Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Virtualization
Uploaded by
Treenu JamesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Virtualization
Uploaded by
Treenu JamesCopyright:
Available Formats
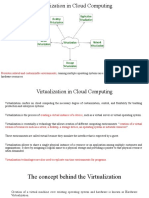
Virtualization, in computing, is the creation of a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as a hardware platform, operating system,
a storage device or network resources.[1] Virtualization can be viewed as part of an overall trend in enterprise IT that includes autonomic computing, a scenario in which the IT environment will be able to manage itself based on perceived activity, and utility computing, in which computer processing power is seen as a utility that clients can pay for only as needed. The usual goal of virtualization is to centralize administrative tasks while improving scalability and work loads.[1]
TYPES OF VIRTUALIZATION:
y y y y y y y
1.1 Hardware 1.2 Desktop 1.3 Software 1.4 Memory 1.5 Storage 1.6 Data 1.7 Network
Hardware
Hardware virtualization or platform virtualization refers to the creation of a virtual machine that acts like a real computer with an operating system. Software executed on these virtual machines is separated from the underlying hardware resources. For example, a computer that is running Microsoft Windows may host a virtual machine that looks like a computer with Ubuntu Linux operating system. Subsequently, Ubuntu-based software can be run on that virtual machine
Desktop
Desktop virtualization is the concept of separating the logical desktop from the physical machine. Software
y y
Operating system-level virtualization, hosting of multiple virtualized environments within a single OS instance Application virtualization and Workspace virtualization, the hosting of individual applications in an environment separated from the underlying OS. Application virtualization is closely associated with the concept of portable applications.
Memory
y
Memory virtualization, aggregating RAM resources from networked systems into a single memory pool
Virtual memory, giving an application program the impression that it has contiguous working memory, isolating it from the underlying physical memory implementation
Storage
y y
Storage virtualization, the process of completely abstracting logical storage from physical storage Distributed file system
Data
y y
Data virtualization, the presentation of data as an abstract layer, independent of underlying database systems, structures and storage Database virtualization, the decoupling of the database layer, which lies between the storage and application layers within the application stack
Network
y
Network virtualization, creation of a virtualized network addressing space within or across network subnets
http://www.kernelthread.com/publications/virtualization/ chk this website too
You might also like
- Hide 1 Types of Virtualization 1.1 Hardware 1.2 Software 1.3 Memory 1.4 Storage 1.5 Data 1.6 Network 2 See Also 3 ReferencesDocument6 pagesHide 1 Types of Virtualization 1.1 Hardware 1.2 Software 1.3 Memory 1.4 Storage 1.5 Data 1.6 Network 2 See Also 3 ReferencesSazid AnsariNo ratings yet
- Types of Virtualization: Autonomic ComputingDocument6 pagesTypes of Virtualization: Autonomic ComputingjattniNo ratings yet
- My Seminar On VirtulizationDocument14 pagesMy Seminar On VirtulizationSulekha PaliyaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes Unit 2Document15 pagesCloud Computing Notes Unit 2kavitha sreeNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Assignment-1 (Virtualization)Document18 pagesCloud Computing Assignment-1 (Virtualization)DarshpreetKaurNo ratings yet
- Tola CSC 103 AssignmentDocument13 pagesTola CSC 103 Assignmentadeloyeheritage1No ratings yet
- Unit/Topic: 3-Compute, Storage, Network Virtualization TechniquesDocument10 pagesUnit/Topic: 3-Compute, Storage, Network Virtualization TechniquesRaghul RajNo ratings yet
- How To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationFrom EverandHow To Do Virtualization: Your Step-By-Step Guide To VirtualizationNo ratings yet
- VirtualisationDocument7 pagesVirtualisationjohn bourkeNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument9 pagesVirtualizationAkmal AzaNo ratings yet
- Concept of VirtualizationDocument25 pagesConcept of Virtualizationnitin goswami100% (1)
- Types of VirtualizationDocument4 pagesTypes of VirtualizationrajenchatNo ratings yet
- What Is Virtualization?Document22 pagesWhat Is Virtualization?muskan guptaNo ratings yet
- Virtulization ForceDocument2 pagesVirtulization Forcekamalmse066072No ratings yet
- Provides Isolated and Customizable EnvironmentsDocument41 pagesProvides Isolated and Customizable Environmentsgirish reddyNo ratings yet
- Virtualization in Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesVirtualization in Cloud ComputingVaibhav MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument4 pagesInformation TechnologyDilpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Hyper VDocument29 pagesHyper VmanjeetNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument1 pageVirtualizationMj SubukiNo ratings yet
- What Is A Virtual Machine?Document7 pagesWhat Is A Virtual Machine?Mike MarquezNo ratings yet
- Unit - I - INTRODUCTION TO VIRTUALIZATION AND TECHNOLOGIESDocument69 pagesUnit - I - INTRODUCTION TO VIRTUALIZATION AND TECHNOLOGIESaishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Unit III CCDocument69 pagesUnit III CCnocej81355No ratings yet
- 22 12 2022 506814215Document113 pages22 12 2022 506814215abizer safdariNo ratings yet
- Memory Management UnitDocument5 pagesMemory Management UnitRishabh MalikNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachinesDocument6 pagesVirtual MachinesKatherine Usquisa TorrenaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To VirtualizationDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To VirtualizationSacha HubbardNo ratings yet
- L11 Virtualization 17062021 030456pmDocument9 pagesL11 Virtualization 17062021 030456pmSehar AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document10 pagesUnit 2Rajamanikkam RajamanikkamNo ratings yet
- Virtualization SurveyDocument5 pagesVirtualization SurveypalashahujaNo ratings yet
- VIRTUALIZATION-Basics & Applications: AbstractDocument10 pagesVIRTUALIZATION-Basics & Applications: AbstractSwathi Bhat MNo ratings yet
- Virtualization Group PresentationDocument10 pagesVirtualization Group PresentationShaban MahekulaNo ratings yet
- Virtualization TypesDocument6 pagesVirtualization TypesNaggula ChinnaNo ratings yet
- 1 Virtual IzationDocument35 pages1 Virtual IzationAyan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- CCL Merged PDFDocument111 pagesCCL Merged PDFRishit RavichandranNo ratings yet
- What Is VirtualizationDocument7 pagesWhat Is Virtualization88awscloudNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesCloud ComputingAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Virtualization & Scheduling in Real Time OS: A SurveyDocument6 pagesVirtualization & Scheduling in Real Time OS: A SurveyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Osu 4Document7 pagesOsu 4bhanuprasadvishwakarNo ratings yet
- Virtual MachinesDocument46 pagesVirtual MachinesNitesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Final Unit III CC 2022Document71 pagesFinal Unit III CC 2022sairabanu pansareNo ratings yet
- Desktop VirtualizationDocument4 pagesDesktop VirtualizationNIRMALYA_NJRCSNo ratings yet
- Grid and Cloud Computing Important Questions Unit 3 Part ADocument5 pagesGrid and Cloud Computing Important Questions Unit 3 Part ASridevi SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Ver Vs HypDocument17 pagesVer Vs HypRushikesh SontakkeNo ratings yet
- VirtulisationDocument19 pagesVirtulisationAntony mutahiNo ratings yet
- Virt-Unit 1,2,4,5Document149 pagesVirt-Unit 1,2,4,5vinit nimkarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument61 pagesIntroductionmehulprajapati1661No ratings yet
- Lecture 06Document15 pagesLecture 06UmairNo ratings yet
- Lect4 VirtualizationDocument79 pagesLect4 VirtualizationcenaanrakNo ratings yet
- DockerDocument14 pagesDockerThretha ReddyNo ratings yet
- LESSON in ELECTIVE 3Document6 pagesLESSON in ELECTIVE 3GENED Bernadine GoyalNo ratings yet
- Prelude: Cloud ComponentsDocument22 pagesPrelude: Cloud ComponentsRogelio Donnet Quiroga GonzalezNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Virtualization in Cloud Computing - ExplainedDocument6 pagesThe Different Types of Virtualization in Cloud Computing - ExplainedFahm AnsariNo ratings yet
- Unit II Notes - VirtualizationDocument49 pagesUnit II Notes - VirtualizationRlp yadavNo ratings yet
- Cloud 2Document53 pagesCloud 2GFx KidNo ratings yet
- Unit-I CCDocument56 pagesUnit-I CCpreethiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Types - Advantages and SolutionsDocument5 pagesVirtualization: Types - Advantages and SolutionsUSMAN ....No ratings yet
- Btech Cloud Computing Unit 2 (Autosaved) (Autosaved)Document128 pagesBtech Cloud Computing Unit 2 (Autosaved) (Autosaved)039 MeghaEceNo ratings yet
- Virtual WordDocument7 pagesVirtual WordSaumya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Au FDPDocument38 pagesAu FDPsridharegspNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet