Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Opce Samples March 2006
Uploaded by
fiena92Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Opce Samples March 2006
Uploaded by
fiena92Copyright:
Available Formats
B
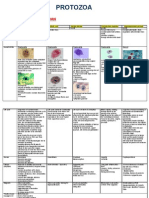
With reference to the above exhibits: a) Describe what you observe (4 Marks)
A: Buff coloured dry waxy colonies on Lowenstein-Jensen medium. B: Thin rods with beaded appearance acid-fast bacilli in Ziehl-Neelsen stain. b) State the likely aetiological agent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. (1 Mark)
c) State the infection caused by the organism (1Mark) Tuberculosis. d) Name two antibiotics in the treatment of this infection (2 Marks) Isoniazid, rifampicin. e) State two complications due to this infection (2 Marks) Military tuberculosis, UTI, meningitis.
With reference to the display: a) What do you observe (4 Marks) A Culture plate pinpoint colonies with -hemolysis on the blood agar. B Stained slide gram positive cocci arranged in chain. a) State the likely organism (1 Mark) Group A -hemolytic streptococci @ Streptococcus pyogenes. b) State two infections it may cause (2 Marks) Streptococcal pharyngitis, Scarlet fever. c) State two complications that may occur due to infection of this organism (2 Marks) Rheumatic heart disease, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. d) What is the antibiotic of choice to treat infections from this organism (1 Mark) Penicillin G.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Briefly describe what is seen in (4 Marks) A: Lancelet-shaped gram positive diplococci. B: -hemolytic draughtsman colonies seen on blood agar (indicates autolytic activity of MO) b) Name the test shown in B used for identifying the organism (1 Mark) Optochin test. c) State the likely aetiological agent. (1 Mark) Strepcoccus pneumoniae. d) State one infection caused by the organism identified (1 Mark) Lobar pneumonia. e) State two virulence factor of the organism. (2 Marks) Capsule, pneumolysin. f) State the antimicrobial of choice used to treat the infection. (1 Marks) Penicillin.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe what you observe (2 Marks) Sucrose fermenting colonies on thiosulfate citrate bile sucrose (TCBS) agar. b) Name the selective medium shown (1 Mark) TCBS agar. c) State the likely aetiological agent. (1 Mark) Vibrio cholerae. d) State the transport medium used to isolate the agent. (1 Mark) Alkaline peptone water. e) State two major symptoms noticed in the infection with the above pathogen. (2 Marks) Diarrhea, vomiting. f) How is the infection transmitted? (1 Mark) Fecal-oral route. g) Name the natural host of this organism and one measure to control its spread? (2 Mark) Man. Proper sewage disposal.
h) With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen. (4 Marks) A: gram positive bacilli arranged in Chinese letter fashion. (if Alberts@methylene blue stain, state metachromatic granules). B: gray-black colonies seen on potassium tellurite blood agar. b) State the likely aetiological agent (1 Mark) Corynebacterium diphteriae. c) State the virulence factor and how is tested (2 Marks) Exotoxin (diphtheria toxin). ELEK plate. d) State two measure to manage this infection. (2 Marks) Antimicrobial (penicillin). Antitoxin. e) Name one preventive measure for this infection (1 Mark) DPT vaccine.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen. (4 Marks) A B Slide: - Conidiophores with swollen rounded ends. - Conidia form radiating chains. Culture: powdery dry colonies, black in appearance on the Sabourauds dextrose agar (SDA)
b) State what method is used to visualize the agent in A (1 Mark) Lactophenol cotton blue. c) State the likely aetiological agent (1 Mark) Aspergillus niger. d) State one predisposing factor for this agent to cause lung infection (1 Mark) Immunocompromised patients, previous tuberculous cavity (aspergilloma). e) State two pathogenic species of the above agent (2 Marks) Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus. f) State one antimicrobial used to treat the infection (1 Mark) Amphotericin B.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen and name the test shown in B to identify the organism (4 Marks) A B Slide: gram positive cocci arranged in clusters. Culture: mannitol fermenter colonies show shiny yellow discolouration.
b) Name the likely pathogen (1 Mark) Staphylococcus aureus. c) Name two infections caused by this pathogen (2 Marks) Infective endocarditis, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning. d) Name two virulence factors of this pathogen (2 Marks) Coagulase, hyaluronidase. e) Name the antimicrobial of choice (1 Mark) Cloxacillin.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen. (4 Marks) A B Culture: mucoid colonies with green pigment production (aeruginosin). Slide: gram negative bacilli.
b) Name a test to presumptively identify this pathogen (1 Mark) Oxidase test (+ve). c) Name the pathogen (1 Mark) Pseudomonas aeruginosa. d) State the natural reservoir of this organism (1 Mark) Soil, water. e) State three infections the pathogen causes (2 Marks) Nosocomial pneumonia, UTI, corneal infection.
With reference to the above exhibit: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen in A. (2 Marks) Gram negative pleomorphic coccobacilli. b) Describe and name the test shown in B to identify this organism (3 Marks) Satellitism around colonies of Staph. aureus on blood agar. c) Name the organism (1 Mark) Haemophilus influenzae. d) Name two infections caused by this pathogen (2 Marks) Community-acquired pneumonia, meningitis. e) Name two complications caused by infection with this organism (2 Marks) Otitis media, epiglotitis.
E.coli With reference to the above exhibit on Maconkey agar: a) Describe the appearance of this specimen. (2 Marks) Pink (lactose fermenting), dry colonies on Mac Conkey agar. b) What will be the Gram reaction of this organism (2 Marks) Gram negative. c) Name three infections it causes (3 Marks) UTI, infantile diarrhea, wound infection. d) Name the normal habitat of this organism in human body (1 Mark) Mans large intestine. e) State two antimicrobials used in treatment of this infection (2 Marks) Gentamicin, co-trimoxazole.
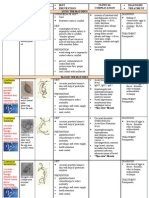
Name and state the principle of this test shown above Coagulase test. Clotting of fibrin after plasma added by Staph. aureus. Name the organism it differentiates Staph. aureus and Staph. epidermidis.
Urease +ve e.g. Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus spp.
Salmonella on SS
Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida krusei, etc.
Salmonella, Klebsiella on blood agar (pale colonies)
You might also like
- Muscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic DrugsDocument4 pagesMuscarinic (M) Receptor Blockers (Antagonists) Anti Muscarinic Drugs Anti Cholinergic Drugsfiena92No ratings yet
- Journal FINAL....Document6 pagesJournal FINAL....fiena92No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Adrenergic AgonistsDocument9 pagesPharmacology of Adrenergic Agonistsfiena92No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System Cholinergic AgonistsDocument6 pagesPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System Cholinergic Agonistsfiena920% (1)
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Helminth Revision 2Document1 pageHelminth Revision 2fiena92No ratings yet
- Helminths - Revision IDocument1 pageHelminths - Revision Ifiena92No ratings yet
- Adverse Drug ReactionDocument5 pagesAdverse Drug Reactionfiena92No ratings yet
- Helminth 5Document5 pagesHelminth 5fiena92100% (2)
- Protozoa RevisionDocument6 pagesProtozoa Revisionfiena92100% (1)
- Helminth 4Document1 pageHelminth 4FarlogyNo ratings yet
- Helminth 3Document2 pagesHelminth 3Farlogy100% (5)
- Protozoa Revision - Toxoplasma GondiiDocument2 pagesProtozoa Revision - Toxoplasma Gondiifiena92No ratings yet
- Brochur A.UDocument2 pagesBrochur A.Ufiena92No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Chemicals For ConsumerDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Chemicals For Consumerfiena9292% (13)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Asthma Aware KitDocument33 pagesAsthma Aware KitEkzHa Noctis CaeleumNo ratings yet
- SRG Test BiologyDocument156 pagesSRG Test Biologypranayallen2006No ratings yet
- Nebulizing & Suctioning TechniquesDocument23 pagesNebulizing & Suctioning TechniquesRifky Octavio PNo ratings yet
- Demand For Beauty by Society (FINAL)Document10 pagesDemand For Beauty by Society (FINAL)Maryhan MukhalalatiNo ratings yet
- Laminectomy Definition: Spine Surgery to Relieve Pressure on Spinal Cord or NervesDocument9 pagesLaminectomy Definition: Spine Surgery to Relieve Pressure on Spinal Cord or NervesEdmarie AmistadNo ratings yet
- PHARMA BulletsDocument6 pagesPHARMA BulletsRhea Anne VeraNo ratings yet
- OtrivinDocument12 pagesOtrivinkanika sengarNo ratings yet
- Dementia Conversion DisordersDocument28 pagesDementia Conversion DisordersAYO NELSON100% (1)
- Bitter PrinciplesDocument6 pagesBitter PrinciplesPankaj BudhlakotiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021Document6 pagesMCQ Bleeding Disorders 2nd Year2021sherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument3 pagesFNCPLander VirayNo ratings yet
- Recuperare 1Document3 pagesRecuperare 1Mihnea TurcuNo ratings yet
- AMHOP Convention LetterDocument3 pagesAMHOP Convention Letterlemonysnicket0008No ratings yet
- TTTTDocument26 pagesTTTTMoataz TrabehNo ratings yet
- NBME Answer With Explanation in DepthDocument10 pagesNBME Answer With Explanation in DepthDejan Zolak100% (3)
- EHAQ 4th Cycle Audit Tool Final Feb.10-2022Document51 pagesEHAQ 4th Cycle Audit Tool Final Feb.10-2022Michael Gebreamlak100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalsDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalskyawNo ratings yet
- Job Description BGDocument4 pagesJob Description BGHamza FaridiNo ratings yet
- AMRI Hospital TariffDocument42 pagesAMRI Hospital TariffsandeepNo ratings yet
- Religare Pre Auth FormDocument3 pagesReligare Pre Auth FormM/s Microtech25% (4)
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Limb Fractures Associated With Acute Peripheral IschemiaDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Limb Fractures Associated With Acute Peripheral IschemiaramadhaniandaNo ratings yet
- 2.4.B DR Denni Clinical Evidence of Ribociclib Into Clinical PracticeDocument40 pages2.4.B DR Denni Clinical Evidence of Ribociclib Into Clinical Practicetepat rshsNo ratings yet
- CTR Master Class CourseDocument15 pagesCTR Master Class CourseCool N CoolNo ratings yet
- CPAP SlidesDocument52 pagesCPAP SlidesAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- Dr. Hossam Eldin Sayed Ali: Lecturer of Medical Biophysics The Research Institute of OphthalmologyDocument32 pagesDr. Hossam Eldin Sayed Ali: Lecturer of Medical Biophysics The Research Institute of OphthalmologyRiya MathurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Immune Responses Against Tumors and TransplantsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 - Immune Responses Against Tumors and TransplantsFYMNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakamemeeeyyyNo ratings yet
- Fellowship Course 3 Program v1Document15 pagesFellowship Course 3 Program v1Joice RumondangNo ratings yet
- Power of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyDocument6 pagesPower of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyBFF BotoxNo ratings yet
- SepanskiDocument13 pagesSepanskiTammy Utami DewiNo ratings yet