Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F αA T β (F F: Moving Averages Weighted Moving Average
Uploaded by
Ppham0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageOriginal Title
11
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageF αA T β (F F: Moving Averages Weighted Moving Average
Uploaded by
PphamCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
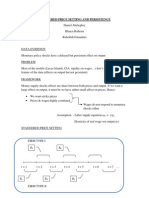
1/Operations management (OM) is:
• The design, operation, and improvement of the systems that create and deliver the firm’s
primary products and services
• These systems are called Production Systems
2/Order Qualifiers I MUST have them in order to compete
Order Winners IF I have them, I will probably win the competition
3/Job shop or “Jumbled Flow” Copy center, Machining shop, Car repair facility
Batch shop or “Batch Process” Similar to Job Shop BUT making a batch of the same product before
switching to some other product Cooking, Dyes and pigments, Shampoo
Assembly Line Automobiles, Electronics
Continuous Flow Oil refinery
4/ A production system transforms resources into outputs, adding value along the way.
In general, the main resource processed by the system is called input, and the final product is called
output
5/ Total productivity
Output / Total resources
Partial measures of productivity Output or Output or Output or Output
Labor Capital Materials Energy
Multifactor productivityOutput or Output
Labor + Capital Materials + Energy
The Naïve approach f= a(t-1)
i=t−1
i=t−1
Moving Averages Weighted Moving Average ∑ wi F i
∑ Fi
Ft = i=t−n
Ft = i=t−n i=t−1
n ∑ wi
i=t−n
Considers the new forecast is a combination of part of the last actual demand and the last forecast
Ft =αA( t−1)+(1−α ) F( t−1) T t =β( F t −F t−1 )+(1−β)T t−1
Factor Rating: Assign values to possible locations for the new facility in terms of several important factors, add up those values
for each location and pick the location with highest score. Takes distance as only one of several important factorsThe “Centre of
Gravity” or “Centroid” method: Locates the new facility at the center of gravity of the combined weights of the existing.
facilities. Assumes the minimization of the sum of squared distances between the new and other facilities. Normally uses
Euclidean (straight-line) distances
You might also like
- BU283 Midterm1 Formula SheetDocument1 pageBU283 Midterm1 Formula SheetClarissa MichaelsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Analog Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument12 pagesUnit 1 - Analog Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inpeacepalharshNo ratings yet
- Homework IIxDocument7 pagesHomework IIxblancaestherbsNo ratings yet
- Formula in Engineering EconimicsDocument2 pagesFormula in Engineering EconimicsWYNDYLL ARTUZNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomicsDocument10 pagesEngineering EconomicsrenegadeNo ratings yet
- Appendix Rev 3 13.6.19Document7 pagesAppendix Rev 3 13.6.19Ramaneish SivaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pemeliharaan - Reliability Concept and CharacterizationDocument15 pagesSistem Pemeliharaan - Reliability Concept and CharacterizationADINDA SUCHIEYATI SAHARANo ratings yet
- TimeSeriesModels - 2022Document30 pagesTimeSeriesModels - 2022Miguel Sacristán de FrutosNo ratings yet
- Productivity Growth in Philippine Agriculture: A Literature ReviewDocument38 pagesProductivity Growth in Philippine Agriculture: A Literature Reviewapi-3748765100% (1)
- Formula Sheet Corporate Finance (COF) : Stockholm Business SchoolDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet Corporate Finance (COF) : Stockholm Business SchoolLinus AhlgrenNo ratings yet
- FIN2074 FormulaDocument15 pagesFIN2074 FormulaBrendan YapNo ratings yet
- Not Sure Macro EulerDocument16 pagesNot Sure Macro EulerLily De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Formulas: F - Future Value P - Present/Principal ValueDocument2 pagesFormulas: F - Future Value P - Present/Principal ValueJimuel Ace SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula Sheetnick07052004No ratings yet
- Chap2 - Security Market IndicesDocument5 pagesChap2 - Security Market Indiceseya KhamassiNo ratings yet
- 1 Clarida-Gali-Gertler Model: T T t+1 TDocument16 pages1 Clarida-Gali-Gertler Model: T T t+1 TMartin ZapataNo ratings yet
- CH Gen Math 7Document18 pagesCH Gen Math 7Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- 201lecture42010web PDFDocument10 pages201lecture42010web PDFJayVNo ratings yet
- 1 The ModelDocument10 pages1 The ModelEdinho BordinNo ratings yet
- Helpful Formulas For Finance 1Document2 pagesHelpful Formulas For Finance 1Falguni ShomeNo ratings yet
- EE Formulas NCITDocument8 pagesEE Formulas NCITYe FengNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Nonparametric Estimation講義 - 學生Document12 pagesCh3 Nonparametric Estimation講義 - 學生Chih-ChunTsaiNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA)Document12 pagesMultivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA)DianaNo ratings yet
- A Monte Carlo Comparison Between The Free Cash Flow and Discounted Cash Flow ApproachesDocument17 pagesA Monte Carlo Comparison Between The Free Cash Flow and Discounted Cash Flow ApproachesShito RyuNo ratings yet
- Analogous System NotesDocument6 pagesAnalogous System NotesDr. C. V.No ratings yet
- Analytic Framework For Implying Yield Curves From Market Data OpenGammaDocument12 pagesAnalytic Framework For Implying Yield Curves From Market Data OpenGammapinakichemNo ratings yet
- Firms, Production Possibility Sets, and Pro T Maximization: Econ 2100, Fall 2019Document21 pagesFirms, Production Possibility Sets, and Pro T Maximization: Econ 2100, Fall 2019saibuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics FormulasDocument2 pagesEngineering Economics FormulasBorja, Alexandra C.No ratings yet
- Math 2280 - Assignment 13: Dylan Zwick Spring 2014Document23 pagesMath 2280 - Assignment 13: Dylan Zwick Spring 2014Akash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income and Credit Risk: Prof. Michael RockingerDocument93 pagesFixed Income and Credit Risk: Prof. Michael RockingergregNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet-2nd QuizDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet-2nd QuizEge MelihNo ratings yet
- Formulas (Weeks 1 To 6)Document5 pagesFormulas (Weeks 1 To 6)Stenley RoyceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document27 pagesLecture 2uckyourabbitNo ratings yet
- Methods Lectures: Financial Econometrics Linear Factor Models and Event StudiesDocument46 pagesMethods Lectures: Financial Econometrics Linear Factor Models and Event StudieshoneyschuNo ratings yet
- I. How To Compute Overall Percentage Changes: Compounded M Times Per YearDocument8 pagesI. How To Compute Overall Percentage Changes: Compounded M Times Per YearTrương Ngọc Trà MyNo ratings yet
- RSM332 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRSM332 Cheat Sheets_786886338No ratings yet
- 2 Slides TF ReviewDocument203 pages2 Slides TF ReviewZoe RossiNo ratings yet
- Green Electric Energy: Engineering EconomicsDocument45 pagesGreen Electric Energy: Engineering EconomicsdishantpNo ratings yet
- Applictions of FT by RajuDocument3 pagesApplictions of FT by Rajuputta rajesh007No ratings yet
- The Fourier TransformDocument20 pagesThe Fourier TransformkathleenNo ratings yet
- Engineering Analysis: Fourier Transform " FT "Document49 pagesEngineering Analysis: Fourier Transform " FT "For SignUpsNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money FormulasDocument1 pageTime Value of Money FormulasAmit Shankar Choudhary100% (1)
- Fysikk Tabell UK 2015-2016Document2 pagesFysikk Tabell UK 2015-2016Maga KhadisovNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICSDocument12 pagesECONOMICSJenielle SisonNo ratings yet
- OpeneconomyDocument107 pagesOpeneconomyshaibal_iujNo ratings yet
- MScFE 620 DTSP-Compiled-Notes-M5Document13 pagesMScFE 620 DTSP-Compiled-Notes-M5SahahNo ratings yet
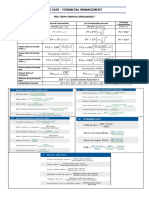
- Financial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial ManagementEilen Joyce Bisnar100% (1)
- Fourier and Laplace Transforms and Their Applications: 1 From Fourier Series To Fourier TransformDocument14 pagesFourier and Laplace Transforms and Their Applications: 1 From Fourier Series To Fourier Transformmamush001No ratings yet
- EE 261 The Fourier Transform and Its Applications Fall 2006 Midterm Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesEE 261 The Fourier Transform and Its Applications Fall 2006 Midterm Exam SolutionsManas ChetryNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Formula SheetDocument1 pageTest 2 Formula Sheetgabriella portelliNo ratings yet
- Correction TD Math INGDocument22 pagesCorrection TD Math INGalicherifbouzaidaNo ratings yet
- Economics 1Document12 pagesEconomics 1jhozabethcarbonelNo ratings yet
- FN3105 Formula Spreadsheet Mid TermDocument1 pageFN3105 Formula Spreadsheet Mid TermGD GamingNo ratings yet
- MATH 01 FormulaDocument3 pagesMATH 01 FormulaJae Bert UbisoftNo ratings yet
- Forward Currency ContractsDocument26 pagesForward Currency ContractsdiegoNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Od 330390050476522100Document3 pagesOd 330390050476522100rjvNo ratings yet
- Atos SyntelDocument2 pagesAtos SyntelSharad MoreNo ratings yet
- Advantages of CloudDocument3 pagesAdvantages of CloudAmanNo ratings yet
- Day 3Document34 pagesDay 3Adrianne Aldrin AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Zomato AnalysisDocument7 pagesZomato AnalysisEton Pinto0% (1)
- CASE STUDY OF RMC PLANT Report 1Document3 pagesCASE STUDY OF RMC PLANT Report 1Radha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Fake Product Review Monitoring System and Real Review Generation by Using Data Mining MechanismDocument10 pagesImplementation of Fake Product Review Monitoring System and Real Review Generation by Using Data Mining MechanismAjayi FelixNo ratings yet
- 202221040Document5 pages202221040R A.No ratings yet
- Price List Grand I10 Nios DT 01.05.2022Document1 pagePrice List Grand I10 Nios DT 01.05.2022VijayNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1 Answer Sheet Tmelect1Document6 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1 Answer Sheet Tmelect1John Ariel Labnao Gelbolingo67% (3)
- Limits, Alternatives, and Choices: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument30 pagesLimits, Alternatives, and Choices: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinWafaFarrukhNo ratings yet
- Governance of Cybersecurity: 2015 Report: How Boards & Senior Executives Are Managing Cyber RisksDocument45 pagesGovernance of Cybersecurity: 2015 Report: How Boards & Senior Executives Are Managing Cyber Risksleo5880No ratings yet
- WWW Citehr Com 5544 I Need Some Kpi HR Dept Compensation HTMDocument19 pagesWWW Citehr Com 5544 I Need Some Kpi HR Dept Compensation HTMjonniebravoNo ratings yet
- Planning 03 Module 1Document49 pagesPlanning 03 Module 1Gwynn Hyacinth TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Onopoly: Presented By: Submitted ToDocument21 pagesOnopoly: Presented By: Submitted ToSimran VermaNo ratings yet
- BUS 206 - Ethical TestDocument5 pagesBUS 206 - Ethical TestAngela PerrymanNo ratings yet
- Form16 Fiserv 2018-19Document8 pagesForm16 Fiserv 2018-19SiddharthNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Ford Motor CompanyDocument5 pagesA Case Study Ford Motor Companysaleem razaNo ratings yet
- University of Pune: Revised With Effect From June 2013Document162 pagesUniversity of Pune: Revised With Effect From June 2013Deepak PaulNo ratings yet
- 21 - Procure 2 Pay Cycle in Oracle Apps R12Document22 pages21 - Procure 2 Pay Cycle in Oracle Apps R12Bala SubramanyamNo ratings yet
- نسخة امتحان ال operation PDFDocument3 pagesنسخة امتحان ال operation PDFAhmed HadadNo ratings yet
- Sbaa1504 - Business Policy and Strategy - Unit Ii - PPT (3) 2Document55 pagesSbaa1504 - Business Policy and Strategy - Unit Ii - PPT (3) 2abcdNo ratings yet
- JomPAY GuideDocument6 pagesJomPAY GuideSai Arein KiruvanantharNo ratings yet
- MGT602 Final Subjective by USMAN ATTARIDocument12 pagesMGT602 Final Subjective by USMAN ATTARImaryamNo ratings yet
- Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Strategy Adaptation For The Global Business of Vodafone Telecommunication CompanyDocument4 pagesMarket Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Strategy Adaptation For The Global Business of Vodafone Telecommunication CompanymullopNo ratings yet
- Business Development Business Development: Punjabi University Patiala School of Management StudiesDocument14 pagesBusiness Development Business Development: Punjabi University Patiala School of Management StudiesPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Negotiable InstrumentDocument21 pagesThe Negotiable InstrumentCaleb GetubigNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Principles of Corporate Finance 12th Edition by BrealeyDocument3 pagesSolution Manual For Principles of Corporate Finance 12th Edition by BrealeyNgân HàNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Management - Intro Levels Notes PDFDocument6 pagesSpare Parts Management - Intro Levels Notes PDFEslam MansourNo ratings yet
- SSS CCL Aka PDFDocument18 pagesSSS CCL Aka PDFVikram VickyNo ratings yet