral HemorrageDocument13 pagesIntracerebral HemorrageChristian JuarezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathoDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pathodrewcel100% (1)
- Atropine: Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDocument6 pagesAtropine: Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyKevin RosalesNo ratings yet
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Document3 pagesCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- Burn Ctu 312 - 2Document1 pageBurn Ctu 312 - 2Shaira Ann CalambaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument52 pagesPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology ErDocument3 pagesPathophysiology ErAlexa A. AldayNo ratings yet
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocument5 pagesPahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaNo ratings yet
- DB13 - Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument2 pagesDB13 - Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisi_vhie03No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)Document3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Hyperglycemia (304 MG/DL, 13.2 MG/DL)John Henry ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Bacterial MeningitisNadira Farah PrayogoNo ratings yet
- PurpuraDocument7 pagesPurpuraMarie Joe AbainzaNo ratings yet
- NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVEr DISEASE (NAFLD) - NASHDocument4 pagesNON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVEr DISEASE (NAFLD) - NASHJason FooNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument60 pagesGroup 4 - Hemorrhagic StrokeKitz T AnasarioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure PDFDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure PDFDewa Made Rendy SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapXtine CajiNo ratings yet
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalance 1Document3 pagesElectrolyte Imbalance 1Marius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument20 pagesAcute PancreatitisMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDocument13 pagesHemorrhagic Stroke: Darpen Subhashbhai Mori Group 2, MD 3BDarpen MoriNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure COncept MapDocument2 pagesHeart Failure COncept MapJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of Portal HYPERTENSION PDFCamilo VidalNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DiarrheaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of DiarrheaFathur RahmatNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument9 pagesUlcerative Colitiskint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Introduction CASE STUDYDocument3 pagesIntroduction CASE STUDYDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Grand Case CHF Final Na Final Na Final Na TrueDocument40 pagesGrand Case CHF Final Na Final Na Final Na Truelyndzy100% (2)
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 pagesPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesDiabetes PathophysiologyShelly_Ann_Del_9959No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Hdu P&PDocument54 pagesHdu P&PianecunarNo ratings yet
- DiovanDocument2 pagesDiovanianecunar100% (1)
- Brand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)Document2 pagesBrand Name: Diflucan Generic Name: Fluconazole Drug Classification: Antibiotics (Antifungal)ianecunar50% (2)
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Critical Care NursingDocument10 pagesCritical Care Nursingianecunar100% (10)
- Standards Guideline For Establishing, Equipping and Operating Renal Dialysis CentresDocument78 pagesStandards Guideline For Establishing, Equipping and Operating Renal Dialysis Centresmohamed radwanNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is IndicatedDocument4 pagesBrand Name: Dilantin Generic Name: Phenytoin Indication: Dilantin Is Indicatedianecunar100% (1)
- Brand Name: Diamicron Generic Name: Gliclazide Indication: For Non-Insulin DependentDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Diamicron Generic Name: Gliclazide Indication: For Non-Insulin DependentianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tranexamic Acid (Cyclokapron)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Tranexamic Acid (Cyclokapron)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cozaar Generic Name: Losartan Potassium Indications: Hypetension, NephepaticallyDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cozaar Generic Name: Losartan Potassium Indications: Hypetension, Nephepaticallyianecunar100% (1)
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Crest orDocument3 pagesCrest orianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dalacin C Generic Name: Clindamycin HCL Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Dalacin C Generic Name: Clindamycin HCL Drug Classificationianecunar100% (1)
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- CelebrexDocument2 pagesCelebrexianecunarNo ratings yet
- Cox IdDocument2 pagesCox IdianecunarNo ratings yet
- Co DiovanDocument2 pagesCo DiovanianecunarNo ratings yet
- ClexaneDocument2 pagesClexaneianecunar100% (2)
- CalpolDocument2 pagesCalpolianecunarNo ratings yet
- Com Bi VentDocument2 pagesCom Bi VentianecunarNo ratings yet
- CiprobayDocument2 pagesCiprobayianecunar100% (1)
- Cat A PresDocument2 pagesCat A PresianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chloromycetin Generic Name: Chloramphenicol Indication: External Ear CanalianecunarNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia IschemiaDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Carnicor Generic Name: L-Carnitine Indications: Chronic Myocardia Ischemiaianecunar100% (1)
- Brand Name: Blopress Generic Name: Candesartan Indications: Management of HypertensionDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Blopress Generic Name: Candesartan Indications: Management of Hypertensionianecunar0% (2)
- Brand Name: Bisacodyl Generic Name: Dulcolax Indication: Constipation Drug ClassificationDocument1 pageBrand Name: Bisacodyl Generic Name: Dulcolax Indication: Constipation Drug ClassificationianecunarNo ratings yet
- BricanylDocument4 pagesBricanylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Calcibloc ODDocument2 pagesCalcibloc ODianecunarNo ratings yet
- BiogesicDocument2 pagesBiogesicianecunarNo ratings yet
- Modified Early Obstetric Warning Score MEOWS MID33 AO13 v4.2Document9 pagesModified Early Obstetric Warning Score MEOWS MID33 AO13 v4.2indirinoor5No ratings yet
- Associate Director of Pharmacovigilance in Newtown Square PA Resume Michael BlohDocument6 pagesAssociate Director of Pharmacovigilance in Newtown Square PA Resume Michael BlohMichaelBlohNo ratings yet
- BleedingDocument14 pagesBleedingRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- CHECKLIST Trach Care and Suctioning.Document6 pagesCHECKLIST Trach Care and Suctioning.Mickey MoraNo ratings yet
- Genu ValgumDocument2 pagesGenu ValgumPurohit_R0% (1)
- Laser Retinopexy PDFDocument4 pagesLaser Retinopexy PDFveerroxxNo ratings yet
- 05 XE-Series Flagging Guide 12-2008 Complete-20110708-114552Document45 pages05 XE-Series Flagging Guide 12-2008 Complete-20110708-114552kajal4evaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve InjuryDocument85 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjurySyed Abudaheer100% (3)
- 2.segaert FINALDocument42 pages2.segaert FINALBagoes LoekmanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Localization and History in NeurologyDocument41 pagesClinical Localization and History in NeurologyRhomizal MazaliNo ratings yet
- Nicu ReflectionDocument2 pagesNicu Reflectionapi-422763411100% (1)
- Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine 6th EdDocument9 pagesFitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine 6th Ednadia salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Sensation MethodDocument5 pagesSensation MethodDr. Nancy MalikNo ratings yet
- Dha 022019 PDFDocument20 pagesDha 022019 PDFDrNishchitha K100% (2)
- Interview PaperDocument7 pagesInterview Paperapi-253699105No ratings yet
- Molar Uprighting Simple TechniqueDocument4 pagesMolar Uprighting Simple TechniqueMariem DelmasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Board - Guidelines - Guidelines On Compounding of Medicines PDFDocument14 pagesPharmacy Board - Guidelines - Guidelines On Compounding of Medicines PDFMaria KandelaNo ratings yet
- FenofibrateDocument7 pagesFenofibrateVikas Karande100% (1)
- EndophthalmitisDocument36 pagesEndophthalmitisHieLdaJanuariaNo ratings yet
- Total Standards: - Total Sub-Standards: - Total ESR StandardsDocument8 pagesTotal Standards: - Total Sub-Standards: - Total ESR StandardsHCX dghhqNo ratings yet
- Espertise: Making Better ImpressionsDocument13 pagesEspertise: Making Better ImpressionsionutmbNo ratings yet
- Robins AromatherapyDocument13 pagesRobins AromatherapyAnaNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument17 pagesCase StudiesDamian Maguire100% (4)
- A&E BlepharitisDocument3 pagesA&E BlepharitisNadine Bär-SchmitzNo ratings yet
- Ug NotesDocument538 pagesUg NotesSteven IStudy SmithNo ratings yet
- PBL Modul 1 Batuk RespiDocument66 pagesPBL Modul 1 Batuk RespiAndiMuhYasserNo ratings yet
- FullDocument59 pagesFullJyotiNo ratings yet
- The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB) Normative Value PDFDocument9 pagesThe Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB) Normative Value PDFIcaroNo ratings yet
- Identification and Treatment of Retinopathy of Prematurity Update 2017Document9 pagesIdentification and Treatment of Retinopathy of Prematurity Update 2017G VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Peformance Checklist Sensory SystemDocument4 pagesPeformance Checklist Sensory System03152788No ratings yet